Chapter 21 & 22
advertisement

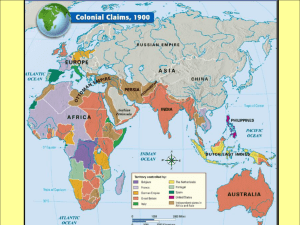
Ch. 21 Age of Imperialism 1800 - 1914 I. Imperialism *domination of one country by another *economic, political or social control A shocked mandarin in Manchu robe in the back, with Queen Victoria (UK), Wilhelm II (Germany), Nicholas II (Russia), Marianne (France), and a samurai (Japan) stabbing into a plate with Chine ("China" in French) written on it.] Africa & Asia *divided up by European powers Natural resources Trading markets Military strongholds A. Forms of Imperialism: 1. Colony *territory directly controlled by imperial power ex. England’s controls India 2. Sphere of Influence *imperial power claims exclusive investment and trading influences (Ex. only UK & China) 3. Protectorate *nation depends on another country for its protection B. Reasons for Imperialism 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nationalism Political Rivalries Military Seaports Economics new markets and raw materials Social Darwinism *superior nations spread civilization to backward countries 6. Population outlets 7. Religious and Humanitarian White Man’s Burden “Take up the White Man’s burden Send forth the best ye breedGo bind your sons to exile, To serve your captives need; To wait in heavy harness On fluttered folk & wild Your new-caught, sullen peoples, Half-devil & half-child.” Rudyard Kipling 1899 II. African Continent Africa: *Unknown Continent Dark Continent A. African Exploration 1. David Livingstone *Greatest African Explorer 1841 - 1873 1st non-African to cross Africa (E2W) Discovered: Victoria Falls 1855 (Mosi-oa-tunya) Smoke that Thunders *native name Missionary Travels & The Zambezi and Its Tributaries *2 Books by Livingstone (best sellers) London Journal *carried stories of his expeditions Motto: “Christianity, Commerce, and Civilization.” Livingstone missing 1871 2. Sir Henry Stanley New York Herald *hired to find Livingstone 8 month search: November 10, 1871 Lake Tanganyika, Ujij *modern Tanzania **“Dr. Livingstone, I presume.” Stanley takes over African exploration “I detest the land most heartily.” Stanley Stanley found source of Congo River Stanley and Livingstone opened door for Colonization of Africa David Livingstone memorial Victoria Falls, Zimbabwe B. Egypt 1. Muhammad Ali *Founder of Modern Egypt 1805 *independence from Ottoman Empire modernization of Egypt 2. Suez Canal 1859 -1869 Ferdinand de Lesseps *French builder of Suez Canal “The canal will open the world to people.” *British take over Suez Canal 1875 “Lifeline of the British Empire” Egypt became protectorate of England 1882 Fashoda Incident 1898 *England & France verge of war over Suez Canal C. North Africa *French Control Barbary States: Morocco, Tunis, Libya, Algeria Barbary Pirates *sailed off North Africa French excuse to intervene in N. Africa D. Ethiopia (On Horn of Africa) Menelik II *Ethiopian Emperor 1896 Battle of Adowa *defeated invading Italians only African nation not under European control E. Liberia 1822 *USA created homeland for freed slaves Monrovia *capital city named after President James Monroe F. Congo 1876 King Leopold II of Belgium “The Civilizer” hired Henry Stanley – Belgian control of Congo exploitation of the Congo (900,000 miles) *ivory, rubber, & copper Brutal treatment of natives 1876-1908 Population dropped 20 million – 10 million Cut off ears & hands of workers Imprisoned wives & workers G. South Africa 1. Zulu Empire 1800’s Shaka “Napoleon of Africa” Great Zulu King (army of 80,000) Battle of Isandhlwana 1870 *Zulu Army defeated British Maxim Gun *1st machine gun British destroyed Zulu’s 1879 “A spear has been thrust in the belly of the nation, there are not enough tears to mourn for the dead.” Cetewayo last Zulu King 2. Cape Colony Cape Town *founded by Dutch 1652 supply station to East Indies Afrikaners *Dutch settlers Boers *Dutch farmers believed they were superior to Black Africans indigenous *natives of a region English took control 1806 (Afrikaners resented British rule) 3. Great Trek 10,000 Boers left Cape Town 1830 *Boers migrated to north form2 new colonies Orange Free State & Transvaal 4. Gold & Diamonds discovered - South Africa 1880’s 5. Cecil Rhodes *British Prime Minister of Cape Colony De Beers Diamond Co. 1880 *monopoly diamond mines Rhodesia *colony founded by Rhodes 1890 “Cape to Cairo” *railroad Rhodes planned to build Crossing at Victoria Falls 6. Boer War 1899 - 1902 *England defeated Boers control of South Africa Concentration Camps 26,000 Boers died 7. Apartheid *Legal Segregation (discrimination of African natives) 3 Classes of People: Brits - Afrikans – Blacks 8. Union of South Africa 1910 combined Cape Colony & Boer Republics H. Liberia & Ethiopia *only 2 free African states 1914 European powers divided up all Africa Ethiopia Liberia III. India A. British East India Co. 1600 *sold Indian products on world market cotton, sugar, & cloth British vs. French for control of India B. Robert Clive 1756 *Chief Official of British East India Co. Battle of Plassey (Seven Years War) *drove French out of India Battle of Plassey Black Hole of Calcutta 1756 *British POW’s suffocated to death number that died? British 123 – 146 Indians said 15 -43 C. Sepoy Rebellion 1858 Sepoys *Indian soldiers in British Army beef & pork fat used to grease bullets Hindu’s cattle sacred / Muslims can’t touch pork *Sepoys killed 50 Europeans House of the Ladies 200 British women & children massacred British Parliament took control of India 1858 dissolved British East India Co. British Raj 1757 – 1947 D. Queen Victoria “Empress of India” 1877 *India “Jewel in the Crown” British Viceroy *Governor of India 3,500 English officials ran 280 million people largest colonial population in world British culture forced on India Impact of British Rule: 1. Market for British products & raw materials *buy only British textiles 2. Shift from growing food to growing cotton *famine killed 30 million 1800 - 1900 3. Social Changes: population growth (improved health care) schools ran by British (upper class only) (90% population illiterate) British outlawed: Suttee - suicide of widow jumped on husbands funeral fire Thugs - religious fanatics who strangled victims (to goddess Kali) E. Indian National Congress 1885 *fought Indian independence Mohandas Gandhi 1913 - 1948 *leader for Indian Independence F. Tagore *famous Indian poet Song Offerings (famous poem) world peace Nobel Prize for Literature 1913 (introduced Indian culture to West) IV. China A. Qing (Manchu) Dynasty 1644 - 1911 *last Chinese dynasty Peking capital city *modern Beijing Internal Problems: gov. corruption, peasant unrest, & famine External Problem: - Western Imperialism B. European Imperialism: 1. Canton *only port open to foreign traders 2. British East India Co. pressure China to receive diplomats & open ports tea, silk, & porcelain *major Chinese exports British exchanged Indian cotton & silver for Chinese products C. Opium War 1839 - 1842 *British East India Co. traded opium for Chinese goods “Drug of the People” drained silver supply of China Chinese gov. destroyed $6 million worth of opium British military seized Canton Unequal Treaties Treaty of Nanking *receive foreign diplomats & opened 5 more ports Hong Kong *acquired by British 1898 pay destroyed opium (99 year lease) July 1, 1997 *Hong Kong returned to China Extraterritoriality *exemption from Chinese law for foreigners D. Taiping (Great Peace) Rebellion 1850 - 1864 *bloodiest civil war in history (20 million killed) peasant uprising - discontent with Qing rule Hong Xiuquan *Rebel Leader *younger brother of Jesus?? “To kill all idolaters generally, & to possess the empire as its true sovereign.” Heavenly Kingdom of Great Peace *Dynasty proclaimed by Taiping Rebels European nations come aid of Qing Empress Devil Soldiers * Chinese troops trained by Frederick Townsend Ward E. Spheres of Influence exclusive trading privileges to regions of China F. Open Door Policy 1899 *USA demanded equal access to trade in China for all nations John Hay *U.S. Secretary of State President Teddy Roosevelt G. Empress Dowager Cixi 1861 - 1908 *most powerful woman in Chinese history? “I have often thought that I am the cleverest woman who ever lived.” “I have 400 million people dependent on my judgment.” Social Reforms: ended footbinding ended civil service exams western education system H. Boxer Rebellion 1900 “Fists of Righteous Harmony” *Boxer nickname (secret society) Goal *expel Qing & all foreigners “Destroy the foreigner!” *Boxer slogan killed 200 missionaries / thousands of Chinese attacked foreign embassies in Peking International Army *crushed Boxers Britain, USA, Germany, Russia, & Japan China forced to pay $333 million Indemnity I. Henry Puyi *Last Emperor of China 1908 - 1911 throne at age of 2 Forbidden City *his prison V. Japan A. Tokugawa Dynasty 1603 - 1868 *Reign called “Great Peace” Tokugawa Ieyasu *united Japan Policy of Isolation: expelled missionaries & forbid foreigners Act of Seclusion 1636 no Japanese could leave country all Japanese residing abroad killed when return Nagasaki *only harbor open for trade Dutch *only nation Japan would trade with B. Commodore Matthew Perry July 8, 1853 White Fleet *U.S. fleet sailed into Edo Bay opened diplomatic negotiations with Japan President Millard Fillmore “To bring a singular & isolated people into the family of civilized nations.” Causes of USA involvement in Japan: 1. refueling station (ships sailing to China) 2. whaling industry 3. American prisoners shipwrecked in Pacific placed in bird cages Gifts brought by Perry: *miniature railroad & telegraph Treaty of Kanagawa *opened Japanese ports to foreign trade ended Japanese isolationism C. Meiji Period *Enlightened Gov. 1868 - 1912 Mutsuhito *Enlightened Emperor Emperor became supreme power in Japan Sat-Cho Alliance Samurai force Shogun to resign 1. End of Feudalism *Samurais outlawed (forced to give up swords) loyalty to Emperor 2. Military State most powerful Asian nation “Rich country & a strong state.” slogan of Meiji compulsory military service - 3 years 3. Japanese Constitution *based on German const. Ito Hirbumi *traveled world study govs. Diet *Japanese Parliament (little power) 4. Modernize Industry: 1870 Zaibatsu large financial & industrial corporations wealthy families who dominated economy ex. Mitsubishi & Sumitomo families Heavy Industry: chemicals, mining, appliances, autos 5. Iwakura Mission 50 Japanese sent *Western culture adapted clothing to baseball strict educational system (modeled after USA) 6. Edo *renamed Tokyo 1868 D. Japanese Imperialism: 1. Sino-Japanese War 1894 *China & Japan fight over Korea Japan gained Korea as a colony 2. Russo - Japanese War 1904 - 1905 surprise attack on Port Arthur (Russian Naval base) Czar Nicholas II called Japanese “Monkeys” Pres. Teddy Roosevelt negotiated treaty bt. Russia & Japan won Nobel Peace Prize E. Hirohito *new Emperor of Japan 1910 - 1990 Tojo *Japanese War Minister VI. Consequences of Imperialism *Hatred *Political Rivalries *Arms Race