FLOWCHART
advertisement

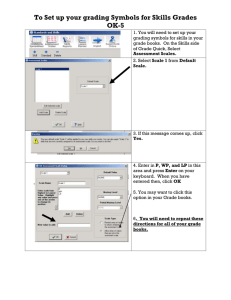
1 FLOWCHART Programming & Algorithm Outline 2 Element of computer Computer language & Interpreter Analysis & Algorithm Algorithm structure Element of computer 3 Computer Hardware Software Peopleware Computer language & Language Translator 4 Computer language Machine Language Low Level Language High Level Language Language Translator Assembler Compiler Interpreter Analysis & Algorithm 5 Analysis Answer Analysis Data Analysis Process Analysis Debug Analysis Algorithm Flowchart Pseudo code Introduction to Flowchart 6 A flowchart is a common type of chart, that represents an algorithm or process, showing the steps as boxes of various kinds, and their order by connecting these with arrows. Flowcharts are used in analyzing, designing, documenting or managing a process or program in various fields Types of flowcharts 7 Consist of Document flowcharts, showing a document flow through system Data flowcharts, showing data flows in a system System flowcharts, showing controls at a physical or resource level Program flowchart, showing the controls in a program within a system Symbol 8 Start and end symbols Represented as lozenges, ovals or rounded rectangles, usually containing the word "Start" or "End", or another phrase signaling the start or end of a process, such as "submit enquiry" or "receive product". Arrows Showing what's called "flow of control" in computer science. An arrow coming from one symbol and ending at another symbol represents that control passes to the symbol the arrow points to. Symbol 9 Processing steps Represented as rectangles. Examples: "Add 1 to X"; "replace identified part"; "save changes" or similar. Input/Output Represented as a parallelogram. Examples: Get X from the user; display X. A Manual input represented by parallelogram, with the top irregularly sloping up from left to right. An example would be to signify data-entry from a form; Symbol 10 Conditional or decision Represented as a diamond (rhombus). These typically contain a Yes/No question or True/False test. This symbol is unique in that it has two arrows coming out of it, usually from the bottom point and right point, one corresponding to Yes or True, and one corresponding to No or False. A Display Output represented by many rectangle Flowchart Symbols Symbols of flowchart to standard from ANSI (The American National Standard Institute) Symbols Description Processing กระบวนการ การคานวณ Auxiliary Processing กระบวนการสารอง 11 Flowchart Symbols 12 Symbols Subroutine Processing Description กระบวนการที่นิยามไว้ การทางาน ย่อย Input/Output Data ข้ อมูล รับหรื อแสดงข้ อมูลโดยไม่ ระบุชนิดอุปกรณ์ Internal Storage ที่เก็บภายใน Decision Symbol การตัดสินใจ การเปรี ยบเทียบ Flowchart Symbols 13 Symbols Preparation Symbol Manual Input Description การเตรี ยมการ การกาหนดค่า ล่วงหน้ าหรื อกาหนดค่าเป็ นชุดตัวเลข ป้อนข้ อมูลด้ วยตนเอง การรับข้ อมูล เข้ าทางแป้นพิมพ์ ขันตอนที ้ ่ทาด้ วยตนเอง การควบคุม Manual Control โปรแกรมทางแป้นพิมพ์ Document Output เอกสารแสดงผล, การแสดงผลทาง เครื่ องพิมพ์ Flowchart Symbols 14 Symbols Description More Document เอกสารแสดงผลหลายฉบับ Monitor จอภาพแสดงผล Card การ์ ดหรื อบัตรเจาะรู ใช้ ใส่ข้อมูล Tape เทป (สื่อบันทึกข้ อมูล) Flowchart Symbols 15 Symbols Start/End Symbol Description เริ่มต้ น/สิ ้นสุด, การเริ่มต้ นหรื อการ ลงท้ าย Connection Symbol จุดเชื่อมต่อในหน้ าเดียวกัน Connection Symbol ตัวเชื่อมต่อไปหน้ าอื่น จุดร่วมการเชื่อมต่อ Flowchart Symbols 16 Symbols Description หรื อ ตรวจเทียบ เรี ยงลาดับ แยก Flowchart Symbols 17 Symbols Description ผนวก ข้ อมูลที่เรี ยง หน่วงเวลา ที่เก็บแบบเข้ าถึงโดยเรี ยงลาดับ Flowchart Symbols 18 Symbols Description ดิสก์แม่เหล็ก หน่วยเก็บแบบเข้ าถึงโดยตรง Flow Line เส้ นแสดงลาดับกิจกรรม Comment Line แสดงคาอธิบายหรื อหมายเหตุ Usually Symbols 19 Read Reading of Keyboard Read Read Reading of other tools Reading data of Symbols by Keyboard & Other tools Usually Symbols 20 Display Display Display on Monitor แสดงผล... Display Display on Printer แสดงผล... Display Display on other tools Display data of Symbols by Keyboard & Other tools Natural Language 21 Find x from equation x = (a+b-c)/100 ; if a, b, c manual input from keyboard and display x on monitor. Start Input a, b, c x <- (a+b-c)/100 x End Program Sample; Uses crt; Var a, b, c, x : real Begin Clrscr; Readln(a,b,c); x := (a+b-c)/100 Writeln(x:8:2); End. Algorithm structure 22 Sequential Step to Step Selection Select part to true and false Repetition Loop Sequential 23 Process 1 Process 2 Process 3 Summations of 2 number define a, b by a, b manual input from keyboard and display answer on monitor. Begin a,b sum=a+b sum End Selection 24 Consist if switch of 2 selection if structure (Single Selection ) 25 Condition no yes Process if structure (Single Selection ) Input number 1 integer manual input from keyboard, brings the number to check number is 0, if true display “Greater than Zero” on monitor Begin n n>0 yes Greater than Zero no End 26 if structure (Double Selection ) 27 Process 2 no Condition yes Process 1 if structure (Double Selection ) Input number 1 integer manual input from keyboard, brings the number to check number is 0, if true display “Greater than Zero” and then false display “Less than or Equal to Zero” on monitor Begin n Less than or Equal to Zero no n>0 Greater than Zero yes End 28 Multi-Selection (if/else if/ else .. Structure) 29 yes Process 1 Condition 1 yes no Condition 2 yes Process 2 Process 3 no Condition 3 no Process 4 Multi-Selection (if/else if/ else .. Structure) 30 Finding Grade 0-49 E 50-59 D 60-69 C 70-79 B 80-100 A Manual input from keyboard and display on monitor Begin score yes no score>=80 yes Grade=’A’ no score>=70 yes Grade=’B’ score>=60 Grade=’C’ yes Grade=’D’ Grade End no score>=50 no Grade=’E’ case/switch Structure 31 case 1 yes Process Process Process Process Process Process no case 2 yes no case n no Process yes case/switch Structure 32 Manual input from keyboard and display on monitor Choice 1 + Choice 2 – Choice 3 * Choice 4 / Begin a,b choice case 1 yes s=a+b s s=a-b s s=a*b s s=a/b s no case 2 yes no case 3 yes no case 4 no End yes Repetition 33 for while do .. while/repeat .. until while .. Structure 34 Condition no yes Process while .. Structure 35 Summations of number 1 – 10 with while loop Begin counter=0 sum=0 counter<=10 yes counter=counter+1 sum=sum+counter counter,sum End no do while Structure & repeat until Structure 36 Process Condition no yes do while Structure & repeat until Structure Summations of number 1 – 10 with do-while loop Begin counter=0 sum=0 counter=counter+1 sum=sum+counter counter,sum yes Counter<=10 no 37 End for Structure 38 Loop Process Process for Structure Summations of number 1 – 10 with do-while loop Begin sum=0 counter=1, counter<=10, step 1 sum=sum+counter counter,sum 39End exercise 40 1. จงเขียนอัลกอริทึมแบบคำอธิบำยและผังงำน ในกำรคำนวณยอดชำระค่ำ น้ ำประปำ โดยมีเงื่อนไขดังนี้ 1 – 50 หน่ วย คิดหน่ วยละ 4.25 บำท 51 – 100 หน่ วย คิดหน่ วยละ 3.25 บำท ตั้งแต่ 101 หน่ วยขึ้ นไป คิดหน่ วยละ 2.25 บำท exercise 41 2.จงเขียนอัลกอริทึมแบบคำอธิบำยและผังงำน เพื่อคำนวณค่ำเดินทำง โดยให้รบั ค่ำระยะทำง 1 จำนวน ซึ่งมีอตั รำ ดังนี้ n ระยะทำง 1 - 5 กิโลเมตร คิดค่ำเดินทำงกิโลเมตร 100 บำท n ระยะทำง 6 - 10 กิโลเมตร คิดค่ำเดินทำงเพิ่ม จำก 5 กิโลเมตร คิด กิโลเมตรละ 80 บำท n ระยะทำง ตั้งแต่ 11 กิโลเมตรขึ้ น ไป คิดค่ำเดินทำงเพิ่ม จำก 10 กิโลเมตร คิดกิโลเมตรละ 60 บ exercise 42 3.จงเขียนอัลกอริทึมแบบคำอธิบำยและผังงำน ของ โปรแกรมตัดเกรด ดังนี้ A 80 – 100 B+ 79 - 75 B 74 – 70 C+ 69 - 65 C 64 – 60 D+ 59 - 55 D 54 – 50 F 49 - 0 โดยรับค่ำอินพุท ตั้งแต่ 0-100 ทำงแป้ นพิมพ์