The Circulatory System
advertisement

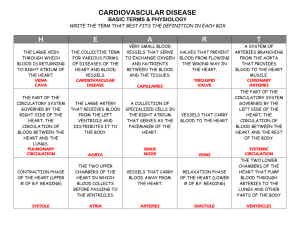
The Circulatory System The circulatory system is the transportation system by which oxygen and nutrients reach the body's cells, and waste materials are carried away. Also carries substances called hormones, which control body processes, and antibodies to fight invading germs. www.biosbcc.net/doohan/ sample/htm/heart.htm The heart, the lungs, and the blood vessels work together to form the circle part of the circulatory system. Circulation • Two parts • Heart acts as a double pump • Blood from the right side pump is dark red and low in oxygen (oxygen-poor) Circulation • Travels through pulmonary arteries to lungs where it gets fresh oxygen and becomes bright red • Blood from lungs through pulmonary veins back to the heart's left side pump • Pumped out into the body http://users.tpg.com.au/users/amcgann/body/circulatory.html 3 Types of Circulation: • Pulmonary circulation • Coronary circulation • Systemic circulation Pulmonary Circulation Movement of blood from the heart, to the lungs, and back to the heart again ***Remember heart lungs and back*** sln.fi.edu/biosci/systems/ pulmonary.html Coronary Circulation Movement of blood through the tissues of the heart ***The way blood moves in the heart*** http://sln.fi.edu/biosci2/systems/ Systemic Circulation Supplies nourishment to all of the tissue located throughout the body , except for the heart and lungs ***Blood moving all over the body (except the heart and lungs)*** http://sln.fi.edu/biosci/systems/systemic.html 3 Parts of the Circulatory System • Divided into three major parts: – The Heart – The Blood – The Blood Vessels The Heart • Size of your fist • Four Chambers: Left Atrium, Right Atrium, Left Ventricle, Right Ventricle • Divided into two sides • Each side has two chambers • Upper chamber - atrium receives blood coming in from the veins • Lower chamber - ventricle squeezes blood out into the arteries http://hes.ucf.k12.pa.us/gclaypo/circdia.html Close up of heart valve Heart sounds are made by the valves as they open and close http://hes.ucf.k12.pa.us/gclaypo/circdia.html Blood • Pumped by your heart. • Carries nutrients, water, oxygen and waste products to and from your body cells. • Made up of liquids, solids and small amounts of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Blood • Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to all the cells of the body. • Takes carbon dioxide and transports it back to the lungs http://hes.ucf.k12.pa.us/gclaypo/circdia.html Blood • Hemoglobin- the chemical that carries oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood • Plasma- the liquid part of the blood that carries nutrients • Platelets- the odd-shaped cell fragments that help clot blood http://hes.ucf.k12.pa.us/gclaypo/circdia.html user.gru.net/clawrence/ vccl/chpt7/plate.htm Blood Vessels Hollow tubes that circulate your blood Three Kinds of Blood Vessels • Arteries • Veins • Capillaries Arteries Arteries • carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart. • They are usually designated by the color red because oxygen-rich blood is red. • ***Remember they carry blood away from the heart** Have strong, muscular walls The inner layer is very smooth so that the blood can flow easily http://hes.ucf.k12.pa.us/gclaypo/circdia.html http://sln.fi.edu/biosci/systems/circulation.html Veins Veins • carry oxygen-poor blood back to the heart from the rest of the body. • They are usually designated by the color blue because oxygen-poor blood is a dark red color. • ***Remember that they carry blood to the heart*** Veins http://sln.fi.edu/biosci/systems/circulation.html Valves are located inside the veins. The valves only allow blood to move in one direction. http://hes.ucf.k12.pa.us/gclaypo/circdia.html Capillaries • Connect arteries to veins and is where oxygen & waste exchange occur. The Capillaries are in between the artery on the left and the vein on the right • They are only big enough for one blood cell to pass at a time. Click here for a video of blood flowing in the blood vessels The little donut-shaped red blood cell (scientific name erythrocyte) squeezes through the capillary and drops off its cargo of nutrients and oxygen http://sln.fi.edu/biosci/systems/circulation.html w3.uokhsc.edu http://users.tpg.com.au/users/amcgann/body/circulatory.html 4 ways to care for the Circulatory System 1. Eliminate excess weight 2. Exercise to strengthen heart muscle 3. Manage Stress 4. Avoid Smoking What is Blood Pressure? Force of blood on the walls of blood vessels Diseases of the Circulatory System • Hypertension- high blood pressure • Atherosclerosis- buildup of fats on the walls of arteries which can cause heart attacks • Leukemia- cancer of the blood which prevents the production of healthy blood cells