Introduction to Psychology
advertisement

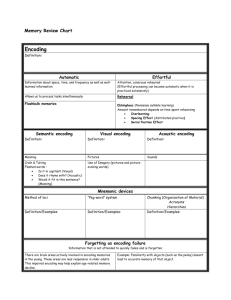
Memory Memory persistence of learning over time through the storage and retrieval of information Encoding: Getting Information In Encoding Automatic Effortful Effortful Encoding Rehearsal: conscious repetition of information Types Maintenance Rehearsal: rote memory Elaborative Rehearsal: associating unlike terms Deep Processing: understand meaning Effortful Encoding Imagery mental pictures Mnemonics techniques that use vivid imagery and organizational devices Effortful Encoding Chunking organizing items into familiar, manageable units • XIBMCIAFBICBSMTV • X IBM CIA FBI CBS MTV Encoding Phenomena • • • • Serial Position Effect Next-in-Line Effect Sleep Effect Spacing Effect – Distributed practice over mass practice Storage Sensory Memory the immediate, initial recording of sensory information in the memory system extremely temporary Iconic memory Echoic memory determine what needs to passed on and what does not bypassed by rehearsal techniques Storage Short-Term Memory consciously activated memory that holds a few items briefly our mental scratch pad will hold approx. 7 +/- 2 items time and space limited Storage Long-Term Memory the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system Storage: Long-Term Memory Subsystems Types of long-term memories Explicit (declarative) With conscious recall Facts-general knowledge (“semantic memory”) Personally experienced events (“episodic memory”) Implicit (nondeclarative) Without conscious recall Skills-motor and cognitive Dispositionsclassical and operant conditioning effects Retrieval • Encoding Specificity Principle: retrieval is affected by encoding situations – context: things going on internally (mood congruent memory) and externally (environment) while encoding – physical state: if under the influence of a substance such as caffeine while encoding, will best retrieve under the influence of that substance (state dependent retrieval) Retrieval Recall measure of memory in which the person must retrieve information learned earlier as on a fill-in-the blank test Recognition Measure of memory in which the person has only to identify (recognize) items previously learned as on a multiple-choice test Retrieval Cues Deja Vu (French)--already seen Often causes the eerie feeling of “having experienced before” cues from a current situation may subconsciously trigger retrieval of an earlier similar experience (priming) Flashbulb memories Vivid recollection of often emotional events Where were you when the 911 attacks took place? Biological Basis of Memory Synaptic changes Long-term Potentiation increase in synapse’s firing potential of memory neurons after brief, rapid stimulation Strong emotions make for stronger memories some stress hormones boost learning and retention Hippocampus