L1.M1.PP.EcosystemNotes
advertisement

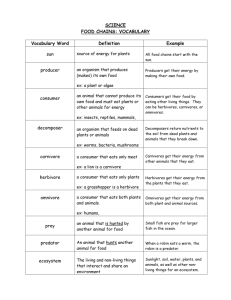
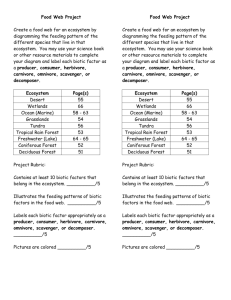
Level 1 Mission 1: Exploring the Ecosystem - Classifying Organisms Guided Notes Ecosystem Notes Mission Debrief In this video, you will… • Learn the key vocabulary and concepts you will need to beat level 1 • Use the vocabulary words to identify and classify organisms from around your landing site in the Deciduous Forest • Prepare for the Performance Task and ELITE Biome Exploration Project. Primary Learning Objective: Biologists will use scientific vocabulary words to classify biotic factors and explain how biotic factors interact with abiotic factors in an ecosystem. Evaluation: Vocabulary application and analysis multiple choice reading quiz about the deciduous forest. What is Biology • -ology means the study of • Bio- means life • Biology: The study of the life. As a biologist you will study the interaction among living things, and between living things and their environments. As an ecologist • You need to define the boundaries of discussion. – Which elements of the environment are included in your analysis and models. The Levels of Organization + Boundaries of conversation • • • • • • • • • • • Atoms Macromolecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ System Organism Population Community Ecosystem Biome What are the levels of organization? • Organism-An individual living thing: Example: Alligator • Population-A group of the same species that lives in one area Example: All the alligators in a swamp • Community-A group of different species that live together in one area Example: Groups of alligators, turtles, fish, plants, in the Everglades What are the levels of organization? • Ecosystem-Includes all of the organisms as well as the climate, soil, water, rocks, and other nonliving things in an area • Biome-Regions of the world with similar climate (weather and temp) and animals and plants • Wetlands/Swamps • Everglades This is a picture of beautiful forest near the landing site What is the boundary of discussion in a. Organism this photograph? b. c. d. e. Population Community Ecosystem Biome What is is ? • Biodiversity-The variety of living things in an ecosystem. • Large variety of species living together. – – – – Plants: Trees, bushes, grass, flowers Animals: Mammals, reptiles, amphibians, birds and fish Insects Bacteria • Biodiversity is important because the diversity in an ecosystem maintains its stability. – Stability means balanced. The populations don’t increase or decrease too much. There is enough of the right food for all the animals. The right molecules are in the air and water. Plants and animals develop traits and characteristics to maximize the use of other plants and animals in their environment. – All the different plants and animals play different roles to keep the ecosystem going Biotic Vs Abiotic Factor • Biotic Factor: Living organisms in an environment/ecosystem: Includes plants, animals, insects, and bacteria • Abiotic factor: Nonliving thing in an environment: Water (river, lakes, ocean), CARBON!!, dirt, rocks, wind, rain, sun, and climate • Both Biotic and Abiotic factors make up an ecosystem and biomes. Photograph A is a picture of your landing site in the deciduous forest. Photograph B is a picture of another ecosystem in the deciduous forest. Question: What important abiotic factor is within the boundaries of the ecosystem in photograph B, but missing from photograph A? a. Turkey b. Deer c. Air d. Water Photograph A Photograph B What Organisms are found in an ecosystem • Producer: Mostly plants! Organisms that take sunlight and produce food and sugar made out of carbon (photosynthesis!) • Consumer: An animal that eats plants or other animals to get their carbon in the form of sugar. The animal then breaks down the sugar to make energy. Consumers eat to get energy!!! • Predator: An animal that eats other animals • Prey: An animal that is eaten by other animals 6th Grade Review! Show me what you know! 1. Which organelle breaks down the sugar you eat to make energy for the cell? a. Nucleus b. Cell Membrane c. Mitochondria d. Golgi Apparatus e. Cell Wall f. Chloroplast g. Ribosome h. Endoplasmic Reticulum 6th Grade Review! Show me what you know! 2. Which organelle traps and uses the energy from sun to make sugar? Sugar is stored energy. a. Nucleus b. Cell Membrane c. Mitochondria d. Golgi Apparatus e. Cell Wall f. Chloroplast g. Ribosome h. Endoplasmic Reticulum Herbivore, omnivore, carnivore oh my! • • • • • Herbivores: Animals that only eat plants Omnivores: Animals that eat plants and animals Carnivore: Animals that eat other animals Insectivore: Animals that eat insects Decomposer: Breaks down dead and dying plants and animals Deciduous Forest Organism Identification You’re exploring the deciduous forest of planet Gorlox and encounter a deer eating berries. Classify this organism. a. Producer b. Herbivore c. Omnivore d. Carnivore e. Decomposer Deciduous Forest Organism Identification Watch out! You don’t want to get to close to the wolves while they eat. They are very territorial! Identify the organism a. Producer b. Herbivore c. Omnivore d. Carnivore e. Decomposer Deciduous Forest Organism Identification Woah, look at the blue fungus growing and feeding on the fallen tree. Not only is fungus important, it can look beautiful too. What is fungus? a. Producer b. Herbivore c. Omnivore d. Carnivore e. Decomposer Deciduous Forest Organism Identification You spot a bear up in the trees of the deciduous forest. Later, you watched a bird catch a fish from a lake. Classify this organism. a. Producer b. Herbivore c. Omnivore d. Carnivore e. Decomposer What are Decomposers • Decomposers eat and break down the remains of dead and dying plants and animal • VERY IMPORTANT ROLE IN THE FOOD CHAIN • Breaks the cells and tissues down into carbon • The left over, uneaten, animal and plant remains become nutrients in the soil that plants use to grow! What happens to the carbon in the bodies of animals that were decomposed? a. b. c. d. The carbon is released into the atmosphere The carbon is buried in the soil The carbon is burned as fossil fuels The carbon diffuses into the atmosphere Levels of Consumers in the forrest • Producer: Animal that produces sugar and food in the form of carbon: Plants! Producers start the food chain. • Primary Consumer: Herbivores that eat producers • Secondary consumer: Carnivores that eat Herbivores or primary consumers • Tertiary consumer: Animals that eat other carnivores. Eats secondary and/or tertiary consumers Food Chain Levels of Consumers • The chloroplast in the grass do photosynthesis to produce sugar and food made out of carbon! • The grasshopper is the primary consumer. Primary consumers are herbivores that eat the producer to get sugar and energy. The grasshopper eats the grass to get sugar and energy. The carnivore frog is the secondary consumer that eats the primary consumer. The Frog eats the grasshopper to get sugar and energy. The raccoon is the tertiary consumer that eats the secondary consumer. The raccoon eats the frog to get sugar and energy. The owl is a tertiary consumer as well because there is no level higher than tertiary and tertiary consumer eats carnivores. As you travel through the forest on planet Gorlox, you find a squirrel eating an acorn from a tree. You see a snake eat a squirrel. You watch a hawk swoop down and eat the snake. Correctly classify these organisms. Chipmunks that eat peanuts are a a. b. c. d. Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary Consumer A tree is a _________ a. b. c. d. Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary Consumer A snake that eats herbivores like chipmunks is a a. b. c. d. Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary Consumer Hawks that eat carnivores like snakes are a. b. c. d. Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary Consumer