What is Cyberinfrastructure?
advertisement

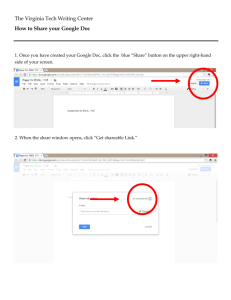
Cyberinfrastructure and EarthScope Science goals: A GEON perspective What is Cyberinfrastructure? What is GEON? How will GEON research facilitate discovery and integration of earth science data? What are the benefits of such a research initiative for EarthScope? How can earth scientists participate in Cyberinfrastructure research opportunities? CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Cyberinfrastructure • Cyberinfrastructure is the organized aggregate of technologies enabling access and coordination of information technology resources to facilitate science, engineering, and societal goals. – Data access from distributed systems – – – – Data inter-operability Computation: grid based and workflows Visualization Tools National Science Foundation’s Cyberinfrastructure NSF Blue Ribbon Panel (Atkins) Report provided a compelling and comprehensive vision of an integrated Cyberinfrastructure – Integration: highlighted today Modified from Berman, SDSC, 2005 CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 A KEY OBSERVATION IN SUPPORT OF CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE RESEARCH IN GEOSCIENCES “Large team** efforts are required to build a federation of data and tools; but smaller groups or individuals working independently and given access to these data and tools can (and likely will) make fundamental discoveries” MODIFIED FROM BLUE RIBBON ADVISORY PANEL ON CYBERINFRUSTRUCTURE REPORT, NSF ** such as GEON and other projects CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 EarthScope Instrumentation and Data USArray PBO SAFOD InSAR Plus semantic integration of other earth science data Cyberinfrastructure Resources Science Investigators Towards an Integrated Earth Science data and knowledge base to achieve EarthScope Science and education goals CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES Educators and the Public A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Adapted from D.Seber,SDSC CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Three dimensional view of the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary and surface topography of the northern Appalachians. Base of lithosphere interpolated from migrated Ps waveform images at 6 labeled stations. (From Rychert et al. 2005) New knowledge about evolution of continents requires complex integration of geophysical data with those associated with sub-crustal lithosphere ages, its composition and physical properties (seismic, thermal etc), surface geology and associated events chronology CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 What is the geologic and geophysical record of SuperContinent assembly and dispersal? CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 EarthScope Science Targets: Examples from eastern North America • What is the geologic and geophysical record of Super-Continent assembly and dispersal? • What are the architectures of terrane boundaries at depth? • How do composition, temperature and strain fabrics vary within the lithosphere and asthenosphere? Are lithospheric and asthenospheric strain coupled? • How sharp is the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary? What defines it? DATA NEEDED TO ADDRESS THESE QUESTIONS ARE DISTRIBUTED ACROSS THE COUNTRY, IN DIFFERENT FORMATS AND CANNOT BE INTEGRATED IN A WEB ENVIRONMENT WITH EXISTING TECHNOLOGIES —overcoming heterogeneity is a priority cyberinfrastructure challenge CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Outline • Data integration problem and solutions • GEON data integration solution: ontology enabled semantic mediation • What is ontology • Registering data to ontologies • Discovering data and using workflows in a web environment to go from queries to questions CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 GEON Architecture addresses problems of : 1. Variety of data sources and types 2. Discovery and relevance 3. Addressing needs of different communities • Platform heterogeneity: different OS platforms • DBMS heterogeneity: different database systems, e.g. SQLServer, mySQL, DB2 • Data type heterogeneity • Schema heterogeneity • Heterogeneity in units, accuracy, resolution • Semantic heterogeneity ( modified from Baru, SDSC, 2005) CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 What is GEON ? How can GEON help integrate heterogeneous and distributed data? CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 GEON: The Geosciences Network www.geongrid.org GEON is a NSF funded collaborative research between IT and Earth Science researchers with the goal of developing cyberinfrastructure to enable new integrative modes of geosciences research GEON is developing a pioneering system to use knowledge-based techniques to discover, query, and integrate data in the Geosciences Project participants include 14 PI institutions, as well as partners from other projects, agencies, and industry. GEON has deployed a Web servicesbased, distributed computing infrastructure, called the GEONgrid, across the PI and partner sites. GEONgrid provides access to distributed data collections, tools, and applications Research and Education Products and Results: Technologies for “Smart Search”, On-the-fly Data Integration, GIS Map Integration, Distributed Portals, and 4D Visualization Earth Science Research within GEON on 3D Lithospheric Structure Integrated Geoscience Modeling Geologic Evolution of North America Ontologic Framework for the Geo-sphere Cyberinfrastructure Summer Institute for Geoscientists and Graduate Courses in Geoinformatics CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 GEON and Cyberinfrastructure • Develop cyberinfrastructure that enables interlinking and sharing multidisciplinary Earth Science data resources, software and tools • Create a scientist-friendly portal to access data, software for analysis , modeling, and visualization • Create the GEONgrid to enable seamless data integration and analysis environment CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 GEON: GEOsciences Network Data Physical model Portal (login, myGEON) Registration GEONsearch GEONworkbench Data Visualization Indexing Workflow Registration Integration & Mapping Services Services Services Services Services Core Grid Services GT3, OGSA-DAI, GSI, CAS, gridFTP, SRB, PostGIS, mySQL, DB2 Modeling Environment Physical Grid RedHat Linux, ROCKS, Internet, I2, OptIPuter (planned) Model results HPCC CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Discovering, sharing and using data in a web environment: GEON style • Discovery of data resources (e.g., gravity, geologic maps, etc) requires registration through use of high level index terms • GEON has deployed extension of AGI Index terms-will be cross indexed to others such as GCMD, AGU • Discovering Item level content of databases requires registration through data level ontologies (e.g. column in geochemical database that represents SiO2 measurement) and is a requirement for semantic integration • Item detail level registration through ontologies reduces schema based data heterogeneities • Computation and modeling tools can be registered for use by community • Visualization capabilities • Easy access to data through GEON Portal • Individual workbench built into GEON Portal • Scientific Workflow Systems provide computational and query capabilities in a web environment CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 GEON Index Ontology AGI Index Terms Index terms from AGI used for identifying type of data CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Integration: a buzz word but with complex solutions • What is Integration? – Relationships in information contained in heterogeneous and multi-disciplinary databases What are our choices? – Layering of data (commonly used) – View based techniques (create a virtual schema) – Schema based integration (merging of schema, but user must be knowledgeable about the organization, e.g. semantics of schema) – Ontology based semantic integration utilizing workflows….favored by GEON Data Registration is Important for integration! CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 What is Ontology? Why use Ontology? • Ontology : An explicit formal specifications of the terms in the domain (e.g. Geology) and relations among them (Gruber 1993) • Why use ontology To share and reuse of domain knowledge To make explicit domain assumptions To separate domain knowledge from the operational knowledge To analyze domain knowledge • Ontology Languages: RDF and RDFS OIL DAMP+OIL OWL: Ontology Web Language fromW3C CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Motivations for Using Ontologies in GEON • A better way to discover and understand datasets Use the knowledge in ontologies to find datasets • A better way to query datasets Query through ontologies without knowing the details of the schemas • A better way to integrate multiple datasets Integrate multiple datasets on-the-fly if they are registered to ontologies • A Better way to segment large data bases Transfer only parts of data bases required for integration An emerging research frontier- Geo-Ontology CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES Modified From Kai Lin, SDSC, 2005 A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Class Diagrams - The Basic Building Block for Semantic Integration Earth Scientists create disciplinary ontologies!!! Earth Science research : stages in developing ontologies Napkin Stage GEON Planetary Structure concepts GEON formal ontology Concept Map Stage High Level Ontology: integrated GEON, SWEET and NADM stage CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 High Level Ontology Packages : representing relationships Imports Numerics Ontology Imports Time Ontology Imports Units Ontology Planetary Material Phy sicalProperty Location Imports Phy sical Property Ontology Planetary Structure ImportsSpace Ontology CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Planetary Material State of Matter Element Rocks Minerals Data Types CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 GEON Cyberinfrastructure … More than just about the data, GEON is about going from simple Queries to complex Questions CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 A Home Buyer’s Information Integration Problem What houses for sale under $500k have at least 2 bathrooms, 2 bedrooms, a nearby school ranking in the upper third, in a neighborhood with below-average crime rate and diverse population? ? Information Integration “Multiple-Worlds” Mediation Bertram Ludäscher, SDSC Realtor Crime Stats School Rankings CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES Demographics A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 A query example: Use SQL to ask a database to show you all white wines from California of 2003 vintage…. A question: "Tell me what wines I should buy to serve with each course of the following menu. And, by the way, I don't like Sauternes." … from W3C This requires two databases (e.g. food and wine) and prescribed relationships between them that are defined for computers as Ontologies Bertram Ludäscher, SDSC CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 The Problem: Scientific Data Integration or: … from Queries to Questions CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Data Registration: key to integration Click on Submission to register a dataset Input a data set name Select a zipped shapefile Choose an ontology class CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Registration at the item detail level using data ontology: working with data SiO2 is an instance of class AnalyticalOxideConcentration and has all information about the element Si Planetary Material Ontology CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 GEONsearch:building on data registration Choose subject (from a “base” ontology) Choose location (from a gazetteer Webservice) Choose a time (numeric range or from a time ontology Webservice) Choose concepts from ontologies CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES Kai Lin, SDSC, 2005 A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Ontology Enabled Map Integration :A Case Study • Geologic Data sets Arizona, Idaho, Montana, Utah, Nevada, Colorado, Wyoming, New Mexico • Ontologies Geologic Time Scale Multihierarchial Rock Classification from Canada Geologic Survey British Rock Classification Scheme Snapshot after querying “Paleozoic” CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Scientific Workflow Systems in GEON • Adding computational capability in a web environment – Promote “scientific discovery” by providing tools and methods to generate scientific workflows – Support computational infrastructure for modeling,classification,computation – Design frameworks which define efficient ways to connect to the existing data and integrate heterogeneous data from multiple resources CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Workflow layout for rock classification, but can be used for any query that requires a classifier Find data on the basis of ontologic registration PointInPolygon algorithm CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Integration Scenario: A-type pluton query • • Classifying A-types from an Igneous rock database Integrating between Relational and Spatial (shapefiles) databases to query and interactively display GIS results CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Integration Scenario: Stages for access to data and tools in a workflow environment The integration scenario: What is the distribution and U/Pb Zircon ages of A-Type Plutons in Virginia? Ontology System 1 2 5 • Location States Virginia •Classification System Rock Classifiers Igneous Pluton A-type 3 •Mineral Zircon •Geologic Time Dating Methods U-Pb Zircon Methods Zr 4 I&S type A type 104 Ga/Al 3 6 5 6 6 CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Distribution and ages of A-Type plutons and their ages based on integration of multiple databases How do earth scientists participate in Cyberinfrastructure research? • Know your data……its content and definitions • Think more broadly…..integration is between databases that are different from yours • Learn more about how to use IT through summer workshop at SDSC, as well as others sponsored by Societies • Register your data using Index Terms through GEON Portal to facilitate discovery of databases; use data ontology for discovery of data • Build and Share tools and services for use in a web environment • Construct concept maps in your discipline….leads to formal ontologies required for semantic integration……remember Geo-Ontology • EarthScope requires integrative capabilities CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 o b j e c t p r o c e s s t r a n s i t i o n melt residual solids cumulate pha ses p a r t s o f c o m p o n e n t s pa rtly-molten crust melting underplating now where? dehydra tion melting crusta l melting intrapla ting wet melting ra dioa ctive heating “fertile” crusta l source decompression melting heating mixed source meta graywa cke meta pelite From Objects to Processes---- just the beginning of a new integrative world amphibolite Some processes and objects typically involved in crustal melting. CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES From Cal Barnes, Texas Tech, 2005 A.K.Sinha, Virginia Tech, 2005 Two important events at GSA DIVISION OF GEOINFORMATICS GEON and EarthScope Reception Data to Knowledge FIRST Business Meeting will take place during the upcoming National GSA meeting ,Salt Lake City Tuesday,18 October, Ballroom D, 5.45-7.45pm Monday, 17 October, Hilton Salt Lake City Center Alpine West Ballroom 5.00-7.00pm