CH 7.2 Notes – Cells
advertisement
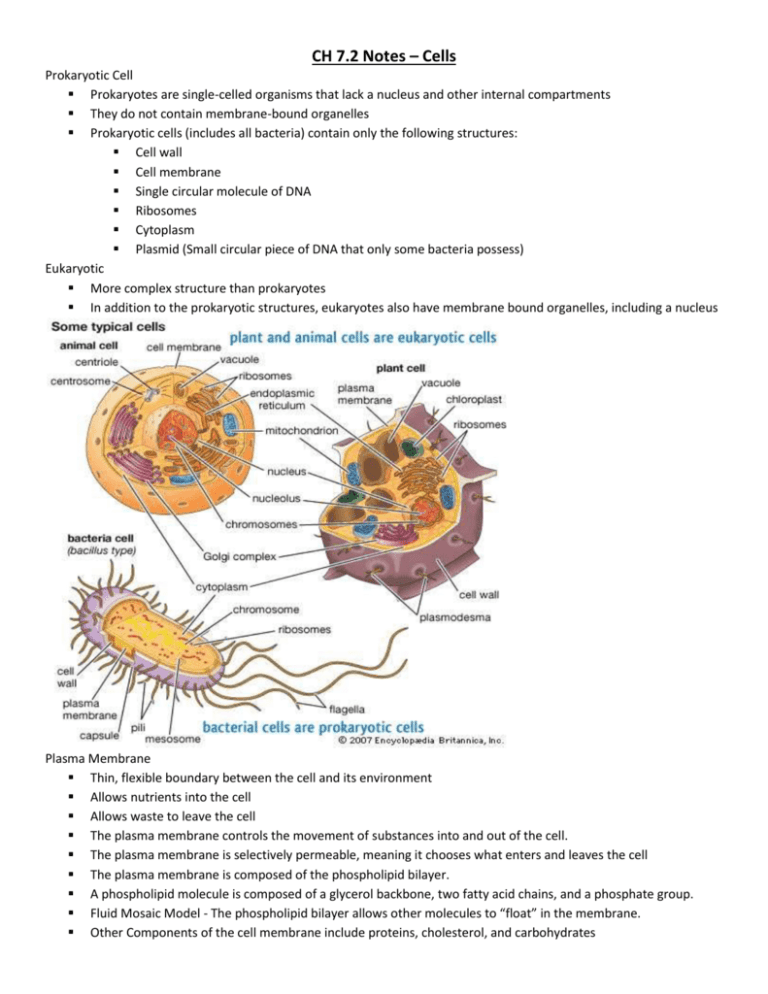
CH 7.2 Notes – Cells Prokaryotic Cell Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus and other internal compartments They do not contain membrane-bound organelles Prokaryotic cells (includes all bacteria) contain only the following structures: Cell wall Cell membrane Single circular molecule of DNA Ribosomes Cytoplasm Plasmid (Small circular piece of DNA that only some bacteria possess) Eukaryotic More complex structure than prokaryotes In addition to the prokaryotic structures, eukaryotes also have membrane bound organelles, including a nucleus Plasma Membrane Thin, flexible boundary between the cell and its environment Allows nutrients into the cell Allows waste to leave the cell The plasma membrane controls the movement of substances into and out of the cell. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable, meaning it chooses what enters and leaves the cell The plasma membrane is composed of the phospholipid bilayer. A phospholipid molecule is composed of a glycerol backbone, two fatty acid chains, and a phosphate group. Fluid Mosaic Model - The phospholipid bilayer allows other molecules to “float” in the membrane. Other Components of the cell membrane include proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates Proteins Transmit signals inside the cell Act as a support structure Provide pathways for substances to enter and leave Plant and Animal Cell Structures Organelles are bodies within the cytoplasm that serve to physically separate the various metabolic reactions that occur within the cells 1. Nucleus 7. Mitochondria 2. Ribosomes 8. Chloroplasts 3. Endoplasmic reticulum 9. Cytoskeleton 4. Golgi Apparatus 10. Flagella & Cilia 5. Lysosomes 11. Centrioles 6. Peroxisomes 12. Vacuoles & Vesicles Nucleus • The nucleus is bounded by the nuclear envelope consisting a phospholipid bilayer, similar to the plasma membrane • The nucleus contains the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), the heredity information of the cell The nucleus is the brain of the cell • Also visible within the nucleus are one or more nucleoli, concentrations of DNA in the process of manufacturing the components of ribosomes Ribosomes • Ribosomes are manufactured in the nucleus and consist of ribosomal RNA and protein • Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis • Ribosomes translate genetic information (DNA) into specific polypeptide chains & proteins Endomembrane System • Composed of the same phospholipid bilayer as the cell membrane • They are membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cells – Similar to the organs of our bodies • Endomembrane systems only occur in eukaryotic cells • Components of the endomembrane system: – Nuclear envelope – Endoplasmic reticulum – Mitochondria (has 2 lipid bilayers) – Chloroplasts (has 2 lipid bilayers) – Golgi apparatus – Lysosomes – Vacuoles – Vesicles Endoplasmic Reticulum • The endoplasmic reticulum or ER, consists of stacks of flattened sacs of membrane • The ER’s functions include: • The best way to determine if the structure is the ER or Golgi apparatus is if it is connected to the nucleus. – ER is connected • When ribosomes are present, the ER is called the rough ER and provides – Aids in protein synthesis • Smooth ER, without ribosomes, is responsible for the synthesis of lipids and hormones. Golgi Apparatus • The Golgi apparatus – The Golgi modifies and package proteins and lipids into vesicles – The Golgi also produces lysosomes – Think of it as Fed Ex Mitochondria • Mitochondria carry out aerobic respiration, a process in which energy (in the form of ATP) is obtained from organic molecules (glucose) – It’s the powerhouse of the cell • Mitochondria are found in both plant and animal cells • Since it converts food to usable energy (ATP), what type of cell would have a lot of mitochondria?? Chloroplasts • Chloroplasts are specialized organelles found in algae and plants that carry out photosynthesis, the process of capturing energy from sunlight and converting it into useable energy (carbohydrates) • Chloroplasts contain chlorophylls, which are responsible for the green color of a plant and are the key lighttrapping molecules in photosynthesis • Chloroplast are not found in animal cells. Why not?? Vacuoles & Vesicles • Vacuoles/ Vesicles are fluid-filled membrane bound bodies – They may contain food particles or digestive enzymes (found in lysosomes) – Transport substances throughout the cell – Release of cellular waste products – – Central vacuoles are large bodies that store water and occupies most of the interior of plant cells • -If the central vacuole runs low on water, the plant will begin to wilt -The central vacuole in plants stores starch, pigments, and toxic substances Lysosomes • Lysosomes are vesicles from the Golgi apparatus that contain hydrolytic digestive enzymes – They are the cell’s stomach • Lysosomes play an important role in: – Intracellular digestion such as breaking down food, cellular debris, and foreign invaders such as bacteria Cytoskeleton • The cytoskeleton is the internal structure of the cytoplasm and is involved in establishing the shape of the cell and coordinating movements Cilia & Flagella Cilia has short, numerous projections that look like hairs Flagella are longer and less numerous than cilia and create movement with a whiplike motion Structures only found in Plant Cells Cell Wall Chloroplasts Central Vacuole








