Muscle - Tamaqua Area School District
advertisement

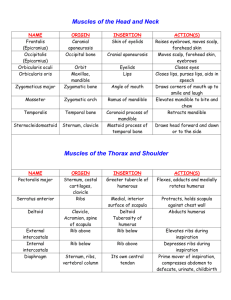
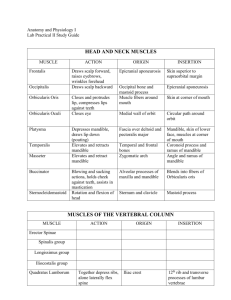
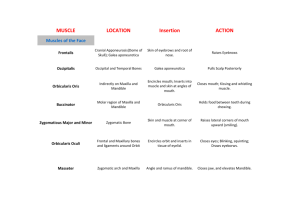
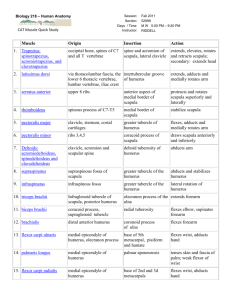
TAMAQUA AREA HIGH SCHOOL LEHIGH CARBON COMMUNITY COLLEGE DUAL ENROLLMENT COURSE OUTLINE BIO 163 - ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I Division/Department: Credit Hours: Lecture Hours: Laboratory Hours: Other: Prerequisite(s): Corequisite(s): Sciences 4 3 3 0 Biology assessment test required. It is strongly suggested that students not passing the assessment test take (and pass with a C or better) BIO 105, or have passed a college-level biology course. None. Course Description Provides students, primarily in health-related programs, with an in-depth understanding of the anatomy and physiology of complex living organisms, including humans. Biological principles, as well as the structural and functional relationships among several organ systems, are discussed. (Considerable dissection is required.) Course Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Demonstrate insight into the normal anatomy and physiology of complex vertebrates, especially the human. Describe how the various parts of the body are structurally and functionally related to one another. Demonstrate the necessity of complexity within living organisms. Demonstrate a knowledge-base essential for advanced study. Develop specific laboratory skills including dissection. Demonstrate fluency and literacy in anatomical and physiological terminology. Employ the scientific method to analyze and interpret physiological test results. -2Course Content – BIO 163 - lecture The student should be able to: 1. Organization of the Body a. Discuss the relationship between the terms "anatomy" and "physiology." b. Describe the structural and functional characteristics necessary for the maintenance of life, including the levels of organization of living things. c. Identify and be able to use the following concepts related to body structure: directional vocabulary, anatomical planes, regions, and positions. d. Define homeostasis, explaining requirements and operation of homeostatic systems, with examples. 2. Tissue a. Identify the four basic types of tissues in the body. b. Describe the physiological characteristics of epithelial tissue. (1) Classify epithelial tissue into several types, including: stratified squamous, transitional, simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, pseudostratified columnar. (2) Describe the general function of epithelial tissue, including protection, secretion, absorption, diffusion, and filtration. (3) Describe the structure, function, and distribution of glandular epithelium. c. Describe the physiological characteristics of connective tissue. (1) Classify connective tissue according to type, including the structural features of at least the following: areolar, adipose, reticular, dense regular, dense irregular, cartilage (3 types), bone, blood. (2) Identify fibers and cell types found in each connective tissue. d. Characterize the three types of muscle, including properties of each. e. Identify, in general terms, the primary components of nerve tissue and describe their functions. f. Describe the structure and function of the various types of membranes, including mucous, serous, synovial, and cutaneous membranes. 3. Integumentary System a. Describe the structure and function of the layers of the integument, including dermis, epidermis and hypodermis. b. Describe the structure, growth and function of the hair and nails. c. Describe the structure and function of the skin glands and their products. 4. Skeletal System a. Describe the functions of the skeletal system. b. Illustrate and identify the gross anatomical structure of the long bone. c. Describe the microscopic components of bone and cartilage, and discuss the dynamic nature of bone (bone remodeling). d. Discuss hormones that affect bone structure. e. Describe the formation and growth of the skeleton from embryonic development through adult structure. -3- 8. 5. Joints a. Describe and give examples of the structural and functional types of joints, including locations and movements of each. b. Describe functions of ancillary joint structures such as ligaments, bursae, joint capsules, etc. 6. Muscle System a. Describe the energy sources involved in muscle contraction. b. Illustrate and label the microscopic structural components of muscle cells. c. Describe the functions of the microscopic and molecular structures of muscle tissue including components involved in the mechanism of skeletal muscle contraction. d. Identify the general functions of muscles. e. Explain factors influencing force, velocity, and duration of muscle contraction. f. Describe the microscopic structure of smooth muscle. g. Discuss the mechanisms and characteristics or smooth muscle contraction. h. Describe the physiology of the neuromuscular junction. i. Discuss the concept of "motor unit" and its relationship to strength and precision of contraction. 7. Nervous System--General a. Describe the structure and function of the various neuroglia and neurons. b. Explain the electrical properties of the resting neuron. c. Define "action potential" and differentiate between various electrical potentials in neurons, such as resting, graded, action, postsynaptic. d. Describe the synapse and its functional mechanisms. e. Differentiate between Excitatory Post Synaptic Potentials (EPSP) and Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potentials (IPSP) and their effects. f. Classify neurotransmitters according to chemical composition and function. g. Explain the basic concepts of neural integration, including organization of neurons, types of circuits, and neural processing. h. Define and be able to use the terms: white matter, gray matter, nerve, tract, ganglion, nucleus. Central Nervous System a. Describe and characterize functions of the following regions of the brain: cerebrum, cerebellum, hypothalamus, thalamus, brain stem, limbic system, reticular formation. b. Discuss the mechanisms for protecting brain tissue, including the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and blood-brain barrier. c. Know the functions of pathways to, from, and within the cerebrum, the roles of the basal ganglia, and the localization of the cerebral areas relative to their roles. d. Understand the gross anatomy and physiology of the spinal cord including its connections with brain and spinal nerves. e. Describe the general organization of the somatosensory system. f. Characterize motor integration, including levels of motor control. g. Discuss higher mental functions, including: brain wave patterns, sleep cycles, consciousness, memory, and language. -49. Peripheral Nervous System a. Characterize the structure and classification of nerves and associated ganglia. b. Describe the regeneration of nerve fibers. c. Know the distribution of the spinal nerves. d. Describe a reflex arc and spinal reflexes, distinguishing between reflexes and voluntary movements. e. Classify sensory receptors and stimuli detected by each. 10. Autonomic Nervous System a. Describe and interrelate the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. b. Discuss the relationship of the ANS to the endocrine system. c. Compare and contrast the parasympathetic and sympathetic ANS divisions, including functions, neurotransmitters, and receptors. d. Discuss control of the autonomic nervous system. 11. Special Senses a. Discuss the concepts of sense reception and transmission, sense receptors and sense organs. b. List and give functions of the special senses (olfaction, gustation, vision, hearing, equilibrium). c. Describe the structure and function of the taste buds. d. Describe the structure and function of olfactory receptors. e. Characterize activation of olfactory receptors, and include a description of the olfactory pathway. f. Give a functional overview of light and optics. g. Describe the photoreceptors on the retina, visual pathway to brain, and visual processing. h Discuss sound and the mechanisms of hearing. i. Discuss the mechanisms of equilibrium and orientation. -5Course Content – Bio 163L - lab The student should be able to: 1L. Organization of the Body a. Discuss the relationship between the terms "anatomy" and "physiology." b. Identify and be able to use the following concepts related to body structure: directional vocabulary, anatomical planes, regions, and positions. 2L. Tissue a. Identify the four basic types of tissues in the body. b. Describe the anatomical characteristics of epithelial tissue. (1) Classify epithelial tissue into several types, including: stratified squamous, transitional, simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, pseudostratified columnar. . c. d. e. Describe the anatomical characteristics of connective tissue. (1) Classify connective tissue according to type, including the structural features of at least the following: areolar, adipose, reticular, dense regular, dense irregular, cartilage (3 types), bone, blood. (2) Identify fibers and cell types found in each connective tissue. Characterize the three types of muscle, including microscopic properties of each. Identify all tissue subgroups listed above, and nervous tissue, using the microscope. 3L. Integumentary System a. Identify skin layers and related structures using microscope and models. 4L. Skeletal System a. Illustrate and identify the gross anatomical structure of the long bone. b. Identify the bones and bone markings from skeletal models, diagrams, and other resource materials. c. Identify and discuss variations between male and female skeletons. 5L. Muscle System a. Identify origins, insertions and actions of muscles presented in class. (See APPENDIX. Human and other models may be used, but use of the cat as the primary dissection and testing specimen is expected.) b. Demonstrate the relationship between muscles and their antagonists. 6L. Nervous System--General a. Describe the structure and function of the neuron. b. Define and be able to use the terms: white matter, gray matter, nerve, tract, ganglion, nucleus. -6- 7L. Central Nervous System a. Describe and characterize functions of the following regions of the brain: cerebrum, cerebellum, hypothalamus, thalamus, brain stem, limbic system, reticular formation. b. Identify the meninges and ventricles of the brain. c. Understand the gross anatomy of the spinal cord including its connections with brain and spinal nerves. d. Identify major structural and functional brain features using human models and dissection of sheep brains. 8L. Peripheral Nervous System a. List names, numbers and functions of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. b. Know the distribution of the spinal nerves. c. Identify features of nerve and spinal cord models. 9L. Special Senses a. Describe the structure of the ear. b. Identify and label features of the vertebrate eye using human eye models and dissected eye specimens. Teaching and Grading Procedures Teaching will be a combination of lecture and lab. The lecture portion may include a traditional lecture format and/or small group sessions in which students discuss topics and reinforce concepts from lectures or some other appropriately organized approach. The laboratory portion of this course includes a comprehensive histology component as well as extensive dissections, the cat being the major model. In addition, human models, sheep brains, and eye specimens are used. Lab tests are non-cumulative practical exams, using dissected specimens and models. Multiple choice questions, matching questions, essay questions and word banks are not appropriate for practical exams. Exam questions should accurately reflect the scope of material covered in the required lab manual. Practical exam scores should constitute a decisive majority of the lab grade. Lecture procedures, topic coverage depth, and grading of students should reflect the depth of coverage presented in the approved textbook for the course. Use of text examples, personal examples, chapter summaries, cross sections of study questions in both text and accompanying study guide, and cross sections of test bank questions are all appropriate means of assessing depth of text coverage. The following topics represent the course sequence: -7- Core concepts of anatomy and physiology Organization of living organisms Tissues Integumentary System Skeletal System Muscular System Nervous System The lecture component of the course accounts for 60 percent of the final grade; the lab component, therefore, accounts for 40 percent of the grade. Extra credit assignments for individual students are not allowed. Textbooks and Materials Current editions of the following textbooks, or their equivalent, are standard for BIO 163, and are available in the LCCC bookstore: Marieb, Elaine and Hoehn, Katja. Human Anatomy and Physiology. Pearson/Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company. (lecture text) Michael G. Wood. Laboratory Manual for Anatomy & Physiology I & II, LCCC compilation. Pearson/Benjamin/Cummings, Inc. (lab manual) Students are expected to provide their own gloves. -8- APPENDIX Human Muscles to Identify Note to instructors: You may compare the ones typed in italics between the human models and the cats. Note difference in size, shape, angle, precise name, and if they are divided into separate parts. HEAD Orbicularis oris #on little torso model 23 #on big torso model 11 Orbicularis oculi 19 7 Muscle Temporalis Masseter Head model Left side of model Right side of model Origin Insertion Action Lips Closes lips Eyelids Blinking, squinting 14 Various facial muscles, maxilla, mandible, septum of nose Nasal portion of frontal bone, frontal process of maxilla, medial palpebral ligament Temporal fossa Coronoid process of mandible Elevates jaw, retracts mandible 27 Zygomatic arch Angle and ramus of mandible Elevates jaw, clenches teeth NECK (Anterior) Muscle Head model Sternocleidomastoid Right side of model Sternohyoid Digastric #on little torso model 28 #on big torso model 68 Origin Insertion Action Manubrium & medial end of clavicle Mastoid process of temporal bone Rotation or flexion of head 29 39 Manubrium and clavicle Hyoid Pulls hyoid down 27 (under chin) Posterior belly-mastoid process, anterior belly-inner surface of mandible Fibrous loop on hyoid bone Raises hyoid, assists in lowering mandible A-1 NECK (Posterior) Trapezius #on little torso model 34 Levator scapulae 36 Splenius group 35 Muscle Head model #on big torso model 1 Origin Insertion Action Occipital bone, ligamentum nuchae, spinous processes of C7 and all thoracic vertebrae 1st to 4th cervical vertebrae Clavicle, spine of scapula and acromion process of scapula Adducts scapula, hyperextends head Superior angle of scapula Ligamentum nuchae, 7th cervical & 1st three thoracic vertebrae Occipital bone and mastoid process Extends head backward and flexes laterally, elevates scapula Extension and rotation of head TRUNK AND SHOULDER (Anterior) Muscle # on little torso model Origin Insertion Action 51 # on big torso model 21 Pectoralis major Clavicle, sternum, costal cartilage Pectoralis minor 52 24 Ribs 3, 4, & 5 Between greater & lesser tubercles of humerus Coracoid process of scapula Deltoid (anterior, middle, posterior) 50 Clavicle, acromion process and spine of scapula Deltoid tuberosity of humerus Serratus anterior 54 1st to 9th ribs Anterior medial border of scapula 26 Inferior borders of ribs Superior borders of ribs Adduction, flexion, and medial rotation of humerus Depresses shoulder by drawing scapula downward Whole muscle abducts humerus; In part, may flex, rotate, extend humerus Pulls scapula downward, forward, inward Elevates ribs (aids in inspiration) 27 Superior borders of ribs Inferior borders of ribs Depresses ribs (aids in expiration) 44 Inferior border of rib and sternum, costal cartilages of last six ribs and lumbar vertebrae Central tendon Inspiration, increases vertical dimensions of thorax, increases intra-abdominal pressure External intercostals (11 pairs) Internal intercostals (11 pairs) Diaphragm 53 A-2 TRUNK AND SHOULDER (Posterior) Muscle # on little torso model # on big torso model Origin Insertion Action Latissimus Dorsi 63 2 Greater tubercle of humerus Extends, adducts, medially rotates humerus Infraspinatus 60 Lower 6 thoracic vertebrae, lumbar and sacral vertebrae, iliac crest, lower ribs Infraspinous fossa of scapula Greater tubercle of humerus Rotates humerus laterally Teres major 61 Inferior angle of scapula Crest of lesser tubercle of humerus Teres minor 69 Lateral border of scapula Lowest portion of greater tubercle of humerus Greater tubercle of humerus Adducts, extends, rotates humerus medially Rotates humerus laterally, weakly adducts it Abduction of humerus Supraspinatus Rhomboideus major 59 Above spine of scapula 4 Rhomboideus minor Just above #59 5 Ligamentum nuchae, spinous processes of 7th cervical, 1st thoracic vertebrae Upper part of medial border of scapula ( root of scapular spine) Adducts scapula 1 Subscapular fossa Lesser tubercle of humerus Medially rotates humerus and holds head of humerus in glenoid cavity Subscapularis Supraspinous fossa Spinous processes of 1st to 5th thoracic vertebrae Medial border of scapula. Adducts scapula A-3 ABDOMINAL MUSCLES Muscle # on little torso model Origin Insertion Action 56 # on big torso model 39 Rectus abdominis Pubic bone Xiphoid process, costal cartilages of ribs 6, 7 & 8 Compresses abdominal viscera, flexes vertebral column External oblique 55 36 Lower eight ribs Linea alba Internal oblique 57 40 Inguinal ligament, iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia Lower 3 ribs, xiphoid process, linea alba, pubis Compresses abdominal viscera, flexes vertebral column Compresses abdominal viscera, flexes vertebral column Transversus abdominis 143 42 Inguinal ligament, iliac crest, costal cartilages of lower 6 ribs, thoracolumbar fascia Linea alba, pubis Compresses abdominal viscera, flexes vertebral column Origin Insertion Action Quadratus lumborum # on big torso model (inside) 166 Iliolumbar ligament, iliac crest Last rib, transverse processes of lower 4 lumbar vertebrae Aids in extending trunk Psoas major 165 Lumbar vertebrae Lesser trochanter of femur Flexion of femur and vertebral column Iliacus 167 Iliac fossa Lesser trochanter of femur Flex femur PELVIC MUSCLES Muscle A-4 UPPER LIMB (Movements of Brachium and Antebrachium) Muscle # on little torso model # on arm model 72 # on big torso model 9 Coracobrachialis Biceps brachii 71 7 9 Brachialis 73 8 10 Brachioradialis 82 13 Triceps brachii 70 10, 11, 12 Origin Insertion Action Coracoid process of scapula Medial surface of humerus Flexion and adduction of humerus Short (medial) head: coracoid process of scapula long (lateral) head: supraglenoid tubercle of scapula Lower half of humerus Radial tuberosity Flexes and supinates forearm Coronoid process of ulna Flexes forearm 20 above lateral epicondyle of humerus lateral surface of radius above styloid process flexes forearm 11 Long head: scapula; lateral head: posterior surface of humerus; medial head: posterior surface of humerus Olecranon process of ulna Extends forearm UPPER LIMB (Hand Movements- Supination and Pronation) Muscle # on little torso model # on arm Model Origin Insertion Action Supinator 86 25 lateral epicondyle of humerus, below radial notch of ulna lateral upper 1/3 of radius supinates forearm Pronator teres 74 12 medial epicondyle of humerus middle lateral surface of radius pronates forearm A-5 UPPER LIMB (Hand Movements- Flexion of Hand) Muscle # on little torso model # on arm Model Origin Insertion Action Flexor carpi radialis 75 13 Medial epicondyle of humerus 2nd & 3rd metacarpals Flexes wrist, assists in pronating, abducting hand Flexor carpi ulnaris 77 15 Medial epicondyle of humerus, olecranon process of ulna Pisiform, hamate, 5th metacarpal Flexes wrist, assist in adducting hand Palmaris longus 76 14 Medial epicondyle of humerus Palmar aponeurosis Flexes wrist UPPER LIMB (Hand Movements- Flexion of Digits) Muscle # on little torso model Flexor digitorum superficialis 85 (under 7476) Flexor pollicis longus # on big torso model 20 # on arm model Origin Insertion Action 24 Humerus, ulna, radius Middle phalanges of digits 2-5 Flexes middle and proximal phalanges of digits 2-5 22 41 Radius, ulna, interosseus membrane Distal phalanx 1 Flexes thumb UPPER LIMB (Hand Movements- Extends Wrist and Hand) Muscle # on little torso model # on arm model Origin Insertion Action Extensor carpi radialis longus 81 19 Humerus 2nd metacarpal Extends wrist, abducts hand Extensor carpi radialis brevis 80 18 Humerus 3rd metacarpal Extends wrist, abducts hand Extensor carpi ulnaris Extensor digitorum 78 16 Lateral epicondyle of humerus 5th metacarpal Extends wrist 79 17 Lateral epicondyle of humerus Proximal and middle phalanges of digits 2-5 Extension of digits 2-5 A-6 UPPER LIMB (Hand Movements- Extends and Abducts Digits) Extensor pollicis brevis 83 # on arm Model 21 (only tendon is visible) 22 Abductor pollicis longus 84 23 Interosseus membrane Trapezium and 1st metacarpal Abduct thumb Abductor pollicis brevis 90 29 flexor retinaculum and tubercles of scaphoid and trapezium proximal phalanx of thumb abducts thumb Muscle # on little torso model Extensor pollicis longus Origin Insertion Action Ulna and radius Distal phalanx of thumb Extends thumb Radius Proximal phalanx of thumb Extends thumb LOWER LIMB (Thigh Movements) # on leg model 3 Origin Insertion Action Gluteus maximus # on little torso model 101 ilium, sacrum, coccyx iliotibial tract, posterior femur extension, outward rotation of femur Gluteus medius 102 4 Ilium Greater trochanter of femur Abduction, medial rotation of femur Sacrum Greater trochanter of femur Lateral rotation of femur Muscle Piriformis Tensor fasciae latae Adductor longus 108 9 anterior superior iliac spine lateral condyle of tibia abducts and flexes thigh 115 13 Pubis linea aspera of femur flexes and medially rotates femur Adductor magnus 117 14 Pubis and ischium Gluteal tuberosity, linea aspera Adducts and extends thigh A-7 LOWER LIMB (Thigh and Lower Leg Movements) # on little torso model 120 # on leg model 18 Origin Insertion Action long head: ischial tuberosity short head: linea aspera of femur head of fibula, lateral condyle of tibia Collective action (Hamstrings): flex lower leg, extends thigh Hamstring: Semitendinosus 118 16 ischial tuberosity tibia Collective action (Hamstrings): flex lower leg, extends thigh Hamstring: Semimembranosus 119 17 ischial tuberosity medial condyle of tibia Collective action (Hamstrings): flex lower leg, extends thigh Quadriceps Femoris: Rectus femoris Quadriceps Femoris: Vastus lateralis Quadriceps Femoris: Vastus medialis Quadriceps Femoris: Vastus intermedius Sartorius Gracilis 110 anterior inferior iliac spine, superior rim of acetabulum patella, tibial tuberosity 11a 112 11c linea aspera lateral condyle of tibia, iliotibial tract collective action (quadriceps): extension of lower leg. Independently flexes femur collective action (quadriceps): extension of lower leg 113 11b linea aspera patella collective action (quadriceps): extension of lower leg 111 11d anterior and lateral surface of femur patella collective action (quadriceps): extension of lower leg 109 116 10 15 anterior superior iliac spine pubic bone medial surface of tibia medial surface of tibia flex and medially rotate thigh adducts, flexes, rotates thigh medially Muscle Hamstring: Biceps femoris A-8 LOWER LIMB (Lower Leg and Foot Movements) # on little torso model 126 # on leg model 24a, b Origin Insertion Action medial and lateral condyles of femur (2 heads) posterior surface of calcaneus plantar flexion Triceps surae: Soleus Tibialis anterior 127 24c heads of fibula and tibia posterior surface of calcaneus plantar flexion 121 19 Medial cuneiform and 1st metatarsal Tibialis posterior 129 28 Lateral condyle and upper 2/3 of tibia Tibia, fibula, interosseus membrane Fibularis longus (=Peroneus longus) Fibularis brevis (=Peroneus brevis) Flexor digitorum longus Flexor hallucis longus Extensor digitorum longus Extensor hallucis longus 124 22 Head and upper surface of fibula Navicular, cuneiforms, cuboid, 2 nd, rd 3 4th metatarsals 1st metatarsal Dorsiflexion, Inverts foot plantar flexion 125 23 Lower lateral surface of fibula 5th metatarsal plantar flexion 130 27 lower posterior surface of tibia distal phalanges of digits 2-5 flexes distal phalanges of 2-5 131 29 Lower posterior fibula Distal phalanx of first toe Flexion of first toe 122 21 Upper anterior fibula Extension of toes, dorsiflexion 123 20 (under 21) Fibula, interosseus membrane Middle and distal phalanges of digits 2-5 Distal phalanx of 1st toe Muscle Triceps surae: Gastrocnemius plantar flexion, everts foot Extends 1st toe, dorsiflexion A-9