Chapter 1
advertisement

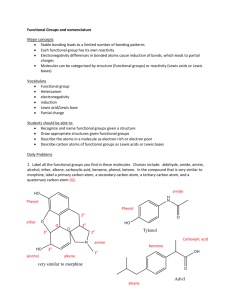
Chapter 1-Continue Introduction to Organic Chemistry Writing Dot Lewis Structure with multiple center atoms Carbons will also be the center atom in the organic molecule ◦ -C-C-C- chains Hydrogen is connected to carbon unless it’s an oxyacids (HClO, etc..) or Carbon has no more valence electrons to share Order of increasing EN ◦ (least) C N O F (most) Write a Dot Lewis structure for CH3COOH Example Write a Dot Lewis Structure for CH3NH2 VSEPR Theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of atoms about a central atom in a covalent compound, or charged ion, is determined solely by the repulsions between electron pairs present in the valence shell of the central atom VSEPR Thoery Common shape and angles ◦ Linear (180o) ◦ Tetrahedral (109.5o) ◦ Trigonal planar (120o) See table 1.2 page 5 Examples Complete the following Dot Lewis structure by adding the missing lonepair then predict the bond angles a. b. c. Elements in Organic Compounds In organic molecules, carbon atoms bond • with four bonds. • mostly with H and other C atoms. • sometimes to O, N, S. • sometimes to halogens F, Cl, and Br. • Table 1.3 page 7 9 Functional Groups Functional groups are • a characteristic feature of organic molecules that behave in a predictable way. • composed of an atom or group of atoms. • groups that replace a hydrogen atom in the corresponding alkane. • a way to classify families of organic compounds. 10 Alcohol An alcohol contains the hydroxyl (-OH) functional group. R-OH Writing structural formulas of Alcohol CH4O Molecular formula CH3OH Condensed formula Writing structural Formulas of Alcohols Draw Lewis structure and condensed structural formulas for the four alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O. Classify each alcohol as primary, secondary or tertiary. ◦ Hints: Consider the connectivity of the four carbon atoms; they can be bonded either four in a chain or three in a chain with the fourth carbon as a branch on the middle carbon. Then consider which carbon should connect to OH with having the same molecule Amines In amines, the functional group is a nitrogen atom. RNH2, R2NH or R3H | —N — Examples Draw structural formulas of the three secondary amines with the molecular formula C4H11N Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids contain the carboxyl group, which is a carbonyl group attached to a hydroxyl group. –COOH O ║ — C—OH Examples Draw condensed structural formulas for the two carboxylic acids with molecular formula C4H8O2 Carboxylic esters An ester contains the carboxyl group between carbon atoms. –COOR or –CO2R Examples Draw structural formulas for the four esters with the molecular formula C4H8O2 Learning Check Classify each of the following as: alcohol, ether, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, amine, or amide. 1) CH3─CH2─CH2─OH 2) CH3─O─CH2─CH3 3) CH3─CH2─NH2 O ║ 4) CH3─C─OH O ║ 5) CH3─C─O─CH3 20 Examples Consider the formula C4H8O2. Write the structural formula for this molecular formula with ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ A carboxyl group Ketone group and a 2o alcohol group An aldehyde and a 3o alcohol group A carbon-carbon double bond and a 1o alcohol