Organic and Biochemical Molecules

Organic and Biochemical
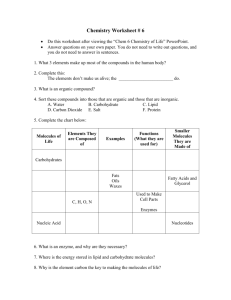
Molecules
Chapter 21
E-mail: benzene4president@gmail.com
Web-site: http://clas.sa.ucsb.edu/staff/terri/
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
1. Classify the following compounds as saturated or unsaturated.
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
2. What is the general formula for a hydrocarbon with one ring and a triple bond?
a. C n
H
2n+2 b. C n
H
2n c. C n
H
2n–2 d. C n
H
2n–4 e. C n
H
2n–6
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
3. Draw the following alkanes: a. 4-bromo-3,3-dimethylhexane b. 3-ethyl-1-methyl-1-propylcyclopentane c. 5-ethyl-2,2-difluoro-3-isopropylheptane d. 4-sec-butyl-1-chloro-1-ethylcyclohexane
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
4. Name and classify the following. Are any of the molecules chiral?
Cl
Br
Cl
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
5. Draw the following alkenes: a. 4,7-dibromo-3-propyl-2-heptene b. 3,3-dipropylcyclobutene c. trans -1,3-pentadiene d. cis -2-chloro-5-ethyl-3-octene
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
Geometric isomers of alkenes – If each sp2 C has 2 different groups attached it will have two possible orientations due the fact that pi bonds do not allow for free rotation – If each sp2 C has only one hydrogen you can classify the structure as cis or trans
H
H
Trans
2 Hydrogens are on opposite sides of pi bond
H
H
Cis
2 Hydrogens are on the same side of pi bond
F
F
Cl
Cl
Although these structures are
Geometric isomers (the 2 halogens are on opposite sides in the left structure and same side in the right) you don’t refer to them as cis/trans
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
6 . Name the following alkenes.
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
7. Draw the following alkynes: a. 3-ethyl-4,5-difluoro-1-pentyne b. 7,7-dimethyl-2,4-octadiyne
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
8. Name the following alkynes: a.
b.
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
9. For each of the following draw all of the structural isomers. Do any of your structures have geometric isomers? If so, draw and label them.
a. C
6
H
14 b. C
5
H
10 c. C
4
H
6 d. C
4
H
7
Br
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
10. Draw the following molecules.
a. para-iodoisobutylbenzene b. metatertbutyltoluene c. 2,4,6-tribromophenol
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
11. Write out the reaction for the mono-chlorination of pentane. What type of reaction is this?
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
12. Predict the product for the following addition reactions: a. 1-pentene + Br
2
b. 2-butene + HCl
c. 2-pentene + HBr
d. 1-butene + H
2
O (in the pressence of H + )
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
13. Which of the following transitions does not represent a hydrogenation reaction?
a. 1-butene
butane b. 1-pentyne
pentane c. pentane 2-pentene d. butanal
1-butanol
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
14. Identify the functional groups that are present in the following compounds: aspartame estrogen vanillin
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
15. For each of the following (1) draw the products of oxidation and (2) name the reactants and products:
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
16. Draw the following: a. 4-bromo-3-ethylbutanoic acid b. 6-chloro-3-hexanone c. 2,3-dimethylpentanal
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
17. Classify the following amines as primary, secondary or tertiary; a. tertbutylamine e. ethylhexylamine
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
18. Predict and name the products for the following: a. propanoic acid + 3-methyl-1-butanol b. methanoic acid + 1-propanol c. 2,3-dibromohexanoic acid + ethanol
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
20. What compounds would you use to synthesize the following esters?
a. methyl ethanoate b. cyclohexyl propanoate
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
21. Circle the chiral carbons in the following:
H
H
H
O
OH
OH
OH
OH
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
22. Peptide bonds in proteins are the result of ___________ reactions between __________. Differentiate between primary, secondary and tertiary structures of a protein? How many possible dipeptides will result if you were to mix valine and leucine together?
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
23. Draw gly-phe-ser-ala
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
24. What type of monomers are used to make addition polymers?
a. Alkanes b. Alkenes c. Alcohols and carboxylic acids d. Amines and carboxylic acids
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
25. What type of monomers are used to make condensation polymers?
a. Alkanes b. Alkenes c. Alcohols and carboxylic acids d. Amines and carboxylic acids
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
26. Draw a short segment of the polymer that is the result of the following monomers: a. tetrafluoroethene b. 4-methyl-2-pentene c. 1,1-dichloro-1-butene
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
27. Draw the monomer used to make the following polymers.
d.
a.
e.
b.
c.
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
28. Which of the following are examples of condensation polymers?
a. Proteins b. DNA c. Polysaccharides d. Polystyrene
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
1. Saturated => all single bonds
Unsaturated => double or triple bonds
2.
3. a. 4-isopropyl-5-methyloctane b. 2,5,5-trichloror-4-propylheptane c. 2-bromo-4-isobutyl-1-methylcyclohexane
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
4.
5. a. 4-fluoro-5-methyl-3-heptane b. 3-chloro-1isopropylcyclohexene c. cis-2-hexane d. trans-8,8-dibromo-4-methyl-2-octene e. 5,8-diethyl-1,7-decadiene
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
6.
7.
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
Organic and Biochemical Molecules
Organic and Biochemical Molecules