Overhead Budgets
advertisement

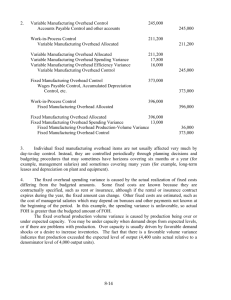
Overhead Budgets Most companies use flexible budgets to control overhead costs. – A flexible budget is not based on only one level of activity but is valid for the firm’s relevant range of activity. – The flexible budget provides the correct basis for comparison between actual and expected costs. – The flexible overhead budget is based on a standard input measure (e.g. machine hours) Flexible Budget Formula The relationship between activity and total budgeted overhead is given by: Total budgeted monthly overhead cost = Budgeted Total activity variableunits overhead cost * per activity unit + Budgeted fixedoverhead cost per month Standard Costing System In a standard costing system, overhead application is based on standard hours allowed, given actual output. – The Manufacturing Overhead account is credited and the Work-In-Process Inventory is debited by the following amount: • Standard allowed hours X Predetermined (Standard) rate Variable-Overhead Spending Variance Variable-overhead spending variance = • Actual variable overhead - (AH x SVR) or • (AH x AVR) - (AH x SVR) • AH x (AVR - SVR) Notation: AH = actual machine hours AVR = actual variable-overhead rate = actual variable overhead AH SVR = standard variable-overhead rate Variable-Overhead Efficiency Variance Variable-Overhead Efficiency Variance = • (AH x SVR) - (SH x SVR) • SVR x (AH - SH) Notation: AH = actual machine hours SH = standard machine hours SVR = standard variable-overhead rate Variance Analysis for Managerial Control Variable Overhead Actual Costs Incurred (a) Flexible Budget based on Actual Output (b) AQ * AR Expected Costs based on Actual Output (c) AQ * SR SQA * SR Variable-Overhead Spending Variance (b-a) Variable-Overhead Efficiency Variance (c-b) AQ(SR - AR) SR(SQA - AQ) Variable-Overhead Budget Variance (c-a) (SQA * SR) - (AQ * AR) Interpreting Variable Variance The variable-overhead efficiency variance simply reflects an adjustment in the managerial accountant’s expectation about variable overhead cost. – It does not indicate inefficient use of variable-overhead. An unfavorable variable-overhead spending variance simply means that the total actual cost of variable overhead is greater than expected. – The spending variance is the real control variance for variable overhead. The spending variance can alert managers if variable overhead costs are exceeding expectations. Fixed-Overhead Variances Fixed-Overhead Budget Variance = • Actual fixed overhead - Budgeted fixed overhead • The budget variance is the real control variance for fixed overhead, because it compares actual expenditures with budgeted fixed-overhead costs. Fixed-Overhead Volume Variance = • Budgeted fixed overhead - Applied fixed overhead • Applied fixed overhead = Predetermined fixed overhead rate x Standard allowed hours • A faulty interpretation of a positive volume variance is that it measures the cost of under-utilizing productive capacity. Perhaps under-utilizing capacity and reducing inventory may be the appropriate response to the current demand. Variance Analysis for Managerial Control Fixed Overhead Actual Costs Incurred (a) Flexible Budget based on Actual Output (b) AQ * AR AQ * SR Expected Costs based on Actual Output (c) SQA * SR Fixed-Overhead Spending Variance (b-a) Fixed-Overhead Efficiency Variance (c-b) AQ(SR - AR) SR(SQA - AQ) Fixed-Overhead Budget Variance (c-a) (SQA * SR) - (AQ * AR) Disposition of Variances Variances are temporary accounts and most companies close them directly into Cost of Goods Sold at the end of each accounting period. – Debit: Cost of Goods Sold Credit: Manufacturing Overhead