Slide 1
advertisement

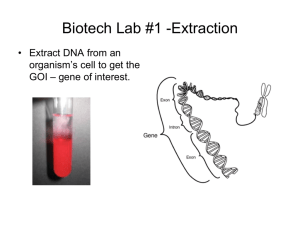
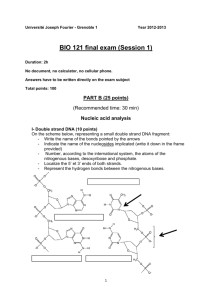
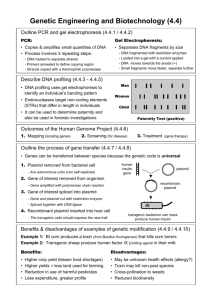
Uses a series of solutions that lyse the cell and a hot water bath to destroy nucleases followed by using 95% cold ethanol to precipitate the DNA. Extracted DNA contains organism’s cell to get the GOI – gene of interest. GOI removed from the genomic DNA and inserted into another type of DNA. Identify the GOI by determining its nucleotide sequence Select a certain restriction enzyme that can cut around the gene. The restriction site should not be in the gene. If restriction enzyme cuts in gene, gene may not function. Perform a restriction digest to cut out the GOI. Remove plasmid from bacterial cell. Use restriction enzyme open up the plasmid and create sticky ends. Use restriction enzyme on the organism’s DNA (GOI) to create sticky ends that are complementary to the plasmid sticky ends Insert the GOI into the plasmid by using ligase. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A Bacterial Plasmid’s Parts What part makes the bacteria antibiotic resistant? What gene is needed for it to replicate? How many restriction sites are present? Where don’t you want to cut ever? If the plasmid were digested with SaII, how many fragments would you get? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What is the GOI? What restriction enzyme is use to cut the DNA samples? Why can the human and bacterium DNA combine? What types of DNA are found in the bacterial cell? What other genes may be found on the plasmid? Find the recombinant plasmid in the diagram. Bioluminescence and Fire flies Top Ten Bioluminescent Organisms Bioluminescence Surfing The objective of the Paper Plasmid lab is to have you create a paper recombinant plasmid, a plasmid with a new gene inserted. The plasmid will contain DNA from two different organisms. You will use colored paper, scissors and tape to do this. If you are successful, you will have a two colored paper ring and extra pieces of paper. Put it back into a bacterial cell Now the new cell has a new trait because the plasmid has the new gene in it. It has a new phenotype. In the above illustration, find the bacteria with a plasmid and find The bacteria that do not have a plasmid. The one with the plasmid can be used to clone the inserted gene. What is Gene Cloning? Above is a picture of millions of bacterial cells. They all Are glowing which means each cell has taken up the plasmid with the lux gene. What would a nonglowing colony of cells tell you about the bacteria? Watch the Transformation Procedure DNA Cloning Glowing Protein Transformation bozeman Transformation Learn how insulin is made using recombinant plasmid Here is another illustration of how to clone a gene using a recombinant plasmid….