Neck VIVA`s - WordPress.com
advertisement
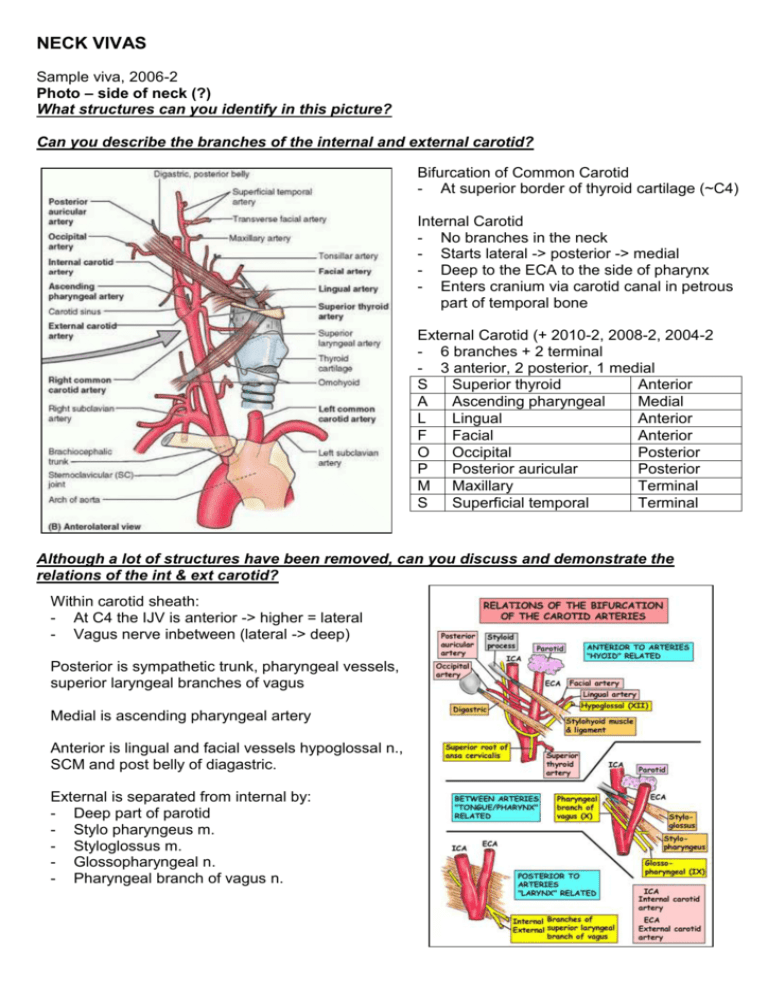
NECK VIVAS Sample viva, 2006-2 Photo – side of neck (?) What structures can you identify in this picture? Can you describe the branches of the internal and external carotid? Bifurcation of Common Carotid - At superior border of thyroid cartilage (~C4) Internal Carotid - No branches in the neck - Starts lateral -> posterior -> medial - Deep to the ECA to the side of pharynx - Enters cranium via carotid canal in petrous part of temporal bone External Carotid (+ 2010-2, 2008-2, 2004-2 - 6 branches + 2 terminal - 3 anterior, 2 posterior, 1 medial S Superior thyroid Anterior A Ascending pharyngeal Medial L Lingual Anterior F Facial Anterior O Occipital Posterior P Posterior auricular Posterior M Maxillary Terminal S Superficial temporal Terminal Although a lot of structures have been removed, can you discuss and demonstrate the relations of the int & ext carotid? Within carotid sheath: - At C4 the IJV is anterior -> higher = lateral - Vagus nerve inbetween (lateral -> deep) Posterior is sympathetic trunk, pharyngeal vessels, superior laryngeal branches of vagus Medial is ascending pharyngeal artery Anterior is lingual and facial vessels hypoglossal n., SCM and post belly of diagastric. External is separated from internal by: - Deep part of parotid - Stylo pharyngeus m. - Styloglossus m. - Glossopharyngeal n. - Pharyngeal branch of vagus n. 2011-1, (2010-2), 2008-2, Lateral neck (+/- face) (pg 43) Identify the major regions or triangles of the neck D: Anterior triangle (aka anterior cervical region) 2010-2, 2009-1 (discussion), 2007-1 Bounded by midline, anterior border of SCM, inferior border of the mandible C: Posterior triangle (aka lateral cervical region) Bounded by posteior border of SCM, anterior border of trapezius, middle 1/3 clavicle Identify the carotid triangle and its boundaries 2011-1 Superior belly of omohyoid, posterior belly of digastric, anterior border of SCM Identify the structures within the carotid triangle - Common carotid (10) and branches: ICA (24), ECA ( - Branches of ECA: superior thyroid (52), lingual (28), facial (15), ascending pharyngeal medially - Internal jugular and tributaries (removed) - Nerves: Vagus, Hypoglossal (20), Superior root ansa cervicalis (24), spinal accessory, cervical plexus - Thyroid gland, larynx and pharynx (22 = inferior constrictor) - Deep cervical lymph nodes Name some structures in the anterior triangle 2010-2, 2005-1 - As above and: - Submandibular (digastric triangle): Submandibular gland almost fills triangle (46), submandibular lymph nodes (20), hypoglossal nerve, mylohyoid nerve, parts of facial artery and vein - Submental triangle: submental lymph nodes and small veins unite to anterior jugular vein (3) - Muscular (omotracheal) triangle: Sternothyroid (44), sternohyoid (43), thyroid (59) and parathyroid Describe the surface markings of the carotid sheath in the neck 2009-1 Carotid sheath runs along a line joining the sternoclavicular joint to a point midway between the mastoid process and the angle of the mandible. What are the contents of the carotid sheath Common carotid -> internal carotid artery, internal jugular vein, vagus nerve, some deep cervical lymph nodes, carotid sinus nerve, sympathetic nerve fibers Describe the location of the thyroid gland in the neck - Located anteriorly in the neck at level of C5-T1 - Lies deep to sternothyroid and sternohyoid muscles - Right and left lobes sit anterolateral to the larynx and trachea - A thin isthmus unites the two lobes across the trachea (usually at 2nd and 3rd tracheal rings) 2007-1 Photo: Neck (pg 44) In this picture the sternomastoid has been removed. Identify the major blood vessels Common carotid (7), external carotid (9), facial artery (11), suprascapular artery (37) Internal jugular (17), anterior jugular (4), retromandibular vein (28), facial vein (12) What other structures can you identify in the picture? Submandibular gland (33), parotid / facial nerve (25), masseter (22), superior (bifid) omohyoid (34), digastric (3), mandible (21), hyoid (15), oblique line of thyroid (24), mylohyoid (23), sternohyoid (31), sternothyroid (32), SCM (30), scalenus anterior (29), thyroid gland (40), root of BP (5), Ansa cervicalis (inf 1, sup 2) How does the internal jugular vein relate to the carotid artery? 2005-2 - Emerges from jugular bulb, initially behind ICA and lying on transverse process of atlas - Passes down to be lateral to ICA within carotid sheath, with the vagus nerve between - The terminal part lies superficial and lateral (deep to the junction of the heads of sternocleidomastoid and joins the subclavian to form the brachiocephalic vein behind the medial end of the clavicle) Please describe the surface marking of the internal jugular vein. From the earlobe (or mastoid) to the sternoclavicular joint (or medial part of clavicle). 2007-2, 2007-1 X-ray: lateral C-spine Identify the structures shown in this xray 1. Nasopharynx/posterior aspect of tongue / soft palate 2. Retropharengeal soft tissue 3. Trachea/oesophagus 4. Epiglottis 5. Vallecula 6. Vestibular fold/vocal fold 7. Bony: C1, C2, BOS, Mandible, Spinous processes, Laminae, Disc spaces, Larynx, Hyoid, Trachea 8. Thyroid cartilage What are the components of the soft tissue shadow located anterior to the upper cervical vertebrae 2007-2 1. Anterior longitudinal ligament 2. Longus colli muscle 3. Prevertebral fascia 4. Retropharyngeal space 5. Alar fascia 6. Buccopharyngeal fascia 7. Pharyngeal muscle 2010-1, 2008-2, 2008-1, 2004-2 Model: larynx Identify the structures that make up the larynx - From epiglottis to inferior border of cricoid (C6) - Cartilages (9): 1. Thyroid: sup/inf horns/oblique line/laryngeal prominence/laminae/thyroid notch. 2. Cricoid: cricothyroid joint allows change in length of vocal cords. 3. Epiglottis 4. Paired: Cunieform, Corniculate, Arytenoid - Membranes: Thyrohyoid and quadrangular - Ligaments: Cricotracheal, median cricothyroid, median and lateral thyrohyoid, aryepiglottic and thyroepiglottic - The lateral cricothyroid (ligament/membrane) and vocal ligament = the conus elasticus Describe the nerve supply of the larynx The main supply to the intrinsic muscles is from the inferior laryngeal nerve, a branch of the recurrent laryngeal form the vagus X. This supplies: - Thyro-arytenoid - Post crico-arytenoid - Lat crico-arytenoid - Trans/oblique arytenoids - Vocalis The external branch of the superior laryngeal which is from the vagus directly supplies: - Cricothyroid Name the muscles of the larynx 2008-2, 2008-1 Extrinsic: Suprahyoid: - Mylohyoid (V3) - Geniohyoid (C1 via XII) - Stylohyoid (VII) - Digastric (ant: V3, post: VII) Infrahyoid: (C1-3, ansa cervicalis) - Sternohyoid - Omohyoid - Sternothyroid - Thyrohyoid Styolpharyngeus (IX, odd one out) Intrinsic (muscles of vocalization): Tensor: Cricothyroid Relaxor: Thyroarytenoid Vocalis relaxes post while tensing anterior Adductors: Transverse and oblique arytenoids Abductors: Posterior and lateral cricoarytenoid











