8C6 Notes
advertisement

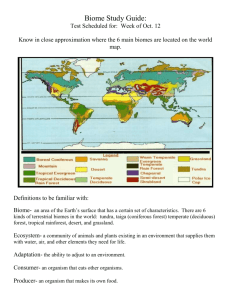
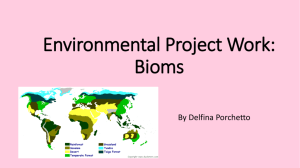
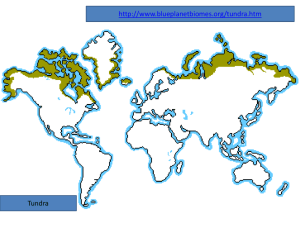
8th Grade Chapter 6 Notes Quiz on 2/10/12 1. Biomes are large geographical areas that have similar climates and ecosystems. 2. Tundra is a cold, dry, treeless region, sometimes called a cold desert. In the tundra, winters are long and there is little precipitation each year. 3. During some of the winter months in the tundra, the sun isn’t visible, and the sky is dark 24 hours a day. During a few days in the summer, the sun is always visible. 4. Because of the temperatures and little sun in the tundra, the soil stays frozen permanently. The layers of permanently frozen soil are called permafrost. 5. Tundra plants include: mosses, grasses, and small shrubs. (no trees) 6. Found south of the Tundra, the taiga is the world’s largest biome. The taiga is a cold, forested region dominated by cone-bearing evergreen trees. (parts of Alaska are tundra and taiga ecosystems) 7. Winters are long and cold in the taiga, like the tundra. However, the taiga is slightly warmer and wetter. (more precipitation, mostly snow.) 8. Permafrost can be found in the extreme northern regions of the taiga, but most of the soil does thaw out during the summer months. 9. Taiga plants include mosses and trees, but not a lot of grasses. Sunlight isn’t able to penetrate the forest floor because of the trees. 10. Temperate regions have four distinct seasons a year with a wide range of temperatures throughout the year. 11. Deciduous trees, trees that lose their leaves in the autumn (fall), dominate temperate deciduous forests. Most of the temperate deciduous forests in the US are located east of the Mississippi River. (like us!) 12. Temperate rain forests have a large amount of rainfall each year and milder temperatures ranges. (in US – california) 13. Trees with needlelike leaves are common in temperate rain forests like the Douglas fir, western red cedar, and spruce. These trees often grow to reach large heights. (California redwood) 14. Tropical rain forests have warm temperatures, wet weather, and lush plant growth and are found near the equator. 15. Tropical rain forests are the most biologically diverse of all biomes. (means they have the most variety of plant and animal life) 16. Deserts are the driest biome and are able to support little plant life. 17. The soil of the desert is thin and sandy or gravelly. The cactus is the main type of plant grown in the desert. 18. Grasslands are prairies or plains that are dominated by grasses. 19. Temperatures of the grasslands can vary from tropical to temperate. 20. Rainfall in the grasslands can vary, but usually include a dry season. 21. Freshwater ecosystems include flowing and standing water, low or no salt 22. There are two types of freshwater ecosystems: 1. rivers and streams, 2. lakes and ponds. 23. Rivers and streams have flowing water and nutrients are washed into the water from the land. 24. The faster the flow of a river or stream, the greater the amount of oxygen in the water. 25. Lakes and ponds have very little water flow. 26. If light is able to reach bottom, the sunlight warms and helps support plant and animal life. 27. Deeper lakes support life along shallow shoreline or surface. 28. Wetlands are regions that stay wet all or most of the year. 29. They lie between solid land and water and are very fertile ecosystems. 30. Saltwater ecosystems consist of 95% of the earth’s water supply. 31. There are four parts of a saltwater ecosystem: open ocean, coral reefs, seashores, and estuaries. 32. Open oceans have a lighted life zone where plankton live and a dark life zones where animals feed on material that floats down or prey on each other. 33. Coral reefs are diverse and fragile ecosystems formed from coral shells. 34. Seashores are found along coastlines and have a intertidal zone, which is covered with water at high tide and exposed to air at low tide. 35. Estuaries are where a river meets an ocean; called bays, lagoons, harbors, inlets, or sounds. 36. These areas are rich in nutrients and have a mixture of salt and freshwater.