Student Handout
advertisement
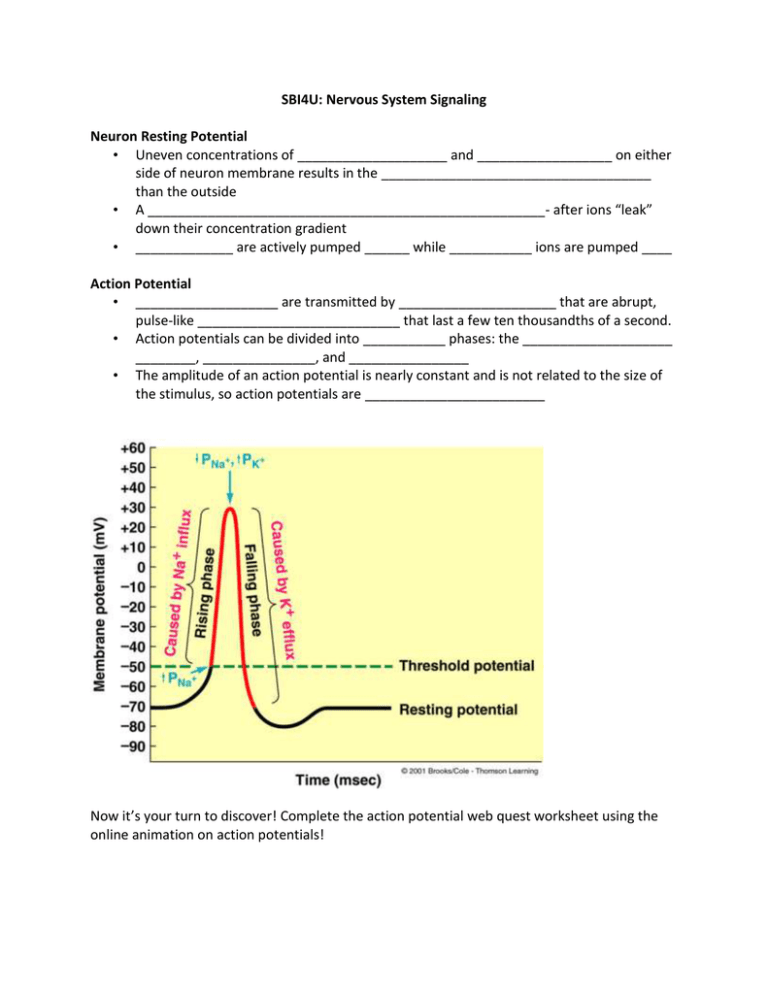
SBI4U: Nervous System Signaling Neuron Resting Potential • Uneven concentrations of ____________________ and __________________ on either side of neuron membrane results in the ____________________________________ than the outside • A _____________________________________________________- after ions “leak” down their concentration gradient • _____________ are actively pumped ______ while ___________ ions are pumped ____ Action Potential • ___________________ are transmitted by _____________________ that are abrupt, pulse-like ___________________________ that last a few ten thousandths of a second. • Action potentials can be divided into ___________ phases: the ____________________ ________, _______________, and ________________ • The amplitude of an action potential is nearly constant and is not related to the size of the stimulus, so action potentials are ________________________ Now it’s your turn to discover! Complete the action potential web quest worksheet using the online animation on action potentials! Terminology • Synapse – Region at which ___________________________________________________. (neuron or effector organ) • Synaptic Cleft – ___________________ (at a synapse) – Impulses can not propagate across a cleft • Synaptic Vesicle – __________________________ in _________________ neuron • Presynaptic Neuron – ___________________________ (before the synapse) • Postsynaptic Neuron – ____________________________ (after the synapse) Neurotransmitters 5 General Criteria: 1) _______________________________ 2) released at the nerve terminal in a 'chemically identifiable' form 3) the chemical should _________________________________________________ 4__________________________________ by competitive antagonist based on concentration 5) active mechanisms to stop the function of the neurotransmitter Classical transmitters _______________________________________________ Non-classical transmitters can be _____________________________________ 5 Steps of Neurotransmission 1) _____________________ of the neurotransmitter precursors and enzymes should be in the correct place 2) storage of neurotransmitter OR precursor ___________________________________________ 3) release of the neurotransmitter generally by vesicle fusion 4) binding to target receptor ionotropic receptors open ion channels metabotropic receptors modulate other signals 5) termination of the signal active termination caused by reuptake or chemical breakdown Using the website http://outreach.mcb.harvard.edu/animations/synaptic.swf answer the following questions: 1. After the action potential has traveled down the axon what signals the neurotransmitter vesicles to migrate toward the presynaptic membrane? 2. What happens to the post-synaptic neuron when neurotransmitter binds to the postsynaptic receptors? 3. What happens to neurotransmitters when they are released from the post-synaptic neuron receptors? Using the following website http://outreach.mcb.harvard.edu/animations/synapse.swf choose 2 drugs and explain what effect they have on synaptic transmission in your brain. Write an explanation for the 2 drugs in the space below.