Running Effective Meetings - Placer County Office of Education
advertisement

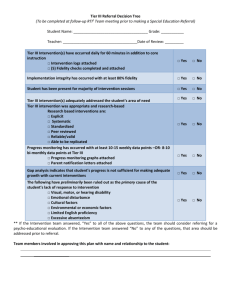
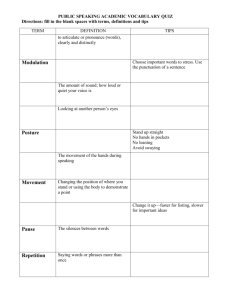
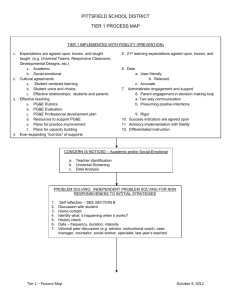
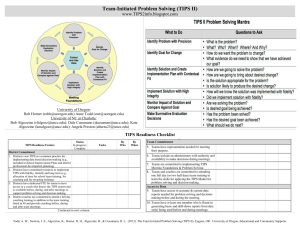
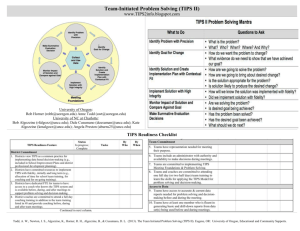
Running Effective Meetings: Team Initiated Problem Solving (TIPS) & Intervention Team Meeting Agenda PBIS Coaches Institute Placer County Office of Education January 20, 2015 Your Hosts: Kim Wood & Kerri Fulton Agenda Why use TIPS? What have been your roadblocks? Meeting Roles & Structure Problem Solving: It shouldn’t create a problem! Monitoring progress…The rest of the story Running effective meetings in Tiers II & III Why use the TIPS meeting agenda & Intervention Team meeting form? A clear model with steps for problem solving routine Access to the right information at the right time in the right format A formal/ predictable process that a group of people can use to build and implement solutions Getting Started? or Getting Stuck? • Discussion: What have been your roadblocks? • Lead your team through the “TIPS Meeting Foundations Checklist” (Worksheet 16) and/or “TIPS Coaching Fidelity Worksheet” Go from this… to this! (TIPS) Research To Date: • Todd, A., Horner, R., Newton, J.S. Algozzine, B., & Algozzine, K. (2011). Effects of Team-Initiated Problem Solving on Practices of School-wide Behavior Support Teams. Journal of Applied School Psychology • Todd, A. W., Newton, J. S., Algozzine, K., Horner, R. H., & Algozzine, B. (2013). The Team Initiated Problem Solving (TIPS II) Training Manual. Eugene, OR: University of Oregon, Educational and Community Supports. Improving Decision-Making PROBLEM SOLUTION PROBLEM SOLVING 8 Keys to Effective Meetings 1. Organization (team roles, meeting process, agenda) 2. Data (right information at right time in right format) 3. Separate (a) Review of On-going Problem Solving (b) Administrative Logistics and (c) New Problem Solving 4. Problems are defined with precision 5. Solutions are comprehensive and built to “fit” 6. “Action Plans” are added for all solutions 7. Fidelity and impact of interventions are reviewed regularly 8. Solutions are adapted in response to data Meeting Foundations Elements Four features of effective meetings: Predictability Participation Accountability Communication • Define roles & responsibilities: Facilitator, Minute Taker, Data Analyst • Use electronic meeting minutes format TIPS Meeting Agenda Make Summative Evaluation Decision Identify Goal for Change Collect and Use Data Monitor Impact of Solution and Compare Against Goal Identify Solution and Create Implementation Plan with Contextual Fit Implement Solution with High Integrity On your Table Tent Card. Lost yours? Print from our website. Meeting Foundations www.uoecs.org Identify Problem with Precision TIPS II Training Manual (2013) Team-Initiated Problem Solving II (TIPS II) Model General Flow of PBIS Team Meeting Call meeting to order – Who is present? 2 Review agenda for today 3 Review Current Status – Compare overall levels to goal/norms 4 Discuss previously defined problem(s) – Were solutions implemented? Discuss current data and relation to goal. Better? Worse? Was goal reached? What next? 5 Discuss administrative tasks and any general issues 6 Discuss any new problems – Identify precise problems, develop solution plans (what, who, when), 7 Wrap up meeting – Review date/time for next meeting and evaluate present team meeting. identify goals, determine fidelity and outcome data needed Match corresponding numbers to TIPS form handout 1 Page 2 a b c d e Page 1 Problem Solving Objectives Use DATA to define… a PRIMARY summary statement 6a a PRECISE problem statement Transforming Data into Useful Information Examine the patterns, trends, peaks Compare your data with the national average 6a Develop a primary summary statement Defining Precision Problem Statements: Start with the PRIMARY problem statement Look at the Big Picture 6a Use DATA to refine the Big Picture Develop PRECISE problem statement What Why Precision Problem Statement Who 6a Where When Designing effective behavior support Define problems with precision Data you are most likely to need to move from a Primary to a Precise statement: WHAT problem behaviors are most common? • ODR per problem behavior WHERE are problem behaviors most likely to occur? • ODR per location WHEN are problem behaviors most likely to occur? • ODR per time of day WHO is engaging in problem behavior? • ODR per student WHY are problem behaviors sustaining? • Use Drill Down report 6a Solution Development & Action Planning Solution Component Pick one or a few! Action Step(s) Prevention How can we avoid the problem context? Ex: schedule lunch times, change lighting Teaching How can we define, teach, and monitor what we want? Ex: build “Quiet” curriculum, teach hallway expectations, buy decibel meter Recognition How can we build in systematic rewards for positive behavior? Ex: 3 quiet days = 5 extra minutes of social time (at lunch or end of day) Extinction How can we prevent problem behavior from being rewarded? Ex: public posting of results Corrective Consequence What are efficient, consistent consequences for problem behavior? Ex: continue current system (Major/Minor ODR) Data Collection Implementation fidelity? Ex: walkthrough reports, observations, self-assessments Impact on student outcomes? Ex: SWIS ODR data 6b Identify a Measureable Goal Goals allow you to analyze, monitor, and adjust professional practice. “Reduce hallway ODRs by 50% per month (currently 24 per month average).” 6c SMART Goals: Specific Measurable Achievable Relevant Timely Implement, then measure fidelity Define ways the team will assess the fidelity and impact of the chosen intervention or solution components. Evaluation Plan for monitoring fidelity of implementation AND impact on student behavior • Evaluate fidelity of implementation compared to the goal • Define how, when, criteria • Evaluate effect of solutions on student behavior (impact) as compared to the goal • Define data to be used, how often and criteria • Data analyst with data summaries and data access 6d Evaluation Planning: Did we do what we said we were going to do? And, did it have an impact? Evaluation Plan for monitoring fidelity of implementation AND impact on student behavior Establish a fidelity check routine that relates to Implementation A 1-5 scale is used for all questions, with up to three questions per week At staff meeting, use fist of five while asking questions In staff room, create number line poster with questions 6e Meeting Evaluation The team rates itself (are we using our time wisely, are we doing what we said we would do, and is it having an impact on student behavior/academics)? Space to capture ideas for things the team can do to improve for next time. 7 Intervention Team Meeting Agenda (Tier II/III) Use for Tier II & III Intervention Team Meetings Intervention Team Meeting Template: Worksheet 8, Tier II Page 1 of 2 Tier II Group Interventions Tier III Individualized Interventions Use for Tier II & III Intervention Team Meetings Intervention Team Meeting Template: Worksheet 8, Tier II Page 2 of 2 Remember…. • The intervention team meeting is not the time to discuss an individual student in great detail. • If a solution or modification cannot be discussed and selected quickly, the team should schedule a follow-up meeting to address that specific issue. • Stick to recommended time allotments as much as possible! Intervention Team Meeting Role Play Activity Questions? Comments? Thank you!