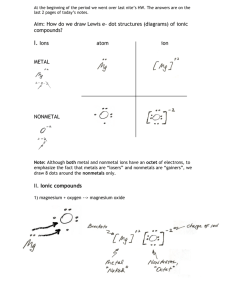
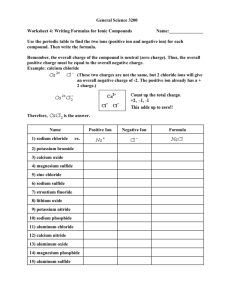
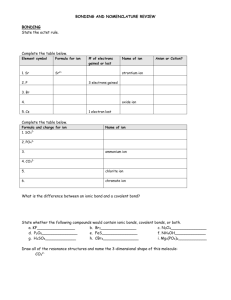
c. Ion Counter Ion
advertisement
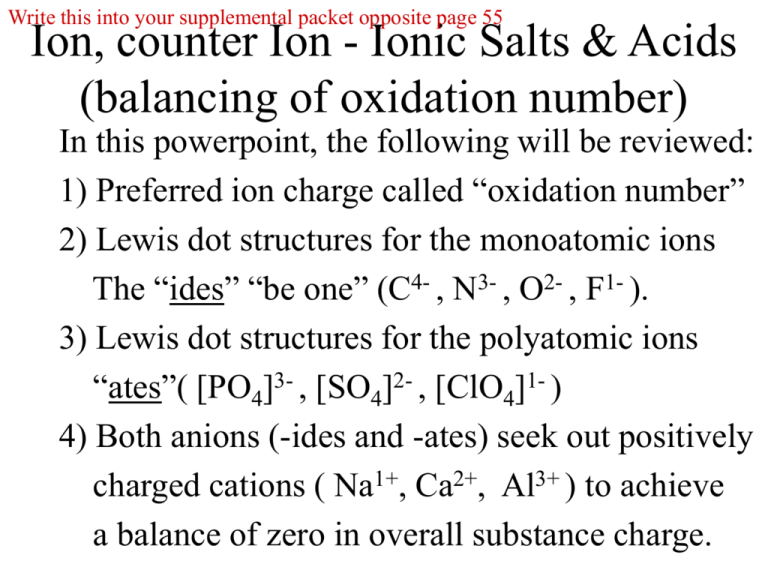
Write this into your supplemental packet opposite page 55 Ion, counter Ion - Ionic Salts & Acids (balancing of oxidation number) In this powerpoint, the following will be reviewed: 1) Preferred ion charge called “oxidation number” 2) Lewis dot structures for the monoatomic ions The “ides” “be one” (C4- , N3- , O2- , F1- ). 3) Lewis dot structures for the polyatomic ions “ates”( [PO4]3- , [SO4]2- , [ClO4]1- ) 4) Both anions (-ides and -ates) seek out positively charged cations ( Na1+, Ca2+, Al3+ ) to achieve a balance of zero in overall substance charge. Where’d me m -ates [PO4]3- , [SO4]2- , [ClO4]1- •* O O •* •* OO •* rrR’ - ides” “be one” (C4- , N3- , O2- , F1- ). Things to keep in mind when considering oxidation numbers: o o o o 1) Any atom in its elemental form [Na(s), O2(g) Mg(s), Cl2(g)] has an oxidation number of zero 2) For monatomic ions, the oxidation number equals an ion’s charge; 4- C carbide ion N 3- 2- O nitride ion oxide ion 1- F fluoride ion 3) For polyatomic ions, the sum of the constituent atoms’ oxidation numbers is equal to the charge of the ion; PO4 3- phosphate ion 2SO4 sulfate ion 1ClO4 perchlorate ion 4) For neutral compounds, the sum of the constituent oxidation numbers is equal to zero. Lewis dot structures for monatomics carbide ion 4- C •• N 3- 2- 1- nitride ion 3- N •• F •• 1- •• •• C •• O •• 2- •• •• 4- 3- •• N •• •• •• •• •• C •• 4- O oxide ion 2- O monatomics F fluoride ion 1- F sulfate ion oxyanions •• •• •• •• •• •• •• •• •• •• •• 2SO4 SO4 •• •• •• •• •• PO4 3- •• •• phosphate ion •• •• •• •• •• 3- 1- O •• O Cl •• O O •• •• •• •• •• PO4 O •• O S •• O O •• O •• O P •• O O 2- •• Lewis dot structures for polyatomics 3- 2- 1ClO4 perchlorate ion 1ClO4 Balancing oxidation numbers in ionic salts “Two atoms are walking down the street….”(yes, we get the joke, DrG) Draw a visual picture for the structure of sodium fluoride, NaF 1+ Na 1- F Draw a visual picture for the structure of calcium fluoride,CaF2 1- F 2+ Ca 1- F One atom says “I think I lost an electron.” The other atom says Are you sure?” and the other atom says “Yes, I’m positive.” Balancing oxidation numbers in ionic salts Draw a visual picture for the structure of aluminum fluoride, AlF3 1- F 3+ Al 1- F 1- F Balancing oxidation numbers in ionic salts Draw a visual picture for the structure of aluminum oxide, Al2O3 2- O 2- 3+ Al 3+ 2- Al O O Balancing oxidation numbers in ionic salts Can chemists have BO???????? No way, chemists have B2O3 Draw a visual picture for the structure of boron oxide, B2O3 2- O 2- 3+ B 3+ 2- B O O Balancing oxidation numbers in ionic salts Draw a visual picture for the structure of magnesium oxide, MgO 2+ Mg 2- O Balancing oxidation numbers in ionic salts Draw a visual picture for the structure of sodium phosphate, Na3PO4 1+ Na 1+ Na 3- PO4 1+ Na Balancing oxidation numbers in ionic salts Draw a visual picture for the structure of sodium sulfate, Na2SO4 1+ Na SO4 2- 1+ Na Balancing oxidation numbers in ionic salts Draw a visual picture for the structure of sodium perchlorate, NaClO4 1+ Na 1- ClO4 Balancing oxidation numbers in ionic salts Does DrG feed his dog AlPO? No way, I feed him AlPO4 Draw a visual picture for the structure of aluminum phosphate, AlPO4 3+ Al 3- PO4 Balancing oxidation numbers in Transition Metal ionic salts Draw a visual picture for the structure of iron (II) phosphate, Fe3(PO4)2 2+ Fe 3- PO4 2+ Fe 3- PO4 Note, transition metal ionic salt names….. Always use a roman numeral in its compound name To represent the oxidation number for the TM ion 2+ Fe Balancing oxidation numbers in ionic salts Draw a visual picture for the structure of iron (III) phosphate, FePO4 3+ Fe 3- PO4 Note, transition metal ionic salt names….. Always use a roman numeral in its compound name To represent the oxidation number for the TM ion The acid proton, no electrons, no neutrons, JUST a proton Draw a visual picture for the structure of a PROTON, H+ 1+ H Note, a substance with hydrogen listed first in its chemical formula (i.e. stomach acid, HCl) is a called an acid. The acid proton, no electrons, no neutrons, JUST a proton Draw a visual picture for the structure stomach acid, HCl, 1+ H Cl 1- Balancing oxidation numbers in an oxyanion acid Draw a visual picture for the structure of phosphoric acid, H3PO4 1+ H 1+ H 3- PO4 1+ H Balancing oxidation numbers in an oxyanion acid Draw a visual picture for the structure of sulfuric acid, H2SO4 1+ H SO4 2- 1+ H Balancing oxidation numbers in an oxyanion acid Draw a visual picture for the structure of perchloric acid, HClO4 1+ H 1- ClO4 Balancing oxidation numbers in an monatomic acid Draw a visual picture for the structure of hydrochloric acid, HCl 1+ H 1- Cl Note, use the word hydro if acid is a monatomic acid (i.e. stomach acid, HCl) is a called hydrochloric acid. Balancing oxidation numbers in a monatomic acid Draw a visual picture for the structure of hydrosulfuric acid, H2S 1+ H 2- S 1+ H Note, use the word hydro if acid is a monatomic acid (i.e. dihydrogen sulfide, H2S) is a called hydrosulfuric acid. Balancing oxidation numbers in an monatomic acid Draw a visual picture for the structure of hydrofluoric acid, HF 1+ H 1- F Other polyatomic ions carbonate ion and nitrate ion Draw a visual picture for carbonate ion, CO32- and nitrate ion, NO31- 2- CO3 1- NO3 Balancing oxidation numbers in a base Draw a visual picture for the structure of sodium hydroxide, NaOH 1+ Na 1- OH Note, use of the word hydroxide is derived from hydro oxide “proton ion” + “oxide ion” combinded equals hydroxide ion (H1+ and O2together equals OH1-) Balancing oxidation numbers in a base Draw a visual picture for the structure of calcium hydroxide,Ca(OH )2 1- 2+ OH Ca 1- OH Note, use of the word hydroxide is derived from hydro oxide “proton ion” + “oxide ion” combinded equals hydroxide ion (H1+ and O2together equals OH1-) Balancing oxidation numbers in a hydro - ate ions Draw a visual picture for the structure of hydrogen carbonate ion, HCO31- 2- 1+ CO3 H equals proton combined with carbonate ion H+ + reactant ions CO3 2- 1- HCO3 hydrogen carbonate ion, HCO31– combination reaction HCO31– product ion Balancing oxidation numbers in a hydro - ate ions Draw a visual picture for the of dihydrogen phosphate ion, H2PO41- 1+ H 3- 1+ H 1- PO4 equals proton combined with phosphate ion 2H+ + reactant ions PO4 3- H2PO4 dihydrogen phosphate ion,H2PO41– combination reaction H2PO41– product ion Supplemental packet page 75 Sparklettes Water Dr. Gergens - SD Mesa College The Crystal-Fresh® Drinking Water ingredient label says the following: “Drawn from our deep protected wells in Santa Ana, CA. Purified using our Crystal-Fresh process, including filtration, ozonation, reverse osmosis, and/or dionization. Contains purified water and specially selected minerals in nutritionally insignificant amounts for great taste (sodium bicarbonate, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride and sodium sulfate). Lets learn to write the correct formulas for these substances (sodium bicarbonate, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride and sodium sulfate) that Sparkletts ® adds to it’s purified water In “nutritionally insignificant amounts for great taste.” Supplemental packet page 76 Lets learn to write the correct formulas for these substances (sodium bicarbonate, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride and sodium sulfate) that Sparkletts ® adds to it’s purified water In “nutritionally insignificant amounts for great taste.” 1+ Na 2- CO3 1+ Na Lets learn to write the correct formulas for these substances (sodium bicarbonate, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride and sodium sulfate) that Sparkletts ® adds to it’s purified water In “nutritionally insignificant amounts for great taste.” 1- Cl 2+ Mg 1- Cl Lets learn to write the correct formulas for these substances (sodium bicarbonate, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride and sodium sulfate) that Sparkletts ® adds to it’s purified water In “nutritionally insignificant amounts for great taste.” 1- Cl 2+ Ca 1- Cl Lets learn to write the correct formulas for these substances (sodium bicarbonate, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride and sodium sulfate) that Sparkletts ® adds to it’s purified water In “nutritionally insignificant amounts for great taste.” 1+ Na 2- SO4 1+ Na Sparklettes Wate r Nomen cla ture Exe rcis e: "Nu triti onal ly ins igni ficant amou nts of these co mpou nds adde d fo r goo d ta ste." Dr. Gerge ns - SD Me sa Col lege + Supplemental packet page 76 – 1. Write th e na me e ach ca tion and each a nion (e.g ., Na is sod ium ion; Cl is ch lorid e io n) 2. Say an d write the nam e of the ion ic salt co mpou nd b y com bini ng e ach ca tion with each an ion in the table (e.g ., s odiu m ch lorid e) 3. Compl ete the tabl e by writing in the i onic sa lt comp ound form ula in e ach ce ll o f th e ta ble (e.g., NaCl). 4. Whe n writi ng a form ula a catio n an d an ion must co mbin e in an appro priate ration to b alan ce cha rge; see exampl es o n back. anions (name these ions) cations (name these ions) Na + sodium ion Mg 2+ magnesium ion Ca 2+ calcium ion – Cl chloride ion NaCl sodium chloride MgCl2 magnesium chloride CaCl2 calcium chloride SO4 2- sulfate ion Na2SO4 sodium sulfate MgSO4 HCO3 – hydrogen carbonate ion NaHCO3 sodium hydrogen carbonate Mg (HCO3) 2 magnesium sulfate magnesium hydrogen carbonate CaSO4 calcium sulfate Ca(HCO3) 2 calcium hydrogen carbonate 5. Predi ct the trans itio n me tal cation cha rge for iro n, Fe, i n th e io nic sal t Fe 2 (SO4 ) 3 , a nd p lace it in the cation box be low. 6. Give a name for Fe 2 (SO4 ) 3 . Since tra nsition meta ls can va riabl e charge , you m ust some how i ndicate metal cati on charg e in its name . 3+ – – 7. Write ad diti onal form ulas for the cation Fe co mbin ed with th e an ions Cl an d HCO3 an d gi ve the ir compo und name s. cation iron (III) ion FeCl3 iron (III) chloride Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 iron (III) sulfate Fe(HCO3) 3 iron (III) hydrogen carbonate Acids . In g enera l, a sub stan ce that has an 'H' listed first in i ts formul a is refe rred to as an acid . Na me the acid b ut p lace a prefi x in its name di = 2, tri = 3, tetra = 4, pen ta = 5, hexa = 6, hepta = 7, o cta = 8 , no na = 9, deca = 10 to in dicate the numb er of hydrog ens in the formul a. anions cations H+ hydrogen ion give a common name and use for each acid – Cl HCl SO4 2- H2SO4 HCO3 – H2CO3 hydrogen chloride hydrogen chloride dihydrogen carbonate hydrochloric acid sulfuric acid carbonic acid stomach acid car battery acid carbonated water