The Cranial Nerves
advertisement

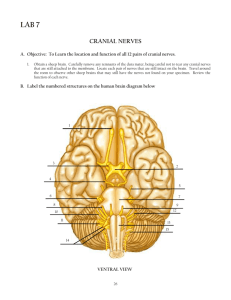
The Cranial Nerves Honors Anatomy & Physiology for copying CRANIAL NERVES • 12-pair • named “cranial” because each passes thru a foramina of the cranium • part of PNS • each with roman numeral (order from anterior posterior in which nerves arise from base of brain) & a name that indicates nerve distribution CRANIAL NERVES • classified as: 1. sensory 2. motor 3. mixed (sensory & motor) Cranial Nerve I: Olfactory • olfact = to smell • sensory • olfactory epithelium on superior surface of nasal cavity just inferior to cribiform plate of ethmoid bone • olfactory receptors are bipolar neurons – each: single odor-sensitive dendrite – their unmyelinated axons join above plate form rt or lt olfactory nerves Course of Olfactory Nerve • olfactory nerves end in pair of olfactory bulbs: masses of gray matter resting just above cribiform plate where they synapse with next neurons in olfactory pathway Course of Olfactory Nerve • axons of these neurons make up the olfactory tracts posteriorly to primary olfaction center in temporal lobe Cranial Nerve II: Optic Nerve • optic = eye • sensory • rods & cones in retina: receptors initiating visual signals & relay them bipolar cells optic ganglion neurons their axons join forming optic nerves • pass thru optic foramen optic chiasm: a cross-over of medial half of each eye to opposite side (lateral half does not cross Optic Tracts • from optic chiasm optic tracts – most axons thalamus synapse with neurons whose axons primary visual area of occipital lobe – some axons synapse with motor neurons in midbrain extrinsic eye muscles Cranial Nerve III: Oculomotor • oculo = eye • mixed, mainly motor • its motor nucleus in ventral part of midbrain • 2 branches pass thru superior orbital fissure Oculomotor Nerve Extrinsic Muscles of Eye Superior Branch • axons innervate: 1. superior rectus 2. levator palpebrae superioris (upper eyelid) • 1. 2. 3. Inferior Branch axons innervate: medial rectus inferior rectus inferior oblique Oculomotor Nerve • inferior branch also: – parasympathetic innervation to intrisic muscle of eye (smooth muscle) 1. ciliary muscle: adjusts lens for near/far vision 2. circular muscle of iris: contracts/relaxes in response to amt of light (pupils constrict/dilate) Oculomotor Nerve: Sensory • proprioception: nonvisual perception of movements & positions of body Cranial Nerve IV: Troclear Nerve • • • • trochle = pulley mixed, mainly motor smallest of the 12 cranial nerves only 1 that arises from posterior of midbrain Cranial Nerve IV: Troclear Nerve • motor: • axons from nucleus in midbrain superior orbital fissure • innervates superior oblique muscle • sensory: proprioception in superior oblique Trigeminal Nerve • largest of 12 cranial nerves • mixed: – sensory: ganglion in temporal bone – motor: neurons in pons Cranial Nerve V: Trigeminal Nerve • tri: has 3 branches 1. Ophthalmic: sensory only: upper eyelids, eyes, lacrimal glands, upper nasal cavity, side of nose, forehead, anterior ½ of scalp 2. Maxillary: sensory only: mucosa of nose, palate, part of pharynx, upper teeth, upper lip, lower eyelids 3. Mandibular: sensory: anterior 2/3 of tongue (not taste), cheek, lower teeth motor: muscles of mastication Cranial Nerve VI: Abducens Nerve • ab: away / ducens: to lead (nerve impulses causes abduction of eyeball) • mixed mainly motor • nucleus in pons (motor): innervates lateral rectus muscle • sensory: proprioception in lateral rectus Cranial Nerve VII: Facial Nerve • mixed • sensory: – taste buds anterior 2/3 of tongue, proprioceptors in face & scalp • motor: – nucleus in pons – innervates muscles of facial expression + stylohyoid muscle & posterior belly of digastric muscle • parasympathetic: lacrimal glands, palatine glands, salivary glands: sublingual & sub-mandibular Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear Nerve • vestibule:small cavity; cochlear: snail-like • mixed, mainly sensory • 2 branches 1. Vestibular: – equilibrium 2. Cochlear: – – hearing motor: hair cells of spiral organ Cranial Nerve IX: Glossopharyngeal Nerve • glosso:tongue, pharyngeal: throat • Mixed • sensory: taste buds & somatic sensory receptors on posterior 1/3 tongue, proprioceptors in swallowing muscles, baroreceptors (stretch) in carotid sinus, chemoreceptors in carotid bodies • motor: from nuclei in medulla, exit thru jugular foramen, innervate stylopharyngeus muscle (elevates pharynx & larynx) • parasympathetic: motor: stimulate parotid gland to secrete saliva Cranial Nerve X: Vagus Nerve • vagus: wanderer, vagrant • mixed • distributed from head abdomen Vagus Nerve • sensory: – – – – skin of external ear taste buds in epiglottis & pharynx proprioceptors in muscles of neck & throat baroreceptors in arch of aorta & chemoreceptors in aortic bodies – visceral sensory receptors in most organs of thorax & abdominal cavities Vagus Nerve • parasympathetic motor: – heart & lungs – glands in GI tract – smooth muscle of airways, esophagus, stomach, gall bladder, small intestine, most of large intestine Cranial Nerve XI: Accessory Nerve • mixed • originates from both the brainstem & spinal cord • cranial root: – motor: from medulla thru jugular foramen – supplies voluntary muscles of pharynx, larynx, & soft palate • spinal root: – mixed, mainly motor – motor: Cranial Nerve XI: Accessory Nerve • spinal root: – mixed, mainly motor – motor: neurons in anterior gray horn of C1 – C5 axons come together fpramen magnum jugular foramen – innervates sternocleidomastoid & trapezius muscles – sensory: proprioceptors in muscles it supplies Cranial Nerve XII: Hypoglossal • hypo: below, glossal: tongue • mixed • sensory:proprioceptors in tongue muscles medulla • motor: nucleus in medulla hypoglossal canal muscles of the tongue (speech, swallowing) Development of the Nervous System • begins developing in 3rd wk from a thickening of ectoderm called the neural plate Development of the Brain & Spinal Cord