North Region AMS Program Inventory & Curriculum

North Region Advanced
Manufacturing Sector
Program Inventory
&
Curriculum Comparison
This report was funded, in part, by California Community College Chancellor’s Office, Workforce & Economic
Development Division grant #13-152-001
Table of Contents
Introduction 1
Discussion 2
Welding 6
Drafting 12
Engineering 20
Electronics 25
Mechatronics 30
Manufacturing Technology 32
Agricultural Mechanics 33
This report was funded, in part, by California Community College Ch ancellor’s Office, Workforce & Economic
Development Division grant #13-152-001
2
North Region AMS Program Inventory
& Curriculum Comparison
Introduction
This report compares North Region community college Advanced Manufacturing Sector (AMS) programs and curricula in response to the AMS Deputy Sector Navigator request for application
(R FA) charge to “put forth efforts to establish & articulate career pathways for stackable certificates across multiple colleges and dist ricts.” The report details the current state of AMS community college programs in the North Region, as well as articulation agreements, to create documentation for a dialog about AMS pathways and certificates across the region.
The counties in the North Region are: El Dorado, Nevada, Placer, Sacramento, Yolo, and Yuba.
The community colleges are American River, Cosumnes River, Folsom Lake, Lake Tahoe,
Sacramento City, Sierra, Woodland, and Yuba. The disciplines that fall under the AMS umbrella include: Agricultural Mechanic, Drafting, Engineering, Manufacturing Technology,
Mechatronics/Electronics, and Welding. Lake Tahoe and Woodland do not have AMS programs at their colleges (See Table 1). While Mechatronics and Electronics are related, they are inventoried separately.
TABLE 1: NORTH REGION COMMUNITY COLLEGES & AMS PROGRAMS
American River
Cosumnes River
Folsom Lake
Lake Tahoe
Sacramento City
Sierra
Woodland
Yuba
Certificates of Achievement Defined
This report is restricted to a review of Certificates of Achievement, and their associated courses, to document programs and curricula as a means to portray AMS education and career pathways in the North Region.
Within the California Community College system “…a certificate of achievement may be awarded for Chancellor’s Office approved programs of study of 18 or more units. ‘Low unit’ certificates may also be offered by a college and awarded as certificates of achievement when
This report was funded, in part, by California Community College Ch ancellor’s Office, Workforce & Economic
Development Division grant #13-152-001
1
the program of study consists of 1218 units and is approved by the Chancellor’s Office.” 1 All of the programs fall under the Taxonomy of Programs (TOP) code 09. While North Region colleges provide Associate degrees, Certificates of Achievement, and Skills Certificates, the scope of this report concentrates mainly on Certificates of Achievement related to AMS career pathways, with the exception of Engineering programs.
Discussion
The North Region is part of the North/Far North Regional Consortium (NFNRC). The NFNRC, like all of the community college consortia, provides “an avenue for coordinating regional programs, increasing collaborative responses to state and regional needs, and serving as a primary link between local colleges, Economic & Workforce Development Program Centers and initiatives, and the California Community College Chancellor ’s Office.” i Advanced
Manufacturing is classified as an emergent sector in the region.
Two main reasons to articulate courses are: 1) to facilitate transfer from one college to another so that students can continue their career preparation without duplication of learning; and 2) employers have confidence that a job candidate with a community college certificate represents the discipline-specific core knowledge a person should have, and what they are able to do, regardless of which college the candidate attended.
The first step in the investigation process was to compare course descriptions/outlines within an
AMS discipline/program across North Region colleges to determine if content and learning outcomes matched. Yuba and Sierra Colleges have their course outlines posted on the Internet with public access at http://www.curricunet.com/yccd/search/course/ and http://webcms.sierracollege.edu
The Los Rios District colleges do not have public Internet access to course outlines. However, selected course outlines for Welding were obtained for this study from American River and Cosumnes River colleges. For the other disciplines reviewed in this study, college catalogs were referenced for certificate requirements and course descriptions, unless otherwise noted.
In the Welding, Drafting, Engineering, and Electronics/Mechatronics, disciplines the course content and learning outcomes were never a complete match. Furthermore, certificate course content and the number of units to earn a certificate did not match. Welding certificates ranged from 12 -37 units; Drafting from 15-38 units; Electronics from14 to 45 units; and Mechatronics from 24 to 38 units. Sierra College was the only one to offer a certificate in Engineering. Yuba
College was the only one to offer either a Manufacturing Technology or an Agricultural
Mechanics certificate.
When comparing welding course outlines , while “Introduction to Welding” at American River and Cosumnes River colleges had the same title and offered the same units, the learning outcomes were difficult to match.
The following are examples from those course outlines.
1 http://www.ccccurriculum.net/certificates/ accessed 1-15-14
This report was funded, in part, by California Community College Ch ancellor’s Office, Workforce & Economic
Development Division grant #13-152-001
2
American River, Welding 300: Introduction to Welding Learning Outcomes and Objectives
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
Apply safety standards to each welding process.
Demonstrate proper welding techniques for each welding process.
Inspect welding projects.
Evaluate welding projects in accordance with D1.1 Welding Procedures and Specifications.
Analyze welding projects and make corrective changes to meet industry standards.
Demonstrate skills in arc welding that meets industry standards
Cosumnes River, Welding 100, Introduction to Welding Learning Outcomes and Objectives
SLO 1:
Demonstrate welding skills sufficient to meet industry certified welder standards.
The student will attempt to demonstrate the ability to produce code quality welds with the
GMAW, GTAW, SMAW and or the FCAW process.
SLO 2: Apply integrated knowledge with incremental skill improvement resulting in functional application of welding techniques.
The student will demonstrate be knowledgeable of the technical differences of the SMAW,
GMAW, GTAW and the FCAW processes.
The student will demonstrate the ability to use a welding machines owner’s manual as a reference guide.
Demonstrate how to correctly operate a cutting torch per manufacturers recommended procedures.
Demonstrate how to correctly operate an electric arc welding machine per manufacturers recommended procedures.
Explain the welding electrode classification system.
Explain the basic concepts of metallurgy, inspection, testing, and distortion.
Explain the basic concepts of welder performance and qualification procedures.
SLO 3: Use proper hand, measuring and layout tools to fabricate welding projects.
Demonstrate proper use of hand and power tools to change out empty welding cylinders of an oxygen acetylene cutting or welding equipment.
Demonstrate proper use of a tape measure, carpenter square, soapstone to layout and cut material with various shop tools to specific dimensions to complete the welding assignments.
SLO 4: Demonstrate knowledge of Cal OSHA regulations pertaining to the welding industry.
Demonstrate how to safely operate high-pressure gas cylinders for welding and cutting operations per manufacturer’s recommendations.
Demonstrate how to safely install, remove, set and adjust high-pressure regulators for welding or cutting operations per manufacturer ’s recommendations.
Demonstrate how to safely adjust, ignite and shut down a cutting torch or welding torch to manufacturer
’s recommended procedures.
Demonstrate how to safely prepare and handle oxygen and acetylene cylinders, regulators, cutting and welding attachments for transportation and long term storage conditions.
This report was funded, in part, by California Community College Ch ancellor’s Office, Workforce & Economic
Development Division grant #13-152-001
3
Drafting programs had varied content, length, and program names , e.g.: Design
Technology, Engineering Design Technology, Architectural/Structural Drafting, Drafting and
Engineering Support, and Architectural Studies. Sierra College’s Design Engineering
Technology, DES 1, Technical Drafting I and Yuba’s Architectural Studies, Draft 30, Technical
Drawing with AutoCAD each had three units. When looking at the course outlines, while both courses had Technical Drawing in their names, there were similarities and differences. Both courses noted computer Aided Design (CAD) and orthographic projection as course objectives.
However, Sierra College emphasized the design process and 3D solid modeling while Yuba
College emphasized AutoCAD (a specific brand of 2D/3Dsoftware) as well as axonometric and oblique projection and sectional views. Overall, Sierra College required between 21.5-25 units for a certificate and Yuba College required 27 units or 15 units.
Only Sierra College offers an Engineering Certificate . American River, Folsom Lake, and
Yuba are transfer-only programs, while Cosumnes, Sacramento City, and Sierra colleges offer
Associates degrees. All North Region colleges with engineering programs have courses that transfer to the University of California (UC) and California State University (CSU) systems.
When comparing engineering programs at Folsom Lake College and Yuba College, each had an introductory circuits course. These courses cover similar and different topics. Both courses are 3 units and transferable to UC and CSU. The following are excerpts from each college’s course catalog.
Folsom Lake College: Introduction to Electrical Circuits And Devices , 3 units - Transferable to
UC/CSU
This course provides an “analysis of circuits with resistors, inductors, capacitors, and independent and dependent voltage and current sources. Many analysis techniques will be applied to DC and AC circuits. Differential equations will be used to find the transient response of circuits. Power calculations will be performed on both DC and AC circuits, including an introduction to three-phase AC power.
”
Yuba College: Circuits for Engineers , 3 units - Transferable to UC/CSU
This course provides “laws and theorems for electrical circuits; natural and forced response analysis of first and second order systems; solutions using differential equations. Some emphasis on steady state AC analysis is made. Introduction is given to devices and systems, including operational amplifiers and frequency-selective circuits.
”
When searching for articulation agreements between the CSU system and North Region community colleges, it became a trail difficult to follow.
A 2011 report titled The Road Less
Traveled: Realizing the Potential of Career Technical Education in the California Community
Colleges , states that “there is one dominant pathway in engineering followed by community college students – transferring to a four-year university without earning a community college certificate or associate degree. Lack of alignment between associate degree requirements and transfer requirements is partly accountable for this pattern, as the heavy unit requirement for some majors does not fit well wi thin the current associate degree format.”
The report goes on to say, “As engineering fields become more specialized, evolving into different disciplines, transfer becomes more problematic. The choices are more difficult for students to navigate and the array of specialized course offerings are more difficult for
This report was funded, in part, by California Community College Ch ancellor’s Office, Workforce & Economic
Development Division grant #13-152-001
4
community colleges to offer.” ii Moreover, the report notes the variety of certificate lengths and units of credit is a challenge for students to navigate; this report reinforces these findings.
Electronics and Mechatronics follow a similar pattern of variable units required for a certificate, and there are numerous certificates with specialties.
Overall, there are 13 electronics certificates between American River and Sacramento City Colleges and two certificates in Mechatronics, one each at Sierra College and American River. Units required for an electronics certificate run from 15 to 45. Units for a Mechatronics certificate range from 24 to
38.
COMMENCING THE DIALOG
After compiling the curricula and program documentation presented in this report and then circling back to the original charge of putting forth efforts to establish & articulate career pathways for stackable certificates across multiple colleges and districts it is clear that, within the advanced manufacturing sector, programs are not well aligned across colleges or districts.
Certificates with the same name but variable course content and units do not support seamless transfer from one community college to another – or to a four-year institution. Furthermore, this situation leaves employers without a reliable way to evaluate a job applicant’s subject matter expertise based on a California community college AMS certificate or associate degree title.
Currently there is not a system-wide effort to coordinate AMS course nomenclature or to standardize course/certificate content or units.
Convening stakeholders (faculty, students, employers, and the Chancellor’s Office) in meaningful dialog regarding how programs and certificates with the same name - but different learning objectives and completion requirements - affect students and their future employers is place to start.
This report was funded, in part, by California Community College Ch ancellor’s Office, Workforce & Economic
Development Division grant #13-152-001
5
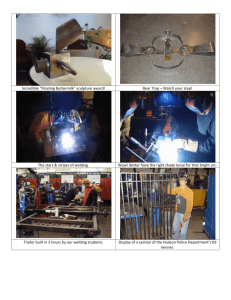
Welding Technology Certificates of Achievement
Welding Technology, falls under TOP code 095650, “welding techniques, processes, and equipment applied in accordance with diagrams, blueprints, or other specifications.” iii All of the
North Region colleges that have welding call their program Welding Technology. The welding programs in the North Region are at American River, Cosumnes River, Sierra, and Yuba colleges.
Each college has at least one Certificate of Achievement. However, the units required for earning a certificate run from 12 to 37, depending on the college (Table 2). Additionally, when comparing courses to earn a certificate, content varies. Due to the range of required units to earn a Certificate of Achievement, courses required, and inconsistent course titles, it is difficult to equate certificates. These facts pose challenges for students wishing to transfer from one college to another in welding without having to repeat courses or experience redundant content.
Additionally, an employer evaluating a job candidate is unlikely to know that a welding certificate of achievement from one college does not represent the same course content.
TABLE 2: WELDING TECHNOLOGY CERTIFICATES OF ACHIEVEMENT TOTAL UNITS
College
American River
Cosumnes River
Sierra
Yuba
Yuba
Total Units
37
18
29-31.5
25
12
Certificate descriptions, courses, and units are ex cerpted from each college’s catalog. Course prerequisites are noted with an * after each certificate.
American River College
Welding Technology – 37 Units
The following coursework represents Welding Technology Certificate of Achievement requirements that when combined with general education requirements result in an AS. The coursework provides skills and knowledge in manual and semi-automatic welding processes used in the metal fabrication and construction industries. Instruction covers materials, equipment, welding procedures, testing techniques, inspection, welding metallurgy, blueprint reading, and welding safety. Competencies include techniques of joining ferrous and nonferrous metals by the use of Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Gas Metal Arc Welding
(GMAW), Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW), and Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW).
Oxyacetylene welding, oxyacetylene cutting and plasma arc cutting, are also covered.
This report was funded, in part, by California Community College Ch ancellor’s Office, Workforce & Economic
Development Division grant #13-152-001
6
AR Course #
WELD 140
WELD 300
WELD 302*
WELD 316*
WELD 320*
WELD 321*
WELD 322*
WELD 330*
WELD 332*
WELD 333*
WELD 334
WELD 335*
WELD 342*
Description
Mathematics for Welding Technicians
Introduction to Welding
Introduction to Welding Metallurgy
Welding Inspection
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (Stick Electrode Welding)
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (Stick Electrode Welding)
Advanced Pipe Welding in Shielded Metal Arc
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (Pipe)
Gas Metal Arc Welding, Semi-Automatic Processes
Gas Metal Arc Welding: Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Metals
Flux Core Arc Welding
Symbol Reading, Layout and Fabrication
*Requires prerequisite
Cosumnes River College
Welding Technology – 18 Units
This program is designed for students interested in seeking employment or advancing their employment in welding fabrication and industrial repairs. Welding encompasses study in
Electrical, Metallurgy, Chemistry, Physics, Design, and Mechanical Engineering.
Classes are for beginning and advanced welders; certification from the American Welding
Society; certification from the American Society Mechanical Engineers; certification from
American Petroleum Institute.
CRC Course # Description Units
WELD 100
WELD 110*
WELD 120*
WELD 135
WELD 136*
WELD 290*
*Requires prerequisite
Introduction to Welding
Advanced SMAW and Semi-Automatic Process
Welding Inspection and Certification
Introduction to Gas Metal Arc Welding Process
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding Process
Advanced Student Projects
3
4
5
1.5
2.5
2
Units
3
3
3
2
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
3
3
This report was funded, in part, by California Community College Ch ancellor’s Office, Workforce & Economic
Development Division grant #13-152-001
7
Sierra College
Welding Technology – 29-31.5 Units
This welding program provides students with employable skills in commercial and industrial welding processes. Completion of the certificate requirements prepares students for state certification tests. Testing and certification is offered.
Sierra Course #
WELD 20*
WELD 30*
WELD 40
WELD 50*
WELD 80/or
WELD 82*
MATH A
WELD 10
WELD 28
WELD 95
ART 22
DES 1
Description
Foundation of Welding Technology – Career Path
Shielded Metal Arc Welding of Structural Plate and Pipe
Wire Feed MIG Welding
Units
3
3
2
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (TIG)
Structural Steel Welding Certification OR
Pipe Welding Certification
3
1-1.5
Elementary Algebra OR more advanced mathematics course 3-5
Plus 12 Units Selected from the Following
Exploring Metals/Introduction to Gas Welding
Independent Study
Internship in Welding Technology
Creative Design in Metal
Technical Drafting 1
2
3
3-4
3
3
DES 2
*Requires prerequisite
Technical Drafting II 3
Yuba
Welding Technology – 25 Units
Yuba College offers two certificates of achievement: one requiring 25 units and a low unit certificate with 12 units.
Yuba Course # Description Units
MFGT 20
WELD 10
WELD 12
WELD 20
Yuba Course
WELD 30
WELD 31
WELD 83
WELD 85*
*Requires prerequisite
Principles of Machine Shop
Introduction to Arc Welding
Intermediate Arc Welding
Introduction to MIG Welding (GMAW)
WELD 22
WELD 40
Intermediate MIG Welding
Introduction to TIG Welding (GTAW)
WELD 50 Flux Core Welding
Welding Technology – 12 Units
Description
Gas Welding
Arc Welding
GMAW/GTAW Production Welding
Structural Design and Fabrication
4
3
2
3
4
4
4
Units
2
2
4
4
This report was funded, in part, by California Community College Ch ancellor’s Office, Workforce & Economic
Development Division grant #13-152-001
8
SKILL TERMS USED IN COURSE DESCRIPTIONS/OUTLINES
This chart, and other “skills cited” charts in this document are a representative list of disciplinespecific skills terms referenced in the curriculum. The lists are not intended to be an exhaustive vocabulary but a comparison of skills referenced by each college program by discipline.
Frequent acronyms used in welding include:
Air Carbon Arc Gouging (CAC-C)
Flux Core Arc Welding (FCAW)
Metal Inert Gas Welding (MIG) – see
GMAW
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) - see GTAW
Selected Welding Skills Cited in Curriculum by College
Term
American Welding Standards
Annealing
Backhand & forehand welding
Basic welding mathematics
Bead, continuous
Bead, stringer
Beading, weave
CAC-C
Cal OSHA welding regulations
Corrective changes to welds
Drawing, blueprint reading
Electrode selection
FCAW
Filler Rod size
GMAW/MIG
GTAW/TIG
Hand tools
Hard facing
Heat treating
Isothermal transformation diagrams
Joint design
Measuring
Metal bending
Metal cutting
Metal properties/welding metallurgy
Metal removal
Open root welding
Out of position welding
Oxy-acetylene cutting
Oxy-acetylene welding
Plasma cutting
American
River
Cosumnes
River
Sierra
Yuba
This report was funded, in part, by California Community College Ch ancellor’s Office, Workforce & Economic
Development Division grant #13-152-001
9
Term
Power sources
Safety
SMAW
Surface hardening
Symbols/terms
Tempering
Tool terms
Weld analysis/evaluation
Weld pool
Weld testing –destructive and non
Welding code
American
River
Cosumnes
River
Sierra
Yuba
Welding coupons
Welding equipment
High School Articulation Agreements
High School
Bear River High
College
American River
El Camino Fundamental American River
Elk Grove Adult & Com. Ed.
Cosumnes River
Elk Grove USD
Florin High
Cosumnes River
Cosumnes River
Bear River High
Del Oro High
Placer High
Colusa High
Davis Senior High
Sierra
Sierra
Sierra
Woodland
Woodland
Course
WELD 300: Introduction to Welding
WELD 300: Introduction to Welding
WELD 100: Introduction to Welding
WELD 100: Introduction to Welding
WELD 100: Introduction to Welding
WELD 20: Introduction to Welding
WELD 20: Introduction to Welding
WELD 20: Introduction to Welding
WELD 10: Intro to Arch Welding
WELD 10: Intro to Arc Welding
Esparto High
Maxwell High
Pierce High
Pioneer High
Winters High
Woodland High
Lindhurst High
Live Oak High
Lower Lake High
Lower Lake High
Woodland
Woodland
Woodland
Woodland
Woodland
Woodland
Yuba
Yuba
Yuba
Yuba
WELD 10: Intro to Arc Welding
WELD 10: Intro to Arc Welding
WELD 10: Intro to Arc Welding
WELD 30: Gas Welding
WELD 10: Intro to Arc Welding
WELD 10: Introduction to Arc Welding
WELD 10: Intro to Arc Welding
WELD 10: Intro to Arc Welding
WELD 31: Arc Welding
WELD 30: Gas Welding
Middletown High
Pleasant Valley High
Sutter County One Stop
Wheatland Union High
Yuba City High
Yuba
Yuba
Yuba
Yuba
Yuba
WELD 31: Arc Welding
WELD 10: Intro to Arc Welding
WELD 10: Intro to Arc Welding
WELD 10: Intro to Arc Welding
WELD 10: Introduction to Arc Welding
Source: http://www.statewidepathways.org/associated_agreements
This report was funded, in part, by California Community College Ch ancellor’s Office, Workforce & Economic
Development Division grant #13-152-001
10
Welding Faculty Perspective
Bill Wenzel, Sierra College
In the classroom you can have competency-based versus time-based learning
A community college course teaches skills and knowledge
A welder that does only routine tasks is a laborer
A welder that knows why they are doing something, as well as what they are doing, is a welding technician
When a topic is introduced during a course it is in the purview of the faculty
A certificate symbolizes to an employer that the student has learned skills and the “rules” in a clean, safe environment under the supervision of faculty
Large employers look for employees with American Welding Society Certifications (AWS) for jobs in high-rise buildings, bridge, or other heavy industrial situations
Welding Employer Perspective
Garrett Kittredge, Ruff Stuff
BUSINESS
Small job shop that designs and manufactures off-road vehicle parts
Sell via e-commerce
Design and fabricate parts for hobby vehicles
MIG and some TIG welding
HIRING
Previous welding experience is important
Candidates are tested on a “de-tuned” machine – can they adjust dials, wire feed and voltage
Candidates are tested on can they make “pretty” welds – good looking and strong welds that are very even because customers know how to weld themselves
Candidate presents well in an interview will have an advantage
MAJOR SKILL SETS
Bead, continuous, stringer, weave
Drawing, blueprint reading
GMAW/MIG
GTAW/TIG
Measuring
Metal cutting
Out of position welding
Safety
Symbols and terms
Welding equipment knowledge
CERTIFICATION
Welding certification is not required, but it helps
Not every certified welder is a good welder
Many welders have learned from family not in a formal education setting
OSHA 10 certification is important
This report was funded, in part, by California Community College Ch ancellor’s Office, Workforce & Economic
Development Division grant #13-152-001
11
Drafting Technology Certificates of Achievement
Drafting is classified under the TOP Code 0953.00, Drafting Technology. Drafting Technology is defined as “Planning, preparation, and interpretation of various engineering sketches for design and drafting duties, for circuits, machines, structures, weldments, or architectural plans.
Includes the application of advanced computer software and hardware (Computer Assisted
Drafting and Computer Assisted Design) to the creation of graphic representations and simulations in support of engineering projects.
” iv
Under the “drafting” classification, there are five subsections organized as follows: 095300,
Drafting Technology; 095310, Architectural Drafting; 095320, Civil Drafting; 095330, Electrical,
Electronics & Electro-Mechanical Drafting; 095340, Mechanical Drafting; and 095360, Technical
Illustration.
North Region colleges have programs that are represented under 095300, 095310, 095330, and
095340. The North region colleges collectively offer 10 Drafting Certificates of Achievement ranging from 15 to 38 units (see Table 3). The colleges include: American River, Sacramento
City, Sierra, and Yuba Colleges. (Source: California Community Colleges Chancell or’s Office, http://curriculum.cccco.edu
).
The scope and topical areas (architecture, HVAC, plumbing, electric, or engineering design) varies by college. Unlike Welding Technology, Drafting Technology is presented under different program titles; this might present a challenge for students seeking general drafting technology skills. For purposes of course comparison, the architectural drafting track is the only one that runs through all four colleges; basic drafting and architectural courses will be compared for skill sets.
TABLE 3: DRAFTING CERTIFICATES OF ACHIEVEMENT TOTAL UNITS
College Program Name
American River Design Technology
Sacramento City Engineering Design Technology
Sacramento City Architectural/Structural Drafting
Sacramento City Electric (Power-Lighting Systems)
Sacramento City HVAC Systems Design
Sacramento City Mechanical (HVAC/Plumbing Systems)
Sierra Drafting & Engineering Support – Architectural/Civil
Sierra Drafting & Engineering Support – Mechanical/Civil
Yuba
Yuba
Architectural Studies
Architectural Studies
Total Units
37-38
37
21
25
24
27
21.5-25
21.5-25
27
15
This report was funded, in part, by California Community College Ch ancellor’s Office, Workforce & Economic
Development Division grant #13-152-001
12
American River College
Design Technology – 37- 38 Units
This program “… emphasizes the knowledge and skills required for entry level success in the architectural, civil, and mechanical engineering professions.” Technical learning outcomes include: applying design and engineering process methodologies; using appropriate representational media; and organizing documents for land planning and site development.
AR Course #
DESGN 300
DESGN 302*
DESGN 310*
DESGN 320
DESGN 325*
DESGN 328*
DESGN 330*
DESGN 340
DESGN 350* or
ENGR 310
Description
Introduction for Design Resources
Technical Documentation with CADD
Graphic Analysis & Documentation
Three Dimensional Graphics & Design
Architectural Modeling & Design
Engineering Modeling & Design
Engineering Systems & Design
Architecture & Construction
Surveying & Land Planning (5) or
Engineering Survey Measurements (4)
Units
3
3
3
3
3
3
5
5
5
DESGN 360
*Requires prerequisite
Commercial Engineering Design & Drafting 4-5
Sacramento City College
Engineering Design Technology – 37-38 Units; Architectural/Structural Drafting – 21
Units; Electric – 25 Units; HVAC Systems Design – 24 Units; Mechanical – 27 Units
This program is designed for employment or upgr ade in “building design using Manual and CAD drafting application in Architectural, Engineering, or Construction related offices.”
Engineering Design Technology 37- 38 Units
Sac City Course # Description Units
EDT 300
EDT 310*
EDT 312*
EDT 314*
EDT 320*
EDT 332*
EDT 336
EDT 340
EDT 342
EDT 350
EDT 352*
EDT 302
EDT 356
EDT 498*
Survey 300
Survey 310
Math 334
*Requires prerequisite
Basic Technical Drafting
Computer Aided Drafting
Intermediate Computer Aided Drafting
Advanced Computer Aided Drafting
Architectural/Structural Design
Air Conditioning, Plumbing and Piping Design Documents
Air Conditioning System Design
Plumbing and Piping Systems Design l
Plumbing and Piping Systems Design ll
Electrical and Electronics Drafting/Design Problem Solving
Electrical and Electronics Drafting Design
A minimum of 2 units from the following
Building Trades Blueprint Reading, 2 units
Building Electrical Systems Design, 3 units
Work Experience in EDT, 1-4 units
Elementary Surveying, 4 units
Survey Map Production, 4 units
Trigonometry, 4 units
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
2
3
3
4
2
13
Architectural /Structural Drafting 21 Units
Sac City Course #
EDT 300 Basic Technical Drafting
Description
EDT 310*
EDT 312*
EDT 314*
EDT 320*
Computer Aided Drafting
Intermediate Computer Aided Drafting
Advanced Computer Aided Drafting
Architectural/Structural Design
EDT 302
EDT 330*
EDT 332*
EDT 336
EDT 340
EDT 342
EDT 350
EDT 352*
EDT 356
EDT 498*
Survey 300
Survey 310
Math 334
A minimum of 6 units from the following
Building Trades Blueprint Reading,
Air Conditioning, Plumbing, & Piping Design
Air Conditioning, Plumbing, & Piping Design Documents
Air Conditioning System Design
Plumbing and Piping Systems Design l
Plumbing and Piping Systems Design lI
Electrical and Electronics Drafting/Design Problem Solving
Electrical and Electronics Drafting Design
Building Electrical Systems Design
Work Experience in EDT,
Elementary Surveying,
Survey Map Production,
Trigonometry,
*Requires prerequisite
Electric (Power-Lighting Systems) – 25 Units
Sac City Course #
EDT 300
EDT 310
EDT 312
EDT 314
EDT 350
EDT 352
EDT 302
EDT 320
EDT 336
EDT 340
EDT 342
EDT 356
EDT 330*
EDT 332*
EDT 498*
Survey 300
Survey 310
Math 334
*Requires prerequisite
Basic Technical Drafting
Computer Aided Drafting
Description
Intermediate Computer Aided Drafting
Advanced Computer Aided Drafting
Electrical and Electronics Drafting/Design Problem Solving
Electrical and Electronics Drafting Design
A minimum of 7 units from the following
Building Trades Blueprint Reading,
Architectural/Structural Drafting
Air Conditioning, Plumbing and Piping Design
Air Conditioning System Design Documents
Air Conditioning System Design
Plumbing and Piping Systems Design l
Plumbing and Piping Systems Design ll
Building Electrical Systems Design
Work Experience in EDT
Elementary Surveying
Survey Map Production
Trigonometry
Units
3
3
3
2
4
Units
3
3
3
2
3
4
14
HVAC Systems Design – 24 Units
Sac City Course #
EDT 300 Basic Technical Drafting
Description
EDT 310*
EDT 312*
EDT 314*
EDT 336
Computer Aided Drafting
Intermediate Computer Aided Drafting
Advanced Computer Aided Drafting
Air Conditioning System Design
EDT 302
EDT 320
EDT 330
EDT 332
EDT 340
EDT 342
EDT 350
EDT 352*
EDT 356
EDT 498*
Math 334
A minimum of 10 units from the following
Building Trades Blueprint Reading,
Architectural/Structural Drafting
Air Conditioning, Plumbing and Piping Design
Air Conditioning System Design Documents
Plumbing and Piping Systems Design l
Plumbing and Piping Systems Design ll
Electrical and Electronics Drafting/Design Problem Solving
Electrical and Electronics Drafting Design
Building Electrical Systems Design
Work Experience in EDT
Trigonometry
*Requires prerequisite
Mechanical – 27 Units
Sac City Course #
EDT 300
EDT 310*
EDT 312*
Basic Technical Drafting
Description
Computer Aided Drafting
Intermediate Computer Aided Drafting
EDT 314*
EDT 332*
EDT 336
EDT 340
EDT 342
EDT 302
EDT 320
EDT 350
EDT 356
EDT 352*
EDT 498*
Survey 300
Survey 310
Math 334
*Requires prerequisite
Advanced Computer Aided Drafting
Air Conditioning, Plumbing and Piping Design Documents
Air Conditioning System Design
Plumbing and Piping Systems Design l
Plumbing and Piping Systems Design ll
A minimum of 3 units from the following
Building Trades Blueprint Reading
Architectural/Structural Drafting
Electrical and Electronics Drafting/Design Problem Solving
Electrical and Electronics Drafting Design
Building Electrical Systems Design
Work Experience in EDT
Elementary Surveying
Survey Map Production
Trigonometry
Units
3
3
3
2
4
3
3
3
Units
3
3
3
2
15
Sierra College
Drafting & Engineering Support – 21.5 - 25 Units
This curriculum “… is designed to prepare students for careers in industry as engineering support technicians who plan, prepare and interpret engineering sketches for design and drafting relative to mechanical and architectural designs, civil structures and developments, weldments, electronic circuits, or landscape architecture and design.
Architectural/Civil Concentration
Sierra Course #
DES 1
DES 2*
DES 10*
DES 20
DES 21*
DES 22*
DES 40*
DES 95
Description
Technical Drafting 1
Technical Drafting 2
Industrial and Civil Applications of Computer Aided Design
Architectural Drawing I
Architectural Drawing II
Architectural Drawing III-BIM
Managing the Computer-Aided Design Environment
Internship in Drafting and Engineering Support
*Requires prerequisite
Mechanical/Civil Concentration - 21.5-25 Units
Units
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
.5-4
Sierra Course #
DES 1
DES 2*
DES 10*
DES 11*
DES 20
DES 21*
DES 40*
DES 95
Description
Technical Drafting 1
Technical Drafting 2
Industrial and Civil Applications of Computer Aided Design
Three-Dimensional Modeling
Architectural Drawing I
Architectural Drawing II
Managing the Computer-Aided Design Environment
Internship in Drafting and Engineering Support
Units
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
.5-4
*Requires prerequisite
Yuba
Architectural Studies – 27 or 15 Units
This program concentrates on architectural studies, with a certificate of achievement of either 27 or 15 units.
Architectural- 27 Units
Yuba Course #
DRAFT 30
DRAFT 32
DRAFT 34*
DRAFT 35*
DRAFT 38*
DRAFT 39*
MATH 21
DRAFT 31
Description
Technical Drawing with AutoCAD
Architectural Delineation
Architectural Drawing
Architectural Design and Presentation
Computer Aided Drafting
Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Plane Trigonometry
Plus 6 units from the following
Descriptive Geometry
Units
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
16
DRAFT 36
ENGR 3
Design Problems in Architecture
Plane Surveying
SPECH 1
*Requires prerequisite
Architectural- 15 Units
Public Speaking
Yuba Course #
DRAFT 30
DRAFT 32
DRAFT 34*
DRAFT 35*
DRAFT 38*
DRAFT 39*
Description
Technical Drawing with AutoCAD
Architectural Delineation
Architectural Drawing
Architectural Design and Presentation
Computer Aided Drafting
Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Units
3
3
3
3
3
3
*Requires prerequisite
Sierra and Yuba course outlines were available online for the skills cited below. American River and Sacramento City outlines were not available online; course catalog descriptions were used thereby reducing skill term details.
Selected Drafting Skills Cited in Curriculum by College
Term
2D, 3D
ANSI Y 14.5M
ASME V14
AutoCAD
Auxiliary view
Axonometric
Building codes
Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Building sections
Ceiling
Computer assisted drawings
Construction detail
Construction materials
Design equipment use
Dimensioning
Documentation
Drafting conventions
Drawing for part fabrication
Electrical
Exterior elevations
Fireplaces
Floor
Foundation
Freehand sketching
Geometric constructions
American
River
Sacramento
City
Sierra
Yuba
17
Term
Interior elevations
Isometric projection
Mechanical specifications
Oblique drawing
Oblique projection
Orthographic
Plan oblique
Plumbing
Residential construction
Rivit
Roof
Scale reading
Site plan
Sketching
SketchUP
Stairs
Surface documents
Surveying
Sustainable building certification
Sustainable materials
Technical lettering
Title 24
XM standards
High School Drafting Articulation Agreements
School College
Antelope High American River
American
River
Center High
Center High
Cordova High
El Camino Fundamental
High
Elk Grove High
Florin High
Folsom High
Franklin High
American River
American River
American River
American River
American River
American River
American River
American River
Sacramento
City
Sierra
Course
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Yuba
18
School
Golden Sierra High
Granite Bay High
Laguna Creek High
Monterey Trail High
College
American River
American River
American River
American River
Course
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Oak Ridge High
Oak Ridge High
Oakmont High
Pleasant Grove High
American River
American River
American River
American River
Design Technology 320 3D Graphics and
Design
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Pleasant Grove High
Woodcreek High
American River
American River
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Design Technology 100: Introduction to
Computer Aided Drafting and Design
Source: http://www.statewidepathways.org/associated_agreements
Employer Perspective
LB Construction, Inc. is located in Roseville, California, doing business in California, Oregon, and Nevada. With about 350 employees, they are a subcontractor serving clients with three divisions: structural steel; metal stud and drywall; and rough carpentry. They have and in-house fabrication shop. They employ welders and drafters.
During the interview, company representatives, (Business Development Manager and Head
Detailer) indicated that a demonstration of skills is primary when considering a new hire.
Experience is key. A degree was considered great to have, but without on-the-job experience, and the ability to demonstrate competency, it is not enough. If a prospective employee has an internship or an apprenticeship on their resume, it is a major “plus”.
Knowing safety and being safety minded is very important. If an employee has an OSHA 10 certification it is advantage when hiring welders. For drafters, they look for Tekla experience, which is rare for a student/new graduate to have. Tekla is model-based software for the construction, infrastructure and energy industries. They will consider someone with architectural drafting experience with 2D and 3D modeling. The Head Detailer indicated that the drafting/detailing work they do is learned primarily on the job.
19
Engineering Certificates of Achievement & Degrees
North Region colleges offer programs represented under TOP Code 09, Engineering and
Industrial Technologies. The programs fall under TOP Code 0924.00 – Engineering
Technology, General.
The only North region college that offers an Engineering Certificate of Achievement is Sierra
College (see Table 4). North Region colleges that offer engineering courses include: American
River, Cosumnes River, Folsom Lake, Sacramento City, Sierra, and Yuba Colleges. (Source:
California Community Colleges Chancellor’s Office, http://curriculum.cccco.edu
).
The scope and topical areas include aeronautical, civil, electrical, general, and mechanical,
Unlike Welding Technology and Drafting Technology engineering programs are primarily transfer preparation. Cosumnes River, Sacramento City, and Sierra offer an Associate degree.
American River, Folsom Lake, and Yuba do not offer a degree.
All North Region colleges with engineering programs state they prepare students for transfer to a four-year institution to pursue an engineering degree. The number of engineering courses offered at these colleges varies from 5 to 10, not including independent study or work experience.
Only engineering courses will be compared in this section. Other disciplines, e.g. math, chemistry, and physics required for a certificate or degree are beyond the scope of this study and will not be compared. Additionally, general education coursework required for an
Associat e’s degree is not compared.
TABLE 4: ENGINEERING CERTIFICATES OF ACHIEVEMENT TOTAL UNITS
College
Sierra
Sierra
Program Name
Civil Engineering Technology Certificate
General Engineering Technology Certificate
Total Units
31-33
31-33
TABLE 5: ENGINEERING ASSOCIATE DEGREE* OR TRANSFER PROGRAM UNITS
College Program Name
American River Transfer Only
Cosumnes River Engineering
– Civil/Mechanical – A.S
Cosumnes River Electrical/Computer Engineering - A.S
Folsom Lake Transfer Only
Sacramento City Civil
Sacramento City Electrical/Computer
Sacramento City General
Sacramento City Mechanical/Aeronautical
Sierra
Yuba
Engineering A.A or A.S.
Transfer Only
Total Units
--
48
39
--
62-63
59-60
58-59
58-59
33-36
--
*Associate degrees must have general education units in addition to program specific units
20
American River College
Engineering – Transfer Only
This transfer program provides the foundation necessary to transfer to a four-year institution to pursue a bachelor’s degree in engineering.
American River #
ENGR 300*
ENGR 305*
ENGR 307*
ENGR 310*
ENGR 312*
ENGR 320*
ENGR 401*
ENGR 413*
ENGR 420*
ENGR 430*
Description
Introduction to Engineering
Basic Technical Drawing
Industrial Materials Testing
Engineering Survey Measurements
Engineering Graphics
Manufacturing Processes
Introduction to Electrical Circuits and Devices
Properties of Materials
Statics
Dynamics
3
3.5
4.5
3
3
Units
1
3
3
4
3
*Transferable to UC/CSU
Cosumnes River College
Engineering A.S
.
This A.S. degree program provides the foundation in mathematics, physics, and engineering for transfer to a four-year institution to pursue a degree in Engineering. Cosumnes River has two tracks: Civil/Mechanical and Electrical/Computer. The following are required engineering courses for the A.S. degree.
Civil/Mechanical Track
Cosumnes River #
ENGR 300*
Description
Introduction to Engineering
Units
1
ENGR 312*
ENGR 400*
ENGR 420*
ENGR 412*
Engineering Graphics
Introduction to Circuits and Devices
Statics
Properties of Materials
3
3
3
3
*Transferable to UC/CSU
Electrical/Computer Track
Cosumnes River #
ENGR 400*
Description
Introduction to Circuits and Devices
*Transferable to UC/CSU
Units
3
Folsom Lake College
Engineering – Transfer Only
This transfer program provides the foundation necessary to transfer to a university for pursue a bachelor’s degree in engineering.
Folsom Lake # Description Units
ENGR 300*
ENGR 303*
ENGR 312*
ENGR 400*
Introduction to Engineering
Introduction to Logic Design
Engineering Graphics
Introduction to Electrical Circuits and Devices
1
4
3
3
21
Folsom Lake #
ENGR 420* Statics
Description Units
3
ENGR 495* Independent Studies
*Transferable to UC/CSU
1-3
Sacramento City College
Engineering – Associate’s Degree
This program provides the foundation necessary to transfer to a four-year institution to pursue a bachelor’s degree in engineering. The college has civil, electrical/computer, general, and mechanical/aeronautical tracks.
Civil Track
Sacramento City Description Units
ENGR 300*
ENGR 310
ENGR 312*
ENGR 400*
Introduction to Engineering
Engineering Survey Measurements
Engineering Graphics
Introduction to Electrical Circuits and Devices
ENGR 405*
ENGR 412*
Engineering Problem Solving
Properties of Materials
ENGR 422* Engineering Mechanics, Statics
*Transferable to UC/CSU
Electrical/Computer Track
Sacramento City
ENGR 300*
ENGR 400*
Description
Introduction to Engineering
Introduction to Electrical Circuits and Devices
ENGR 405*
ENGR 412*
ENGR 422*
Engineering Problem Solving
Properties of Materials
Engineering Mechanics, Statics
*Transferable to UC/CSU
General & Mechanical/Aeronautical Track
Sacramento City
ENGR 300*
ENGR 312*
ENGR 400*
Description
Introduction to Engineering
Engineering Graphics
Introduction to Electrical Circuits and Devices
ENGR 405*
ENGR 412*
Engineering Problem Solving
Properties of Materials
ENGR 422* Engineering Mechanics, Statics
*Transferable to UC/CSU
3
3
3
1
4
3
3
3
3
3
Units
1
3
3
3
3
Units
1
3
3
22
Sierra College
Engineering – Associate’s Degree and Certificate of Achievement
This program provides the foundation necessary to transfer to a four-year institution to pursue a bachelor’s degree in engineering. The college has civil and general engineering Certificates of
Achievement and an Associate’s degree in Engineering.
Certificate - Civil Engineering Track
Sierra College Description Units
ENGR 10*
ENGR 22A*
ENGR 22B*
ENGR 150*
Engineering Survey Measurements
Engineering Drawing and CAD
Descriptive Geometry and Solid Modeling
Introduction to Engineering Profession
4
3
3
1
Chemistry, Computer Information Science, Mathematics, Mechatronics, and Physics courses are also required for this certificate.
*Transferable to UC/CSU
Certificate – General Engineering Technology Track
Sierra College Description Units
ENGR 22A*
ENGR 22B*
Engineering Drawing and CAD
Descriptive Geometry and Solid Modeling
3
3
ENGR 150* Introduction to Engineering Profession 1
Chemistry, Computer Information Science, Mathematics, Mechatronics, and Physics courses are also required for this certificate.
*Transferable to UC/CSU
Associate’s Degree - Engineering
Sierra College
ENGR 10*
ENGR 17*
Description
Engineering Survey Measurements
Introduction to Circuit Theory
Circuit Theory Laboratory
Units
4
3
1 ENGR 17L*
ENGR 22A*
ENGR 22B*
ENGR 35*
Engineering Drawing and CAD
Descriptive Geometry and Solid Modeling
Statics
3
3
3
ENGR 45*
ENGR 150*
Materials Science
Introduction to Engineering Profession
3
1
*Transferable to UC/CSU
Yuba College
Engineering
– Transfer Only
This program provides the foundation necessary to transfer to a four-year institution to pursue a bachelor’s degree in engineering.
Yuba College
ENGR 3* Plane Surveying
Description Units
4
ENGR 4*
ENGR 6*
ENGR 10*
Engineering Graphics
Computational Problem Solving for Engineers
Introduction to Engineering and Science
3
3
3
23
Yuba College
ENGR 17*
ENGR 17L*
ENGR 33**
ENGR 35*
ENGR 45*
Description
Circuits for Engineers
Circuits Lab for Engineers
Surveying a Parcel Boundary
Statics
Properties of Materials
*UC/CSU
**CSU only
Selected Engineering Skills Cited in Curriculum by College
Term
Analyze problems
Axles, fixed & rotating
Centroids & moment of inertia
Computer aided design
(CADD)
Computer hardware design
Digital logic design
American
River
Cosumnes
River
Folsom
Lake
Sacramento
City
Drafting
Geometric dimensioning
& tolerancing
Distributed loads
Electrical circuits
Engineering design
Equations, differential
Equations, energy
Equations, momentum
Equations, motion
Ethics/responsibilities
Fabrication techniques
Force systems analysis
Friction
Interpret drawings
Karnaugh maps
Logic gates
Manufacturing processes
Material properties
Material testing
MATLAB
Orthographic projection
Parcel Boundary
Particles, kinetics
Particles, systems
Power calculations
Problem solving
Programmable logic devices
Sierra
Units
3
1
1
3
4
Yuba
24
Term
Record of survey
Statics
Steady state
Surveying
Technical drawings
Three-phase AC power
Truss analysis
Welding
American
River
Cosumnes
River
Folsom
Lake
Sacramento
City
Sierra
UC and CSU Transfer/Articulation
Courses that are transferable to UC or the CSU system are designated with an * in each program track table above.
Engineering Employer Perspective
Don Whitaker, Principal, and John Enright, Engineering Assistant, at Ceronix were interviewed regarding engineering programs. Ceronix is a manufacturer of drop-in replacement monitors and LCDs for the gaming industry. Ceronix hires production technicians and engineers with electronics/mechatronics skills ranging from an Associates degree to a Bachelors degree. They are looking for an individual with basic knowledge of electronics/mechatronics, and interdisciplinary skills that can be trained to the company’s needs. A good understanding of mathematics, computer skills, and an ability to write a report and instructions are important.
They want someone with good listening and critical thinking skills that can explain their thought process and function as part of a group. Other industry advisors suggested an emphasis on technical sketching by hand, using hand and machine tools, welding, 3D printing, and an understanding of advanced manufacturing practices, e.g. lean manufacturing and supply chain management, were recommended.
Electronics Certificates of Achievement
Electronics is the design and construction of electronic circuits to solve practical problems in the
AMS. Electronics courses may include basic DC and AC circuits, semiconductor devices, analog and digital circuit operation and design, computer-aided electronic circuit analysis, and troubleshooting. Electronics applications may include communications, medical monitoring devices, navigational equipment, machine tool numerical controls and computers.
The programs are classified under the TOP code 093400.
TABLE 6 CERTIFICATES OF ACHIEVEMENT TOTAL UNITS
College Program Name
American River Advanced Electronics and Telecommunications
American River Biomedical Equipment Technology
American River Digital Home Technology Integration
American River Digital Repair and Upgrade Technician
American River Electronic Systems Technology
American River Fiber Optics
American River Robotics
American River Telecommunication Specialist
Sacramento City Automated Systems Technician
Total Units
17
17
15
14-17
36
17
15
22
45
Yuba
25
College Program Name
Sacramento City Electronics Facilities Maintenance Technician
Sacramento City Microcomputer Technician
Sacramento City Telecommunications Technician
Sacramento City Electronics Mechanic
Total Units
49
31.5-33
45
31
American River College
American River offers certificates and an Electronics Systems Technology degree. The college offers eight skills certificates with specialty areas in Advanced Electronics and
Telecommunications; Biomedical Equipment Technology; Digital Home Technology Integration;
Digital Home Technology Integration; Fiber Optics; Robotics; and Telecommunication
Specialist.
Certificate - Electronics Systems Technology – 36 Units
American River
ET 115
Description
Fiber Optics and Telecommunication Cabling
ET 302
ET 308
Principles of Electricity and Electronics
Technical Soldering Practices and Techniques
ET 312
ET 322
ET 112
ET 253
ET 335
ET 380
ET 420
Mathematics for Circuit Analysis
Semiconductors and Nanotechnology
Communication Units
Industrial Communication Systems Support
Integrated Circuits with Computer Applications
Introduction to Electronic Communications
Microcontrollers and Digital Signal Processors
Certificate - Advanced Electronics and Telecommunications – 17 Units
American River
ET 115
ET 302
Description
Fiber Optics and Telecommunication Cabling
Principles of Electricity and Electronics
ET 308
ET 312
ET 322 Semiconductors and Nanotechnology
Certificate - Biomedical Equipment Technology – 17 Units
American River
ET 302
ET 322 or 335 or
380
ET 425
ET 426
Technical Soldering Practices and Techniques
Mathematics for Circuit Analysis
Description
Principles of Electricity and Electronics
Semiconductors and Nanotechnology; Integrated Circuits with Computer Applications; Introduction to Electronic
Communications
Introduction to Biomedical Equipment Technology
ET 260
ET 261
ET 262
ET 263
Advanced Biomedical Equipment Technology
Plus one of the following:
Introduction to Medical Ultrasound Equipment
Introduction to Biomedical Equipment Networking
Introduction to Respiratory Therapy Ventilators
Introduction to Medical X-ray Imaging Equipment
.5
.5
.5
1
4
4
4
3
4
3
4
4
Units
4
2
2
3
4
4
Units
4
4
Units
4
4
4
26
Certificate - Digital Home Technology Integration – 15 Units
American River
ET 115
Description
Fiber Optics and Telecommunication Cabling
ET 302
ET 385
Principles of Electricity and Electronics
Digital Home Technology Integration
ET 386 Fiber Optic Splicing, Connectivity and Testing
Certificate - Digital Repair and Upgrade Technician – 14-17 Units
American River
CISC 320
CISC 361
CISC 363
ET 253
ET 298
ET 308
Description
Operating Systems 1
Microcomputer Support Essentials
– A+ Certification Prep
3
Microcomputer Support Technical – A+ Certification Prep 3
Units
Industrial Communication Systems Support
Work Experience in Electronics Technology
Technical Soldering Practices and Techniques
Certificate - Fiber Optics – 17 Units
4
1-4
2
American River
ET 115
ET 302
Description
Fiber Optics and Telecommunication Cabling
Principles of Electricity and Electronics
4
Units
4
ET 380
ET 386
Introduction to Electronic Communications
Fiber Optic Splicing, Connectivity and Testing
ET 387 Advanced Fiber Optics
Certificate – Robotics – 15 Units
4
3
2
American River
ET 192
ET 194
ET 195
Introduction to Robotics
Description
Intermediate Robotics
Electrical and Mechanical Power and Control Systems
ET 196
ET 302
Sensors, Measurement, and Control
Principles of Electricity and Electronics
ET 308 Technical Soldering Practices and Techniques
Certificate -Telecommunication Specialist – 22 Units
American River Description
ET 112
ET 115
ET 302
ET 308
ET 380
ET 386
ET 387
Communication Units
Fiber Optics and Telecommunication Cabling
Principles of Electricity and Electronics
Technical Soldering Practices and Techniques
Introduction to Electronic Communications
Fiber Optics Splicing, Connectivity and Testing
Advanced Fiber Optics
4
4
4
3
2
4
2
2
Units
2
3
3
4
4
2
4
3
2
Units
Units
27
Sacramento City College
Sacramento City offers five Certificates of Achievement in Electronics Technology: Automated
Systems Technician; Electronics Facilities Maintenance Technician; Microcomputer Technician; and Telecommunications Technician. (Source: 2013-2014 Sacramento City College Catalog)
Certificate - Automated Systems Technician – 45 Units
Sacramento City
ET 300
ET 301
ET 306
ET 310
ET 311
ET 315
ET 320
ET 330
ET 340
ET 360
ET 390
ET 400
CISC 310
ET 490
Sacramento City
ET 300
ET 301
ET 306
ET 310
Description
DC Theory and Circuit Fundamentals
AC Theory and Circuit Fundamentals
Electronics Fabrication and Soldering Techniques
Mathematics for DC Circuit Fundamentals Part I
Mathematics for DC Circuit Fundamentals Part II
Mathematics for Semiconductor Theory
Semi Conductor Theory
Analog and Digital Integrated Circuit Applications
Basic Microprocessors
Electronic Servicing and Calibration Techniques
Microprocessor Systems – Troubleshooting
Microwave Communications Techniques
Introduction to Computer Information Science
Advanced Student Projects Laboratory
ET 490 Advanced Students Projects Laboratory
Certificate - Electronics Facilities Maintenance Technician – 49 Units
Description
DC Theory and Circuit Fundamentals
AC Theory and Circuit Fundamentals
Electronics Fabrication and Soldering Techniques
ET 311
ET 315
ET 320
ET 330
Mathematics for DC Circuit Fundamentals Part I
Mathematics for DC Circuit Fundamentals Part II
Mathematics for Semiconductor Theory
Semi Conductor Theory
Analog and Digital Integrated Circuit Applications
ET 340
ET 350
ET 390
ET 400
Basic Microprocessors
Receiver Circuits
Microprocessor Systems – Troubleshooting
Microwave Communications Techniques
Transmitter Fundamentals
Trigonometry
ET 410
MATH 334
Certificate - Microcomputer Technician – 31.5-33 Units
Sacramento City
CISC 310
CISP 301
CISC 320
Description
Introduction to Computer Information Science
Algorithm Design and Implementation
Operating Systems 1 or CISC 323
3
4
1
Units
3
2
2
5
3
3
4
1.5
3
5
5
Units
2.5
2.5
2
1.5
3
4
5
4
5
5
5
5
Units
2.5
2.5
2
1.5
1.5
3
28
Sacramento City
CISA 310
CISA 311
CISC 323
ET 145
ET 340
ET 390
Description
Introduction to Electronic Spreadsheets
Intermediate Electronic Spreadsheets
Database Management using Microsoft Access
Basic Computer System Repair & ET146 or CISC 360
Basic Microprocessors
Microprocessor Systems – Troubleshooting
ET 490
CISC 355
Advanced Student Projects Laboratory 2
Introduction to Data Communications or CISC 300 or 303 1.5-3
4 units Plus four units from the following: ET 300, 301, 306, 310, 311, 320, EDT 310,
352, CISN 300, 303, 304; CISC 351
Certificate - Telecommunications Technician – 45 Units
Sacramento City
ET 300
ET 301
Description
DC Theory and Circuit Fundamentals
AC Theory and Circuit Fundamentals
Electronics Fabrication and Soldering Techniques
2.5
2.5
2
Units
ET 306
ET 310
ET 311
ET 315
Mathematics for DC Circuit Fundamentals Part I
Mathematics for DC Circuit Fundamentals Part II
Mathematics for Semiconductor Theory
1.5
1.5
3
5
5
5
5
3
2
4
5
3
1
Units
1
ET 320
ET 330
ET 340
ET 350
ET 360 or 390
Semi Conductor Theory
Analog and Digital Integrated Circuit Applications
Basic Microprocessors
Receiver Circuits
ET 400
Electronic Servicing and Calibration or Microprocessor
Systems – Troubleshooting
Microwave Communications Techniques
ET 410 Transmitter Fundamentals
Certificate - Electronics Mechanic - 31Units
Sacramento City
ET 300
Description
DC Theory and Circuit Fundamentals
ET 301
ET 306
ET 310
ET 311
ET 315
ET 320
AC Theory and Circuit Fundamentals
Electronics Fabrication and Soldering Techniques
Mathematics for DC Circuit Fundamentals Part I
Mathematics for DC Circuit Fundamentals Part II
Mathematics for Semiconductor Theory
Semi Conductor Theory
Plus 13 units from the following: CISC 310; ET 490, 494, 495; Mechanical-
Electrical Technology (MET) 256, 257, 351, 352
4
5
Units
2.5
2.5
2
1.5
1.5
3
5
13
29
Mechatronics Certificate of Achievement
Sierra College and American River are the two colleges that have Mechatronics Certificates in the North Region.
TABLE 7 MECHATRONICS CERTIFICATES OF ACHIEVEMENT TOTAL UNITS
College Description Units
American River Mechatronics
Sierra College Mechatronics Technology
35-38
24
American River College
This certificate provides training in a multi-disciplinary field of which the primary focus is industrial automation. The certificate requires Electronics Technology courses coupled with
Design, Welding, Management, Physics, and Engineering
Mechatronics – Certificate of Achievement – 35-38 Units
American River
ET 302
Description
Principles of Electricity and Electronics
Units
4
Design 100
Weld 300
Design 302
ET 192
ET 194
ET 195
MGMT 360
PHYS 310
Introduction to Computer Aided Drafting and Design (CADD) 3
Introduction to Welding
Technical Documentation with CADD
Introduction to Robotics
3
3
2
Intermediate Robotics
Electrical and Mechanical Power and Control Systems
Management Communication
Conceptual Physics
2
3
3
3
----- Engineering 307 & Math 100 or Design 310 and Design 330 or Welding 342 and ET 196
5-8
Sierra College
In 2004 the Sierra College Computer Integrated Electronics program re-designed courses to become a Mechatronics program. Mechatronics is the study of electronics, mechanics, hydraulics, and pneumatics under computer control. The field includes robotics, industrial automation, industrial process control, and electro-mechanical systems integrated into one program. The Certificat e of Achievement has 24 units. The Associate’s degree also has 24 units, plus the general education requirement.
Mechatronics – Certificate of Achievement – 24 Units
Sierra College Description Units
MECH 4
MECH 10
MECH 14
MECH 25
MECH 44
MECH 54
MECH 90
Fundamentals of Mechatronics
Fundamentals of Electronics
Fabrication Techniques
Personal Computer Configuration and Repair
Mechatronics Processes and Materials
Mechatronics System
Microcontroller Embedded Systems
2
4
4
4
4
2
4
30
Selected Electronics/Mechatronics Skills Cited in Curriculum by College
Term
American
River
Sacramento
City
A+ Certification
AC and DC motor control
Analog integrated circuit
Analyze electronic circuitry
Atomic theory
Audio
Automation
Batteries
Cabling
Capacitor
Circuit boards, printed
Circuits, electronic
Circuits, integrated
Computer configuration and repair
Computer integrated electronics
Communication systems
Conversion: analog to digital, digital to analog
Diode
Digital integrated circuit
Digital logic gates
DMM, oscilloscopes, signal sources
Electrical power and control systems
Electro-static discharge
Electronic communications
Electronics technology
Engineering diagrams/drawings
Fabrication techniques
FCC General Class Radiotelephone examination
Fiber optics
Fiber optics connectors
Fluid power
Hydraulics
Inductor
Kirchhoff’s Law
Mathematical relationships voltage, current, resistance, capacitance, inductance, reactance, frequency and phase angle
Mechanical power and control systems
Mechanical components
Mechatronic systems, design, installation, repair
Microcontroller based embedded systems
Microprocessors
Nanotechnology
Networking
Ohm’s law
Operating system software installation
Optical encoders
Parallel circuit
Parallax stamp micro-controllers
Sierra
College
31
Pneumatics
Printed circuit board design
Term
Programmable Logic Controllers
Resistor
Robotics
Safety
Schematic symbols
Semiconductors
Sensors
Series circuit
Soldering, high-tech
Surface mount techniques
Systems design
Telecommunication systems
Thyristors
Transformer
Transistors
Through-hole techniques
Trouble Shooting
Voltage
Watt’s law
American
River
Sacramento
City
High School Electronics Articulation Agreements
High School
Rio Americano High
College
American River
Course
ET 385: Introduction to Electricity and
Electronics - Digital Home
Rio Americano High American River ET 302: Introduction to Electricity and
Electronics
Sierra
College
Employer Perspective
Ceronix was also interviewed regarding electronics/mechatronics programs. The majority of the skills listed in the Electronics/Mechatronics Skills Cited table above were confirmed as important skills. They noted that they look for a “basic” understanding of these skills. Additionally, other program advisors emphasized the following skill sets: accurate measuring, soldering skills, reading schematics, interpreting and applying documentation, troubleshooting, exposure to
Solid Works, and welding knowledge.
Manufacturing Technology Certificate of Achievement
Yuba College offers the only Manufacturing Technology program in the North Region.
Manufacturing Technology is represented TOP Code 0956.30 – Manufacturing and Industrial
Technology – Machining and Machine Tools. It is described as, “Fabrication, assembly and repair of parts and components or systems on machines, such as lathes, grinders, drill presses, milling machines, and shaping machines. Includes Computer Numerical Control and tool design.”
The course catalog describes the program as a “comprehensive program of instruction designed to develop knowledge of scientific principle, mathematical concepts, and technical
32
skills.” The degree requires a combination of drafting, welding, and automotive courses to support manufacturing technology courses. The Associate degree has 30 required units plus general education units and the Certificate of Achievement requires 24 units. This certificate relies on combining the disciplines of automotive, drafting, and welding to round out the learning outcomes.
Manufacturing Technology Certificate of Achievement – 24 Units
Yuba College
Auto 22 Hydraulics
Description Units
3
Draft 30
MFGT 20
MFGT 21
MFGT 34
Technical Drawing with AutoCAD
Principles of Machine Shop
Intermediate Machine Shop
Computer Numerical Control
3
3
3
3
MFGT 35
MFGT 60
MFGT 62
WELD 30 or 10
Computer-Aided Manufacture
Problems in Manufacturing Technology
Advanced Machine Shop
Gas Welding or Arc Welding
3
2
3
2
Selected Manufacturing Technology Skills Cited in Curriculum
Term
CNC Lathe
CNC Mill
Computer aided manufacturing (CAM)
Computer numerically controlled machine tool programming (CNC)
Drilling machines
EDM machining
Engine lathe
G code
Grinding machines
Horizontal milling machine
Interpolation, circular
Interpolation, helical
Interpolation, linear
Lathe, tracing
Lathe, turret
Machine tool repair
Mechanical testing
Metallurgy
Part design
Precision layout
Safety
Tool and cutter grinder
Vertical milling machines
Agricultural Mechanics Certificate of Achievement
This new (proposal approved spring 2014) certificate offers a practical hands-on skill set required to fabricate and repair agriculture equipment. This program is included in the AMS curricular comparison due to the skills related to welding and automotive. The cross-disciplinary certificate has 24 required units.
33
Agricultural Mechanics Certificate of Achievement – 24 Units
AG 32
Yuba
Internship
Description
WELD 89
AUTO 20
AUTO 22
AUTO 30
AUTO 34
WELD 10
Agriculture Welding
Automotive Technical Skills
Hydraulics (Fluid Power)
Manual Drive Trains/Gas and Diesel Vehicle
Basic Electrical Systems
Introduction to Arc Welding (SMAW)
WELD 20 Introduction to MIG Welding (GMAW)
Selected Agriculture Mechanics Skills Cited in Curriculum
Term
Arc Welding (SMAW)
MIG Welding (GMAW)
Hydraulics
Electrical systems
Fabricate equipment
Repair equipment
Measuring skills
Bolt, nut, thread repair
Problem solving
Electrical circuit
Automotive drive trains
Gear, bearing, lubrication theory
Vehicles, gasoline
Vehicles, diesel
Electron theory
DC circuits
DC wiring
GTAW
GWAW
Weld stringer
Weave bead
Butt weld
Fillet weld
Positions, flat, horizontal, vertical, overhead
Gases
Spot weld
3
3
3
4
4
Units
2
2
3
34
References
American River College “ARC Catalog” 2013-2014 Online - http://www.arc.losrios.edu/catalog.htm
Cosumnes River College “Cosumnes River College Catalog” 2013-2014 Print
Sacramento City College “Sacramento City College Catalog” 2013-2014 Print
Sierra Colle ge “Sierra College Catalog 2013-2014” 2013 Print
Yuba College “Yuba College Catalog 2013-2014” 2013 Print i
Accessed online 6-2-2014 at www.nfnrc.org
ii Shulock, Nancy, Colleen More, and Jeremy Offenstein. The Road Less Traveled . Rep.
Sacramento: California State University, Sacramento, 2011. Print, p. 10 iii
C alifornia Community Colleges “Taxonomy of Programs” February 2004, Sixth Edition
Revised September 2009, p 26 . http://www.cccco.edu » Chancellor's Office » Divisions »
Academic Affairs » Credit Program and Course Approval » Reference Materials iv Ibid, p. 25
35