Listen carefully to each song and answer the following questions:
advertisement

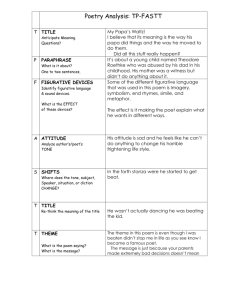
L I S T E N C A R E F U L LY T O E AC H S O N G A N D A N S W E R T H E F O L L OW I N G QU E S T I O N S : 1. What kind of mood does this song put you in? 2. What type of music do you think this is? 3. What about the song indicates the type of music it is? THE SONGS WERE… 1. “Gangsta’s Paradise” by Coolio 2. “Spring” by Vivaldi 3. “Who Could Ask for Anything More?” by George Gershwin 4. “Single Ladies” by Beyonce 5. “Sigh No More” by Mumford and Sons 6. “Bohemian Rhapsody” by Queen REFLECTION What did the songs all have in common? How were they different? How did you know that all of the songs were music? Write a paragraph in which you explain your answer to these questions. Use specific examples from the songs to help you. W H AT D O M U S I C A N D P O E T RY H AV E I N C O M M O N ? There are many forms, or genres of music, and there are also many forms of poetry. Like music, poetry is meant to be heard. All music and poetry always share these core qualities: Rhythm Sound Word Choice ELEMENTS OF POETRY 1) Rhythm– the beat of a poem, created by stressed and unstressed syllables in words Meter– the pattern of rhythm in a poem. The poet chooses specific words and puts them in a specific order to create this. ELEMENTS OF POETRY 2) Sound Devices– rhyme, as well as figurative language such as alliteration, onomatopoeia, and even repetition. Poets use sound devices to draw our attention to certain words and ideas, as also to help set a tone. ELEMENTS OF POETRY 3) Word Choice (Diction)– Poets choose words carefully. Poetic language is specific, imaginative, and rich with emotion. Poets think carefully about shades of meaning: Denotation– the literal, dictionary definition of a word Connotation– the ideas and feelings that the word brings to mind Ex. canine, dog, pooch, mongrel ELEMENTS OF POETRY 4) Figurative Language– writing that is not meant to be taken literally. Common examples are similes, metaphors, and personification. Poets use figurative language to state ideas in vivid and imaginative ways, just like other authors do. STRUCTURE OF POETRY Lines– groups of words in a poem. Like the sentence of a poem. Stanzas– lines organized into units of meaning. Like the paragraph of a poem. Rhyme Scheme– the pattern of rhyme in a poem. POETIC FORMS Every form of poetry requires its own unique structure. Different forms of poetry include: haiku, cinquain, sonnet, ode, etc. Poems that do not stick to the rules of an established form are called free verse poetry. CLOSE READING POETRY 1. Analyze the structure, considering the form of poetry. 2. Identify any imagery and figurative language that the author uses. Consider why the poet used it. 3. Look closely at the words the poet chose. Think about how the poem might be different if certain words were exchanged for others that share their denotation, but not their connotation. LET’S PRACTICE! My stick fingers click with a snicker And, chuckling, they knuckle the keys; Light-footed, my steel feelers flicker And pluck from these keys melodies. POEM PRACTICE 2 Some days my thoughts are just cocoons—all cold, and dull and blind, They hand from dripping branches in the gray woods of my mind; And other days they drift and shine—such free and flying things! I find the gold-dust in my hair, left by their brushing wings.