Infrahyoid Neck Anatomy
advertisement

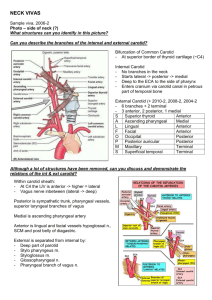
Infrahyoid Neck Anatomy Spencer Clark MS4 Infrahyoid Neck • Below hyoid bone continuing into the mediastinum – – – – – – Retropharyngeal Space Perivertebral Space Posterior Cervical Space Carotid Space Anterior Cervical Space Visceral Space • Hypopharynx-Larynx • Thyroid Gland • Parathryoid Glands Retropharyngeal Space Space running behind the esophagus, in front of the danger space and between the carotid spaces from the skull base to the mediastinum. Below the hyoid bone it only contains fat. Retropharyngeal space and danger space are indistinguishable on CT and MRI. Pathology can include infection and tumor. Retropharyngeal Space Retropharyngeal Space Hyoid Bone Area representing the retropharyngeal space on an axial CT scan at the level of the hyoid bone. Retropharyngeal Space Trachea Left lobe of thyroid gland Area representing the retropharyngeal space at the level of the midinfrahyoid neck on an axial CT scan. Perivertebral Space Cylindrical space surrounding the vertebral column from the skull base to the upper mediastinum. Bounded by the deep layer of the deep cervical fascia. Divided into prevertebral and paraspinal portions. Prevertebral-prevertebral and scalene muscles, brachial plexus roots, phrenic nerve, vertebral artery and vein, vertebral body. Paraspinal-paraspinal muscles and posterior elements of the vertebral column. Most perivertebral space lesions are found in the vertebral body. Perivertebral Space Perivertebral Space Perivertebral Space Perivertebral space. Prevertebral portion of the perivertebral space. Paraspinal portion of the perivertebral space. Perivertebral Space Left vertebral artery Scalene muscles Vertebral body Paraspinal muscles Spinous process Posterior Cervical Space Posterolateral space in the neck extending from the posterior mastoid to the clavicle. Fat is the main component but also includes the accessory nerve, the spinal accessory lymph node chain (level 5), and part of the brachial plexus. Makes the posterior triangle of the neck. Divided by the omohyoid muscle into occipital triangle and subclavian triangle. During neck dissection the accessory nerve can be injured resulting in paresis of the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. Posterior Cervical Space Posterior Cervical Space Posterior Cervical Space Left external jugular vein Posterior Cervical Space Transverse cervical artery Carotid Space Two tubular spaces surrounded by the carotid sheath traveling from the jugular foramen to the aortic arch. In the infrahyoid neck contains the carotid arteries, internal jugular veins, and cranial nerve X. Surrounded by the visceral and retropharyngeal spaces medially, perivertebral space posteriorly, anterior cervical space, and the posterior cervical space laterally. Pathology can include carotid artery dissection, internal jugular vein thrombosis, paraganglioma, and schwannoma. Carotid Space Carotid Space Carotid Space Carotid Space Internal jugular vein Common carotid artery Anterior Cervical Space Anterior cervical space is continuous with the submandibular space and lateral to the visceral space. Anterior Cervical Space Anterior Cervical Space Anterior Cervical Space Anterior jugular vein Visceral Space Midline cylindrical space surrounded by the middle layer of deep cervical fascia extends from the hyoid bone to the mediastinum. Contains the hypopharynx, larynx, trachea, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands and esophagus. Pathology can include soft tissue mass as well as symptoms related to mass effect such as hoarseness from recurrent laryngeal nerve, dysphagia, and stridor or shortness of breath. Visceral Space Visceral Space Thyroid cartilage Cricoid cartilage Thyroid gland True vocal cord Visceral Space Visceral Space Trachea Esophagus Thyroid gland Larynx Larynx Thyroid cartilage Vestibule Piriform sinus Arytenoid cartilage Cricoid cartilage Subglottis Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands References Harnsberger HR, Osborn AG, Ross JS. Diagnostic and Surgical Imaging Anatomy: Brain, Head and Neck, Spine. 1st edition. Salt Lake City: Amirsys, 2006. Neck CT. Retrieved Sept. 11, 2012. http://headneckbrainspine.com