regulation 9.1.2
advertisement

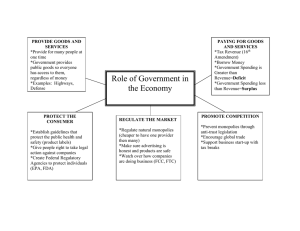
REGULATION One of the Ways Government and Businesses interact in a Mixed Economy Reference 9.1/9.2 Antitrust Law to protect free markets by ensuring competition • Sherman Antitrust Act – 1890 – “every contract, combination…conspiracy in restraint of trade…illegal.” – “attempt to monopolize…guilty of misdemeanor” • Clayton Act – 1914 – – – – No price discrimination No tying contracts No stock acquisition that reduces competition No interlocking directorates • Federal Trade Commission Act – 1914 • Robinson-Patman Act – 1936 – Discounts must be offered to all • Wheeler-Lea Act – 1938 – FTC can intervene in cases of false, deceptive advertising Regulating the behavior of businesses • Business firms must operate under the law. • Business firms must abide by rules or regulations developed by the regulatory agencies that are tasked with enforcing the law. 1990’s • 60,000 employees in 27 federal agencies • additional employees in state and local agencies – public and private employees • social workers • building inspectors • smog stations • Members of the executive branch • • • • • • • • • • • • Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) Army Corps of Engineers Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF) Commodity Credit Corporation (CCC) Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) Consumer Product Safety Commission Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Drug Enforcement Administration Employment and Training Administration (ETA) Employment Standards Administration (ESA) Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Farm Credit Administration (FCA) Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Federal Deposit Insurance Commission (FDIC) Federal Election Commission (FEC) Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EREN) Federal Highway Administration (FHA) Federal Maritime Commission (FMC) Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Government seeks to protect consumers against natural monopolies • Natural monopolies-such low per-unit costs that they can outcompete everyone else. • distribution of water, natural gas, distribution and generation of electricity, cable service • Natural monopolies in the public interest may be regulated in 2 ways. • Price Regulation—setting prices • Profit Regulation—setting profit margins – may result in the removal of incentive to lower costs=higher price to consumer Theories of Regulation Positive • Public Interest Theory – government sets “reasonable” limits on price/profits – businesses earn “reasonable” profits – consumers benefit from “reasonably” lower prices It doesn’t always work out so “reasonably” Theories of Regulation Negative • Capture Theory • Public Choice Theory Capture Theory of Regulation Supporters of the regulated industry will “capture” the regulatory agency • Revolving Door • Lobbyists • Social Bonds • Regulatory Agency serves the interests of industry, not the consumer Public Choice Theory • Since increasing regulation increases the power of regulators, their self-interest is in increasing levels of regulation • Regulators will favor the regulators over either business or consumers • “Big Government” Another Branch of Regulation • Social Good Regulation • concerned with the conditions under which goods and services are produced and with the safety of these items to consumers – – – – – – – OSHA FDA FCC EPA Consumer Product Safety Commission ATF SEC Costs and Benefits of Regulation • Costs – higher unemployment – higher costs to consumers – unfair competition from foreign suppliers – “fairness” • Benefits – – – – – cleaner environment safer products conservation improved quality of life “fairness” Regulation will have both intended and unintended consequences