Arthropods!
advertisement

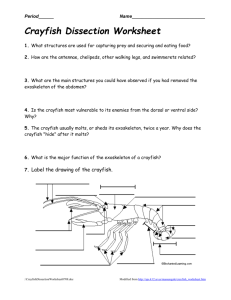
Biology What percentage of animals belong to the Phylum Arthropoda? ◦ 2/3, 67% List some examples of arthropods: ◦ Lobsters, crabs, spiders, and insects Like annelids, arthropods are segmented animals. Body segments bear jointed extensions called appendages such as legs and antennae. What does “arthropod” mean? ◦ Jointed foot Describe the exoskeleton of arthropods. What is the function of each layer of the exoskeleton? ◦ Outer layer: repels water and helps prevent dessication ◦ Middle layer: provides the primary protection ◦ Inner layer: provides flexibility at the joints What is a compound eye? ◦ An eye composed of many individual light detections, each with its own lens What is molting? ◦ The process by which an arthropod sheds its exoskeleton and develops a new one. Identify the difference between chelicerae and mandibles. ◦ Chelicerae-pincerlike mouth parts ◦ Mandibles- jawlike mouth parts What are the five main subphyla of arthropods? ◦ Trilobita, Crustacea, Chelicerata, Myriapoda, and Hexapoda What characteristics are shared by most or all crustaceans? ◦ Have two pairs of antennae and paired appendages (some branched). ◦ Most have mandibles and a nauplius larva. What is the most important role of copepods in marine ecosystems? ◦ Abundant in the plankton and serve as a food sources What are some examples of terrestrial crustaceans? ◦ Sow bugs and pill bugs Why do terrestrial crustaceans only live in moist environments? ◦ They lack adaptations for conserving water Crayfish ◦ What are the functions of the mandibles and chelipeds on a crayfish? Mandibles are used for chewing Chelipeds are used for capturing food and defense. ◦ What structural adaptations of crayfish promote effective respiration in water? Walking and branches of maxillae circulate water over the gills. ◦ Crayfish (continued): ◦ Describe the type of circulation found in a crayfish. Open circulatory system; the heart pumps hemolymph into several large vessels. Hemolymph then enters the spaces w/in the body where it bathes the tissues. Hemolymph returns to the gills where it exchanges O2 and CO2. Then, the hemolymph returns to the heart. List the major characteristics of arachnids: ◦ Have a cephalothorax and abdomen. ◦ Cepalothorax usually has 6 pairs of jointed appendages: Chelicerae, pedipalps, and 4 pairs of walking legs Describe the functions of pedipalps: ◦ Aid in holding food and chewing ◦ In spiders, they transfer sperm from the male to the female’s seminal receptacle. Describe three ways in which spiders are adapted to catching prey: ◦ Some spiders spin webs to trap prey. ◦ They also have chelicerae modified as fangs that inject venom. ◦ Spiders can also immobilize their prey by wrapping them in silk. Name two ways in which scorpions differ from spiders: ◦ Scorpions have large pincerlike pedipalps and a stinger at the end of their abdomen How do mites and ticks differ? ◦ Mites are usually less than 1 mm in length, while ticks are a few millimeters to 3cm in length. Mites can be free living, but ticks can only be parasites. How do millipedes and centipedes differ? ◦ Millipedes are herbivorous, have rounded bodies, and have two pairs of legs on most segments. ◦ Centipedes are carnivorous, have flattened bodies, and have one pair of legs on most segments.