Response - Bakersfield College
advertisement

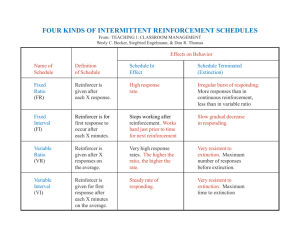
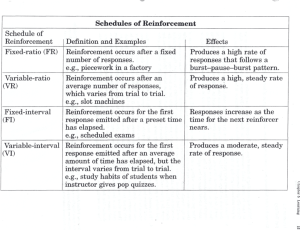
Principles of Behavior Sixth Edition Richard W. Malott Western Michigan University Power Point by Nikki Hoffmeister Chapter 17 Ratio Schedules What is a Schedule of Reinforcement? Schedule of Reinforcement: • The way reinforcement occurs • because of the number of responses, • time between responses, • and stimulus conditions. What is Continuous Reinforcement? Continuous Reinforcement (CRF): • A reinforcer follows each response. Intermittent Reinforcement: • Reinforcement occurs, but not after each response. When should you use CRF? • Continuous reinforcement is usually best for shaping or maintaining difficult behavior. – Shaping vocal responses What is a Fixed-Ratio Schedule? Fixed-Ratio (FR) Schedule of Reinforcement: • A reinforcer follows • a fixed number of responses. What kind of responding does a fixed-ratio schedule produce? Fixed-Ratio Responding: • After a response is reinforced, • no responding occurs for a period of time, • then responding occurs at a high, steady rate • until the next reinforcer is delivered. Non-Cumulative Graph Non-Cumulative Graph • The horizontal line (x-axis) indicates the passage of time • Each vertical line indicates a response • At the end of each ratio of 8 responses a reinforcer is delivered (indicated by star) • After each star, the line is flat, indicating no response occurs for a while – Post-reinforcement pause Post-Reinforcement Pause • Characteristic of fixed-ratio-maintained behavior • The length of the pause is proportional to the size of the ratio High Ratios • If you wish to establish a high ratio requirement, • you need to do so gradually, • raising the ratio from 2 to 4 to 6 responses and up. • Otherwise the response may extinguish. What is the general rule for establishing intermittently reinforced behavior? • First, use continuous reinforcement • and gradually increase the intermittency of reinforcement • as responding stabilizes at a high rate. The Cumulative Graph Cumulative Graph • Behavior analysts often use this type of graph when studying schedules of reinforcement. • The vertical axis (ordinate) is labeled cumulative frequency of responses as opposed to a non-cumulative graph in which the ordinate is labeled responses. • The post-reinforcement pause is where the slope of the line is zero. What is a Variable Ratio Schedule? Variable-Ratio (VR) Schedule of Reinforcement: • A reinforcer follows • after a variable number of responses. What type of responding does a VR schedule produce? Variable-Ratio Responding: • Variable-ratio schedules produce • a high rate of responding, • with almost no post-reinforcement pausing. VR Schedules • VR 50 – This means that a reinforcer is delivered after an average of 50 responses – An FR 50 means the reinforcer is delivered after exactly 50 responses • Intermittent Reinforcement: – Generic term that includes both fixed and variable ratio schedules Reinforcer vs. Reinforcement • What is a specific pellet of food for a deprived rat? – A reinforcer – Reinforcement • The immediate delivery of a pellet contingent on a deprived rat’s lever press with a resulting increased rate of pressing? – Reinforcer – Reinforcement Reinforcer vs. Reinforcement • What is a quarter for a deprived professor? – Reinforcer – Reinforcement • What is the immediate delivery of a quarter, contingent on a deprived prof’s pleading for a raise, with a resulting increased rate of pleading? – Reinforcer – Reinforcement Ratio Schedules in Everyday Life • Are slot machines in casinos examples of everyday VR schedules? • No; there are 5 reasons why 4 Reasons Why Slot Machines are Not VR Schedules 1. It’s loaded with learned reinforcers in addition to the silver dollars • • Like those fruits that appear in the window, one after the other You get 2 cherries in a row…a big reinforcer 4 Reasons Why Slot Machines are Not VR Schedules 2. The variable amount of the reinforcer you get at the end of the so-called VR • • • Sometimes you get only one silver dollar Sometimes it’s 10, 18, so on None of that’s like the ratios the behavior analysts study in the Skinner box 4 Reasons Why Slot Machines are Not VR Schedules 3. The size of the ratio is much smaller than is typical in the Skinner box of the professional research lab • • Like a VR 100 In a casino, people would not play if machines had ratios of 100 4 Reasons Why Slot Machines are Not VR Schedules 4. The emotional reaction is itself reinforcing • Near misses are reinforcing Intermediate Enrichment • Free-operant procedures – Most Skinner-box research involves freeoperant responding – The animal is free to respond at various frequencies (1 lever press per minute to 100 lever presses per minute) – There is no S∆ after each response, so there is no inter-trial interval between each response and the next SD Discrete-Trial Procedure • • • • • There is an SD, a single response, and an outcome, followed by an S∆ (intertrial interval); then the next trial starts. In the Classroom: Discrete-Trial Procedure SD: Sue says, “Jimmy point to the horse.” Response: Jimmy points to the horse. Outcome: Sue says, “Good boy, Jimmy.” (a learned reinforcer for Jimmy) S∆ (Inter-trial Interval): Sue says nothing In the Classroom: Free-Operant Procedure SD: Sue and Jimmy at the snack table. Response 1: Jimmy says, “Juice please.” Outcome: Sue gives him a sip of juice. Response 2: Jimmy says, “Juice, please.” Outcome: Again, Sue gives him a sip of juice. S∆: Sue and Jimmy leave the snack table. Discrete Trial vs. Free Operant Discrete Trial Free Operant Is there an SD and an S∆? Yes Sometimes Is there an inter-trial interval? The measure is… Yes Usually not Latency or accuracy Rate Advanced Enrichment • Hybrid Discrete-Trial/Free-Operant Procedure – Each free-operant response, itself, consists of a discrete trial. Example • Sue and Jimmy are in the structured-play area Response 1: Jimmy picks up a piece of the puzzle and puts it in the puzzle form Response 2: Jimmy picks up a 2nd piece and puts it in the puzzle form Response 3: Jimmy picks up a 3rd, final piece, and puts it in the form Outcome: Jimmy has completed the puzzle and sees a picture of Barney. Sue says, “Good job.” Why Hybrid? • This is an example of a discrete trial, because each piece Jimmy puts in the puzzle is an SD for the next response. • It is also an example of free operant because Jimmy is free to place each puzzle piece as fast as he “wants,” and… • A measure of his behavior would be a rate measure (e.g., 8 pieces per minute). On DickMalott.com • Chapter 17 Advanced Enrichment Section – In Search of the Everyday Variable Ratio Join us for Chapter 18: Interval Schedules