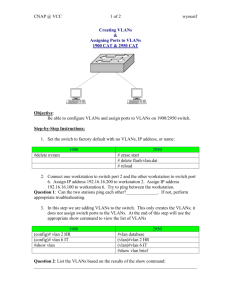
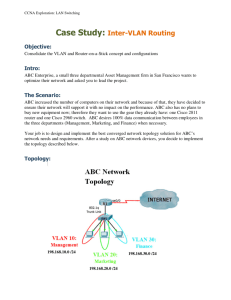
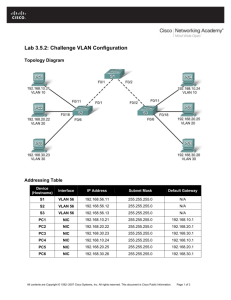
Integrating Cisco Press Resources into the
advertisement

Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Chapter 8 www.ciscopress.com Virtual LANs Introduction • Ethernet switches can create virtual LANs (VLANs) – A VLAN is a logical broadcast domain that spans multiple physical LAN segments – Can be grouped by job functions or departments, regardless of physical location – Modern VLANs typically are localized, spanning only one or two switches www.ciscopress.com Virtual LANs Introduction • Traffic between VLANS is restricted – Switches and bridges forward unicast, multicast, and broadcast traffic only on LAN segments that serve the VLAN to which the traffic belongs – Devices on a VLAN communicate only with devices on that VLAN unless a router is configured to enable inter-VLAN routing • Layer 3 Switches (multilayer switches) commonly do inter-VLAN routing www.ciscopress.com Virtual LANs Introduction • Properly designed VLANs are powerful tools, providing: – Segmentation – Flexibility – Security – Simplification of additions, moves, and changes to the network – Control of Layer 3 broadcasts www.ciscopress.com VLAN Concepts Introduction • VLANs allow almost complete independence of physical and logical topologies – Can define groups of workstations, separated by switches and on different LAN segments, as one broadcast domain • A VLAN is a logical group of network services, workstations, and devices not restricted to one physical LAN segment www.ciscopress.com VLAN Concepts Introduction • VLANs facilitate easy administration of logical groups of workstations and servers – Can communicate as if they were on the same LAN segment • VLANs can be configured with the Catalyst switch CLI or via centralized management software – A group of switch ports can be assigned to a single VLAN www.ciscopress.com VLAN Concepts Introduction Traditional VLAN Implementation www.ciscopress.com VLAN Concepts Introduction • A workstation in a VLAN is restricted to communicating with file servers in the same VLAN group unless a router is used to provide inter-VLAN connectivity • VLANs logically segment the network into different broadcast domains – Packets are only switched between ports that belong to the same VLAN www.ciscopress.com VLAN Concepts Introduction • Original purpose of VLANs was to supply segmentation services traditionally done by routers • VLANs offer segmentation, flexibility, and security • Routers in VLAN topologies provide broadcast filtering, security, and traffic management • Switches do not bridge traffic between VLANs as this would violate the integrity of the VLAN broadcast domain; traffic is routed between VLANs www.ciscopress.com VLAN Concepts Broadcast Domains with VLANs and Routers • A VLAN is a logical broadcast domain – Can span multiple physical segments – Within a switched network, can offer segmentation and organizational flexibility – Workstations can be segmented logically by functions, project teams, and applications • A switch port can be assigned to only one VLAN, adding a layer of security • Ports in the same VLAN share broadcasts; ports in different VLANs do not share broadcasts – Containing broadcasts helps network performance www.ciscopress.com VLAN Concepts Broadcast Domains with VLANs and Routers • A VLAN can: – Exist on a single switch or span multiple switches – Include workstations in a single building or multiple-building infrastructures such as a campus – Connect across WANs using service provider technologies such as IEEE 802.1Q-in-Q VLAN Tag Termination www.ciscopress.com VLAN Concepts Broadcast Domains with VLANs and Routers • Routing or Layer 3 switching enables traffic to flow between VLANs – Layer 3 switching is basically wire-speed routing enabled by dedicated applicationspecific integrated circuits (ASICs) • ASICs are microchips designed for a specific function www.ciscopress.com VLAN Concepts Broadcast Domains with VLANs and Routers Inter-VLAN Communication Requires a Router www.ciscopress.com VLAN Concepts Broadcast Domains with VLANs and Routers • VLAN implementation on a switch causes certain actions to occur: – The switch maintains a separate bridging table for each VLAN • If the frame comes in on a port in VLAN 1, the switch searches the bridging table for VLAN 1 – When the frame is received, the switch adds the source address to the bridging table if it is currently unknown – The destination address is checked so a forwarding decision can be made – For learning and forwarding, the search is made against the the address table for that VLAN only • If the destination IP address of an IP packet is on a different VLAN (subnet), a router or Layer 3 switch must route the packet www.ciscopress.com VLAN Concepts VLAN Operation • A Cisco Catalyst switch operates in a network like a traditional bridge – Each VLAN on the switch implements address learning, forwarding, and filtering decisions – Loop avoidance mechanisms are used on each VLAN as if they were separate bridges • Internally, the switch forwards data only to ports on the same VLAN – Limits the transmission of unicast, multicast, and broadcast frames to the same VLAN – Floods only to other ports in the same VLAN www.ciscopress.com VLAN Concepts VLAN Operation • For a VLAN to span across multiple switches, a trunk is required Trunk Carrying Traffic for Three VLANs over the Same Link www.ciscopress.com VLAN Concepts VLAN Operation • A trunk can carry traffic for multiple VLANs • Summary of VLAN operations: – Each logical VLAN is like a separate physical bridge – VLANs can span across multiple switches – Trunks carry traffic for multiple VLANs – Trunks use special encapsulation to distinguish between different VLANs www.ciscopress.com VLAN Concepts VLAN Operation • VLAN ports have membership modes: – Static: an administrator statically configures the assignment of VLANs to ports – Dynamic: Catalyst switches can use VLAN Management Policy Server (VMPS) – not widely deployed; must be running the CatOS operating system • Catalyst 2950 cannot use VMPS as it runs the Cisco IOS • VMPS contains a database that maps MAC addresses to VLAN assignments • When the switch receives a frame, it examines the source MAC address and assigns the port to the correct VLAN www.ciscopress.com VLAN Concepts VLAN Operation Static and Dynamic VLAN Membership Modes www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Introduction • Before creating a VLAN, decide whether to use the optional VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) to maintain global VLAN configuration on the network • Most Catalyst switches support up to 64 active VLANs (2950 switches with standard image support up to 250 VLANs, some advanced IOS images up to 4094 VLANs) • A separate instance of spanning tree is run on each VLAN www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Introduction • Various default VLANs are configured to support various media and protocol types – The default Ethernet VLAN is VLAN 1 – Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) and VTP advertisements are sent on VLAN 1 • CDP is a proprietary Layer 2 protocol used to discover information about neighboring Cisco devices • The switch must have an IP address to be remotely managed – Assigned to the management VLAN, VLAN 1 www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Configuring Static VLANs • The most common method of configuring VLANs is to assign port-to-VLAN mappings on each switch • VLANs are created with the vlan command – By default, a switch is in VTP server mode so that you can add, change or delete VLANs – Cannot make these changes in VTP client mode www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Configuring Static VLANs Adding a VLAN www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Configuring Static VLANs Adding a VLAN www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Configuring Static VLANs • To modify an existing VLAN, use the same command syntax Changing the Name of a VLAN www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Configuring Static VLANs • After creating a VLAN, a single port or multiple ports can be manually assigned to it – When assigning a port to a VLAN with this method, it is known as a static-access port • Use the switchport access command to configure the VLAN port assignment from interface configuration mode • Use the vlan vlan-number option to set staticaccess membership • Use the dynamic option to have VMPS control and assign the VLAN www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Configuring Static VLANs Assigning Ports to a VLAN (continued on next slide) www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Configuring Static VLANs Assigning Ports to a VLAN (continued) www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Configuration • Use the show vtp status command to verify a recent configuration change www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Configuration • Use the show interfaces interfaces switchport command and the show interfaces interfaces trunk command to display the trunk parameters and VLAN information for the port www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Trunking Information www.ciscopress.com (continues on next slide) VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Trunking Information (continued) www.ciscopress.com (continues on next slide) VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Trunking Information (continued) www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Configuration • After configuring the VLAN, validate its parameters with the show vlan id vlan-id or the show vlan-name vlan-name command Validating VLAN Parameters (continues on next slide) www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Configuration Validating VLAN Parameters (continued) www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Configuration • Use the show vlan brief command to display one line about each VLAN – Shows VLAN name, status, and switch ports www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Configuration • Use the show vlan command to display information on all configured VLANs – Shows: • switch ports assigned to each VLAN • Type (default is Ethernet) • Security association ID (SAID) used for the FDDI trunk • MTU (default of 1500 for Ethernet) • Other parameters for Token Ring and FDDI www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Information with show vlan www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Information for a Particular Interface with the show interfaces interfaces switchport command www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Configuration Verifying Spanning Tree Information for a Particular VLAN with the show spanning-tree vlan command (continued on next slide) www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Verifying VLAN Configuration Verifying Spanning Tree Information for a Particular VLAN with the show spanning-tree vlan command (continued) www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Adding, Changing, and Deleting VLANs • To add, change, or delete a VLAN, put the switch in VTP server or transparent mode – When changes are made in server mode, they are automatically propagated to other switches in the VTP domain – VLAN changes made in transparent mode affect the local switch only; changes are not propagated to the VTP domain www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Adding, Changing, and Deleting VLANs • After creating a new VLAN, make necessary changes to port assignments – Separate VLANs imply separate IP networks – Plan the new IP addressing scheme and its deployment to workstations before moving users to the new VLAN – Separate VLANs require inter-VLAN routing • Set the appropriate default gateway and other services such as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Adding, Changing, and Deleting VLANs • To modify VLAN attributes, use the vlan vlan-id global configuration command – Can change VLAN name but not VLAN number – To use a different VLAN number, create a new VLAN and then assign the ports to it • To move a port to a different VLAN, use the same commands used to make the original assignment – On a Catalyst 2950, use the switchport access interface configuration command • Do not need to remove a port from a VLAN to make this change www.ciscopress.com VLAN Configuration Adding, Changing, and Deleting VLANs • If a VLAN is removed from a switch in that is in VTP server mode, it is removed from all switches in the VTP domain • If a VLAN is removed from a switch in that is in VTP transparent mode, it is removed only from that switch – Use the no vlan vlan-id command to remove a VLAN – Before deleting a VLAN, be sure to move all ports to another VLAN or communication will be lost – To reassign a port to VLAN 1, use the no switchport access vlan command www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs Introduction • VLANs are common in campus networks – Give network engineers flexibility in designing and implementing networks – Enable broadcast containment, security, and connection of geographically separate communities of interest (workgroups) • Misconfiguration of a VLAN is one of the most common errors in a switched network www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs Introduction Switched LAN Troubleshooting Process www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs Troubleshooting VLAN Problems • Possible throughput problems: – Bad adapter card – Duplex mismatch • Look for FCS errors, alignment errors, runts • Auto-negotiation or mismatched settings • Use this approach: – Is problem on local side or remote side of the link – What path is the packet taking (across trunks or nontrunks to other switches) – If the show interfaces command shows rapidly increasing collisions, may be an overloaded link or duplex mismatch www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs Troubleshooting VLAN Problems • Remember, switches minimize collisions only in full-duplex mode – In half-duplex mode, collisions still occur because two devices can attempt to transmit at the same time • The only cure for collisions on Ethernet is to run it in full-duplex mode – Almost always done today www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs Troubleshooting VLAN Problems VLAN Problems and Solutions www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs VLAN Troubleshooting Scenarios • Scenario 1: One Device Cannot Communicate with Another Device – Make sure the IP address, subnet mask and VLAN membership of the switch interface is correct by using the show interfaces command – If the host is in the same subnet as the switch interface, make sure the switch interface and the switch port to which the host is connected are in the same VLAN, using the show interfaces and the show vlan commands www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs VLAN Troubleshooting Scenarios • Scenario 1: One Device Cannot Communicate with Another Device (continued) – If the host is on a different subnet, ensure the default gateway on the switch is configured with the address of a router in the same subnet as the switch interface, using the show ip route command – Check the spanning-tree state on the port using the show spanning-tree interface configuration command • If port is in listening or learning mode, wait until it is in forwarding mode and try again – Check that speed and duplex settings on host and switch ports are correct; show interfaces command www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs VLAN Troubleshooting Scenarios • Scenario 1: One Device Cannot Communicate with Another Device (continued) – If the connected device is an end station: • Enable spanning-tree PortFast on the port, using the spanning-tree portfast interface command – Places port in forwarding mode immediately • Disable trunking on the port, using the no switchport trunk interface command • Disable channeling on the port with the no channel-group interface command – Make sure the switch is learning the MAC address of the host, using the show mac-address-table dynamic command www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs VLAN Troubleshooting Scenarios • Scenario 2: A Device Cannot Establish a Connection Across a Trunk Link – Make sure trunking mode has a valid configuration on both ends of the link, using the show interfaces trunk command – Make sure the trunk encapsulation type on both ends is valid, using the show interfaces interface-id [switchport | trunk] command – On IEEE 802.1Q trunks, check that the native VLAN is the same on both ends of the trunk, using the show interfaces interface-id [switchport | trunk] command www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs VLAN Troubleshooting Scenarios • Scenario 3: VTP Is Not Updating the Configuration on Other Switches When the VLAN Configuration Changes – Make sure the switches are connected with trunk links as VTP updates occur only over trunk links; use the show interfaces trunk command – Ensure the VTP domain name matches on the appropriate switches; use the show vtp status command www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs VLAN Troubleshooting Scenarios • Scenario 3: VTP Is Not Updating the Configuration on Other Switches When the VLAN Configuration Changes – Check to see if the switch is in transparent mode • Only switches in VTP server or client mode update their configuration based on VTP updates • Use the show vtp status command – If using VTP passwords, the password must be the same on all switches in the VTP domain • To set or change the password, use the vtp password command; clear a password with the no vtp password command www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs Summary • A VLAN is a set of network services – Creates a single broadcast domain – Not restricted to a physical LAN segment or single LAN switch – Configured through software, making it unnecessary to move equipment and cables • VLANs provide: – Segmentation – Design flexibility – Security www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs Summary • Routers in VLANs provide: – Broadcast filtering – Security – Traffic management • Routers route traffic between VLANs – Switches can’t be used to bridge traffic between VLANs; would violate integrity of broadcast domain www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs Summary • Primary benefit of VLANs is that they permit the network engineer to organize the LAN logically instead of physically • A VLAN is a broadcast domain that one or more switches create – Improves overall network performance – Switch keeps a separate bridging table for each VLAN – When a switch receives a frame, it examines the source MAC address and adds it to the bridging table for that VLAN if it was previously unknown – Switch then makes a forwarding decision www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs Summary • Static VLANs are ports on a switch that are manually assigned to a VLAN – Can use a management application or the switch operating system commands – Ports maintain their assignments unless they are manually changed • Dynamic VLANs do not rely on ports being assigned by an administrator to specific VLANs www.ciscopress.com Troubleshooting VLANs Summary • Use these commands to verify VLAN configuration: – show vtp status, show vlan, show vlan brief, show vlan id vlan-id, show vlan name vlan-name, show interfaces switchport, show interfaces trunk, and show spanning-tree vlan • Use a systematic approach to troubleshoot – Start with physical indications, such as LED status – Then proceed to Layer 2 and Layer 3 problem isolation www.ciscopress.com