CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-I
advertisement

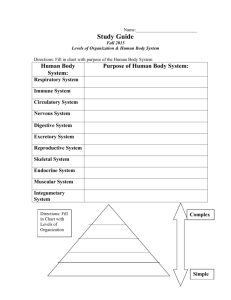
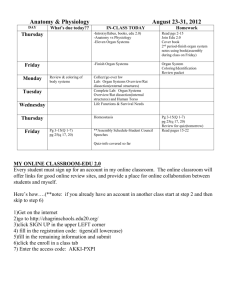
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-I YEAR II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY Assist. Prof. Dr. Ipek Erbarut Seven Assoc. Prof. Dr. Pelin Bağcı CHANGES IN THE SIZE, CONSISTENCY, COLOUR& COMPOSITION OF ORGANS HD-l . HYPERTROPHY ORGAN: Heart Gross findings: The thickness of the ventricular wall is thickened. NODULE Normal size of the prostate HD-2 HYPERPLASIA ORGAN: Prostate Gross Findings: Two prostatic lobes are seen. They are enlarged, firm and nodular. The cut surfaces are also nodular and contains some minute cysts. The size of nodules vary from 0.5 to 1.5cm. Descriptive Notes: This increase in size is in response to hormonal changes that occurs with the aging process. NODULE HD-3: HYPERPLASIA ORGAN: Thyroid (Nodular Hyperplasia) Gross Findings: Thyroidectomy specimen with glistening, jelatinous, nodular surfaces is seen. At cut section you can discriminate fibrous bands causing nodular structures. Descriptive Notes: In the adult, the normal thyroid gland weighs 20 to 25 gm. The most common cause of the nodular hyperplasia is lack of iodine in the diet resulting insufficient production of throid hormones. This cause increase the sythesis and release of TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone), resulting in enlargement of the thyroid. HD-4: LYMPHOMA ORGAN: Spleen Gross Findings: In the cut section of the spleen, you see numerous nodular masses(approximately 0.6-0.8 cm. in dimension). This leads to diffuse enlargement of the spleen. Descriptive notes: These nodular masses are formed by neoplastic proliferation of lymphocytes which are actually local cells of the spleen. NODULE HD-4: LYMPHOMA ORGAN: Spleen Gross Findings: In the cut section of the spleen, you see numerous nodular masses(approximately 0.6-0.8 cm. in dimension). This leads to diffuse enlargement of the spleen. Descriptive notes: These nodular masses are formed by neoplastic proliferation of lymphocytes which are actually local cells of the spleen. Granulomatous foci HD-5: MILLIARY TUBERCULOSIS ORGAN: Lung Gross Findings: There are multiple small (pin-point to a few millimeters), yellow white distinct foci. This leads to diffuse enlargement of the lungs. Descriptive notes: These foci are formed by granulomatous inflammation. HD-7: ACUTE REJECTION ORGAN: Kidney Gross Findings: The kidney is larger, harder,and paler than normal. Descriptive Notes: Enlargement of the kidney caused by edema, and diffuse mononuclear cell infiltration. Result of humoral rejection extensive renal parenchymal necrosis seen. HD-8: LINITIS PLASTICA ORGAN: Stomach Gross Findings: There is diffuse thickening of the gastric wall which has given rise to a term “leather-bottle” stomach also called linitis plastica. Descriptive Notes: Tumour cell infiltration to the gastric wall ends up with diffuse thickening of the gastric wall. trabeculation HD-9: HYPERTROPHY – DILATATION ORGAN: Urinary Bladder Gross Findings: This is a partial cystectomy spesimen. The bladder is turned inside out so that you can see the pale mucosa. The cavity of the urinary bladder is enlarged. The bladder wall is thicker than normal. Descriptive Notes: Vesical obstruction caused hypertrophy of the muscle layer. Hypertrophy of the muscle bundles produce trabeculation. Vesical obstruction caused dilatation of the bladder and hypertrophy of the muscle layer. Hypertrophy of the muscle bundles produce trabeculation. HD-11: FATTY CHANGE ORGAN: Liver Gross Findings: A slice of the liver is seen. Liver is enlarged, yellow, smooth, firmer than normal and greasy. The capsule remains smooth and glistening.The lumina seen on the cut surface are the branches of the portal vein. Descriptive Notes: the normal adult liver weighs 1400 to 1600 gms. Fatty change results from defective oxidation of fatty acids and aberrant mitochondrial function. HD-12: ANTHROCOSIS ORGAN: Lung Gross Findings: Accumulation of this pigment blacken the tissue of the lung Descriptive Notes: The most common exogeneous pigment is carbon or coal dust, which is a virtually ubiquitous air pollutant of urban life. HD-12: ANTHROCOSIS ORGAN: Lung Gross Findings: Accumulation of this pigment blacken the tissue of the lung. Descriptive Notes: The most common exogeneous pigment is carbon or coal dust, which is a virtually ubiquitous air pollutant of urban life. LipidLIPID plaque PLAQUE HD-13: ATHEROSCLEROSIS-CHOLESTEROL ACCUMULATION ORGAN: Vessel Wall Gross Findings: You see an opened vessel wall. On the inner surface there are elevated areas of different diameter in size, yellow-white in colour and with irregular lipid plaques.Some plaques are calcified, these can be recognised with their white color and rigid appearance. The size of the atheromatous plaques are varible and some show coalescence. Descriptive Notes: Endothelial cell damage and increased total cholesterol and decreased HDL cholesterol cause atherosclerotic plaq formation. HD-14: FATTY CHANGE Gross Findings: The heart is enlarged and softened. It is yellow in colour. You can also see atherosclerotic yellow lipid plaques in the opened vessels. HD-15: AMYLOIDOSlS ORGAN: Kidney Gross Findings; Kidney is enlarged , firm and have a waxy appearance. Descriptive Notes: Extracellular hyaline amorphous material is accumulated in glomeruli and vessel wall. Painting the cut surface with iodine imparts a yellow colour is transformed to blue violet. HD-16: PASSIVE CONGESTION ORGAN: Ovary Gross Findings : The organ is diffusely enlarged, firm, and cyanotic. Descriptive Notes: This is due to twisting of ovary that cause obstruction of venous return resulting in intense congestion. Ovarian torsion is uncommon. NUTMEG HD-17: CHRONIC PASSIVE CONGESTION ORGAN: Liver NUTMEG LIVER (normal adult liver weight is 1400-1600gm.) Gross Findings: There is dusky red cyanosis and diffuse increase in liver size and weight. On the cut surface the central congested areas appear darker than the pale peripheral portions of the lobules and thus compose the so-called nutmeg pattern. Descriptive Notes: Passive congestion of the liver results from right-sided heart failure or obstruction of the inferior vena cava or hepatic vein. When you think about the normal circulation of the liver you will easily understand why the central areas axe primarily affected. We see hemorrhagic necrosis in the pericentral zones. Whereas the peripheral hepatocytes, suffering from less hypoxia, develop fatty change. This zonal difference gives red [centre of the lobule) and yellow (periphery-of the lobuie) discoloration so-called "nutmeg" liver to the organ. NUTMEG HD-17: CHRONIC PASSIVE CONGESTION ORGAN: Liver NUTMEG LIVER (normal adult liver weight is 1400-1600gm.) Gross Findings: There is dusky red cyanosis and diffuse increase in liver size and weight. On the cut surface the central congested areas appear darker than the pale peripheral portions of the lobules and thus compose the socalled nutmeg pattern. Descriptive Notes: Passive congestion of the liver results from right-sided heart failure or obstruction of the inferior vena cava or hepatic vein. When you think about the normal circulation of the liver you will easily understand why the central areas axe primarily affected. We see hemorrhagic necrosis in the pericentral zones. Whereas the peripheral hepatocytes, suffering from less hypoxia, develop fatty change. This zonal difference gives red [centre of the lobule) and yellow (periphery-of the lobuie) discoloration so-called "nutmeg" liver to the organ. HD-18: PASSIVE CONGESTION ORGAN: Testis (Torsion) Gross Findings: Testis shows slight but diffuse enlargement. The organ is tense and cyanotic. Descriptive Notes: There is an impairment of venous return from the testis due to the twisting of the spermatic cord resulting compression of testicle veins. CEREBRAL LOBES ENGORGED VESSELS CEREBELLUM HD-19: CONGESTION ORGAN: Brain —> Meningeal Congestion Gross Findings: The blood vessels of the meninges are engorged with dark red blood. There is also diffuse increase in the size and weight of the organ due to secondary edema formation. HD-20: ABSCESS ORGAN: Spleen Gross Findings: Spleen is enlarged. Acute inflammatory cell infiltration results with a tissue defect (arrows) that you can notice on the cut section of the spleen. Descriptive Notes: Normally in the addult spleen weighs, about 150 gm and measures 12 cm in lenght, 7 cm in width, and 3 cm in thickness. HD-21: TUBERCULOSIS ORGAN: Apex of the Lung Gross Findings: At the apex of the lung there is an intraparanchymal tissue defect (arrow) .At the centre of the defect with a close inspection one can easily identify the necrosis. Descriptive Notes: Mycobacterium cause tuberculosis.The type of the necrosis is called caseification necrosis NECROSIS HD-21: TUBERCULOSIS ORGAN: Lung Gross Findings: At the apex of the lung there is an intraparanchymal tissue defect. There is a caseification necrosis at the center. Descriptive Notes: Mycobacterium cause tuberculosis.The type of the necrosis is called caseification necrosis. DILATED CALYCES PARENCHYMAL THINNING HD-22: ATROPHY ORGAN: Kidney Gross Findings: The cut section of the kidney reveals dilatation and deformation of the calyces, irregular loss of renal parenchyma with scarring. Its surface is granular with depressed scars. Descriptive Notes: Atrophy is due to progressive destruction and loss of renal parenchyma. HD-23: HYPOPLASIA(congenital) ORGAN: KIDNEY The size of the kidney is diffusely decreased. Its surface is smooth. There are some hemorhagic areas in cortex. The number of renal lobes and pyramids is 6 or fewer (normal kidney has about 12 pyramids). Corcical thinning calculi HD-24: CHRONIC PYELONEPHRITIS WITH CALCULI ORGAN: KIDNEY The cortical surface of the kidney contains irregular, broad depressed area (scar formation) of cortical fibrosis and atrophy leading to focal decrease in size of the organ. On cut section you see dilatation of calyces with atrophy, calculi and scarring of the overlying cortex. Medullary and perirenal fatt tissue is increased. INFARCT INFARCT HD-25: INFARCTION ORGAN: SPLEEN Gross Findings: On the cut section of the spleen you see multiple, pale, wedge shaped, well deliniated infarcts beneath the capsule. The infarcts which are wedge shaped have their apex pointing toward the focus of vascular occlusion. Since all the dependent tissue out to the periphery of the organ is affected, the external aspect of the organ forms the base of the wedge. Descriptive Notes:This is an example of white infarct which is seen secondary to the arterial occlusion of the solid organs. INFARCT HD-26: INFARCTION ORGAN: Placenta Gross Findings: On cut section of the placenta reveals a white-tan and firm area of necrosis. It is also wedge shaped with apex at maternal surface. Descriptive Notes: This is also an example of white infarct. It results from cessation of blood supply to intervillous space and necrosis of villi . HD-27: TRANSMURAL INFARCT ORGAN: Small bowel Gross Findings: A segment of small bowel is seen. A large part of this segment is intensly congested and dark purple. This discoloration fades gradually into the adjacent segments of the normal bowel, that is the demarcation is not sharply defined. Descriptive Notes: This is also an example of a red infarct. We see red infarct both in arterial and venous occlusions of the small bowel due to the fact that it has rich in arterial anastomoses. Fibrous bands HD-29: CIRRHOSIS ORGAN: Liver Gross Findings: The liver is harder than normal due to fibrosis. Its surface shows diffuse nodularity that reflects nodular regeneration and scarring. Descriptive Notes: Cirrhosis of the liver is the terminal sequel of repeated injury to the liver parenchyma. The result is the formation of broad fibrous bands separating regenerative nodules that do not have the normal achitecture of liver lobules. HD-30: BRONCHOPNEUMONIA ORGAN: Lung Gross Findings: The lung shows patchy distributed firm and gray-red to yellow colour, elevated nodular airless areas due to inflammatory infiltration.These nodules are distributed along with the bronchioles so called bronchopneumonia. Descriptive Notes: It results from aspiration of organisms causing inflammation and necrosis of underlying parenchyma. Cholesterol accumulation HD-31: CHOLESTEROLOSIS ORGAN: Gall bladder Gross Findings: Its mucosal surface shows minute yellow patches due to cholesterol accumulation . This is called as a "strawberry gallbladder". Descriptive Notes: It is results from abnormal deposition of mixtures of cholesterol and triglyceride in macrophages in the lamina propria of the gallbladder. HD-32: FIBROMA ORGAN: Ovary Gross Findings: The tissue is harder and bigger than a normal ovary because of infiltration by neoplastic cells arising in the ovarian strorna. The ovary appears as a white firm, mass composed of interlacing bundles of fibers. Descriptive Notes:It is a benign neoplasm of the ovary.