Crayfish Physiology
advertisement

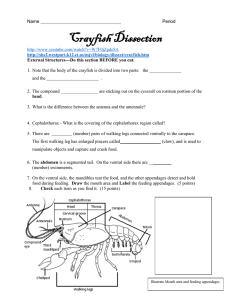
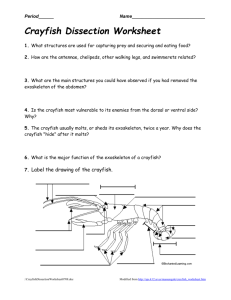
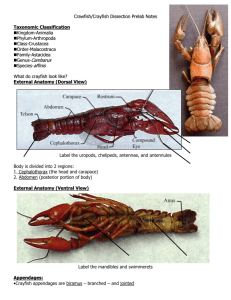
Crayfish Physiology External Anatomy Carapace – Outer covering of the crayfish that provides support to the internal structure and also provides protection from predators. Rostrum – Part of the carapace. Antennae and Antennules – These sense organs allow the crayfish to sense touch and chemical differences in their environment as well as provide balance. Eyes – Provides the crayfish with sight. Chelipeds – Used to breaking up food and pass it onto the mandibles at the mouth. Also used in defending itself from predators. Uropod and Telson – These flippers aid the crayfish in backward swimming to escape from danger. Walking Legs – Used for locomotion. Swimmerets – Used for backward locomotion. Digestive System Mouth - The opening to the digestive system. 1st, 2nd and 3rd Maxillapeds – Mainly used for moving food onto the mandibles at the mouth. Mandibles – Act as teeth to grind up the food before it passes into the mouth. Esophagus – The tube connecting the mouth to the stomach. Very short and hard to see in the crayfish. Digestive Gland – Produces digestive enzymes (juice) that help break down food. Green Gland – These structures help to filter out waste material from the body. They act like our kidneys. Intestine – This organ continues to absorb the nutrients from the food and puts it into the circulatory system. Anus – The exit door of the digestive system. Found on the ventral side of the telson. Circulatory System Heart – Pumps the blood throughout the body of the crayfish. Abdominal Artery – transports blood to the tail end of the crayfish. Respiratory System Gills – feather like structures the take in oxygen from the water and get rid of carbon dioxide. Nervous System Cerebral Ganglion (brain) – Controls all of the animal’s body functions. Nerve Cord – Transmits impulses from the brain throughout the crayfish’s body. Reproductive System Oviduct – This opening at the base of the 2/3rd walking legs of the females carry eggs from the ovaries to the exterior of the body. Sperm Duct – This opening at the base of the 4/5th walking legs of the males pass sperm to the exterior of the body. Seminal receptacle – This opening at the base of the 4/5th walking legs of the females receive sperm. Muscular System Mandibular Muscles – Controls the movement of the mandibles. Abdominal Muscles – Control the extension and contraction of the abdomen. Thorax Muscles – Control movement in the thorax. Other __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________