Cells - K12Share
advertisement

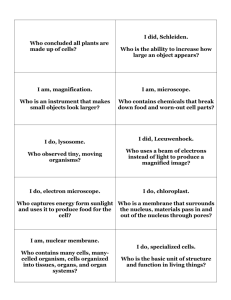
Friday, September 19th OBJ 1: State the parts of the cell theory. OBJ 2: Explain why cells are so small. OBJ 3: Calculate a cell’s surface-to-volume ratio. OBJ 4: List the advantages of being multicellular OBJ 5: Explain the difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Warm-up: When Hooke saw “juice” in some cells, what was he looking at? Why did Hooke think cells existed only in plants and fungi and not in animals? Homework: Read pages 4-8 and 9-15. Protein Deficiency presentations due 10/. *Microscope QUIZ on 9/25 Quick notes Microscope To Do Robert Hooke (1665) Cork Cells only in plants Anton van Leeuvenhoek (1673) Compared blood cells of fish, birds & frogs to that of humans & dogs Yeasts in bread = unicellular First Cells All organisms are composed of 1 or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. 3. All cells come from existing cells. 1. Cell Theory Cell membrane DNA Cytoplasm- jelly-like substance that protects organelles and provides an internal highway to transport materials. Organelles- structures INSIDE cells Small in size* Cell Similarities Cells need a larger surface area When cells grow, (as the volume increases) outer surface grows too!(but not as fast!) Surface Area to Volume Ratio Ability to grow larger without loosing its ability to get the materials for survival Specialized cells perform a variety of functions Benefits of Being Multicellular Does not have a nucleus also known as bacteria world’s smallest cells DNA is long, circular (like a rubber band) No membranes around their organelles Prokaryotic Cells Have a nucleus & many other membrane-covered organelles DNA stored in the nucleus (and there’s more of it!) May have a cell wall Cell divided into compartments Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic Eukaryotic No Nucleus Nucleus No Membranecovered organelles Membrane-covered organelles Circular DNA Linear DNA Bacteria All other cells http://www.brainpop.com/te chnology/scienceandindu stry/microscopes/ Label worksheet The Microscope Questions?! Conclusion Monday, September 22 OBJ 1-5. See previous notes/ slides. Warm-up: Complete SR on page 15. Homework: Study parts of the microscope and notes. Begin reading pages 16-24. *Protein Deficiency presentations due 10/. *Microscope QUIZ on 9/25 Finish notes Label parts of the microscope Movie Your Creatures! To Do… Label parts of the microscope. See the following PowerPoint's: 1-Microscopes 2- Parts of the microscope and their function The Microscope Microscopes in this lab are descendants of those made in the 1600s. Still use similar models- compound microscopes. Use 1 or more lenses to magnify objects. Light microscopes: use compound lenses and light. Lens bends or refracts light to make object larger. *See next slide for convex lens Intro to the Microscope: Facts Scanning electron microscopes (SEMs): use electrons (negatively charged electrical particles) to magnify objects up to two million times. *Used to view objects smaller than that which can be seen by light microscopes. Microscopes continued http://www.discoveryeducation.com/teachers /free-lesson-plans/virtual-electronmicroscope.cfm http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Swcz_TJ Mz0I http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9nUseN_ E-l0 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PMIU1fkI PQs How to prepare slides: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GHnndVu aync Virtual Tour Remember: how do we carry a microscope? TWO HANDS The SCOPE!! Review part of Microscope Conclusion Tuesday, September 23 OBJ 1-5. See previous notes/ slides. Warm-up: Microscopes continued: name the powers for each objective lens. Homework: Study parts of the microscope and notes. Continue reading pages 1624. *Protein Deficiency presentations due (TBA)*Microscope QUIZ on 9/25 Addition to microscope diagrams ◦ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PMIU1fkIPQs Movie Preparing slides ◦ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GHnndVuaync Your turn to try Parts of the microscope song- one more time! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Swcz_TJMz0I To Do… Can you name and describe two organelles you read about last night for homework? Conclusion Wednesday, September 24 OBJ 1-5. See previous notes/ slides. Warm-up: Microscopes continued: describe the difference between the fine adjustment knob and coarse adjustment knob. Homework: Review parts of the cell; finish packets. Microscope QUIZ tomorrow! Protein Deficiency presentations Movie Preparing slides ◦ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GHnndVuaync Parts of the microscope song- one more time! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Swcz_TJMz0I Notes: parts of the cell To Do… Can you name and describe two organelles you read about last night for homework? Conclusion Thursday, September 25 OBJ 1-5. See previous notes/ slides. OBJ 6: Explain the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell. Warm-up: Microscope Quiz Homework: Finish packet questions 6-10. Review day’s notes; POP QUIZ potential! Bibliography of your text book due tomorrow (use www.easybib.com). Diseases that lack protein project due 10/6. QUIZ Review: Cell Similarities Parts of the cell Explain lab: The Letter E-Lab To Do… Eyepiece Base Fine adjustment knob Stage Arm Revolving nose piece Body tube Stage clips Diaphragm Coarse adjustment knob Light source Low objective lens (x10) Medium objective lens (x40) High objective lens (x100) Word Bank Cell membrane DNA Cytoplasm- jelly-like substance that protects organelles and provides an Organelles- structures INSIDE cells Small in size* Cell Similarities Organelles: structures within the cell, sometimes surrounded by a membrane. When we talk about cells we need to know the appropriate WORDS! - Looking Inside Cells All cells are covered by a cell membrane Separates outside materials from inside materials Allows nutrients & waste products in & out Interacts with things outside the cell Cell Membrane 33 - Looking Inside Cells - Provides strength & support to the cell membrane of a PLANT cell Cell Wall 34 - Looking Inside Cells The nucleus is the cell’s control center, directing all of the cell’s activities. Nucleus 35 - Looking Inside Cells Mitochondria are known as the “powerhouses” of the cell because they convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use to carry out its functions. Mitochondrion 36 - Looking Inside Cells Is similar to the system of hallways in a building. Proteins and other materials move throughout the cell by way of these “hallways”. The spots on this organelle are ribosomes, which produce proteins. Endoplasmic Reticulum 37 - Looking Inside Cells Receives proteins and other newly formed materials from the endoplasmic reticulum, packages them, and distributes them to other parts of the cell. Golgi Body 38 - Looking Inside Cells Stores water, waste and other materials. Help support the cell. Vacuole 39 - Looking Inside Cells Digest food particles, wastes, cell parts, and foreign invaders ONLY in Animal cells Contain ENZYMES Lysosomes 40 - Looking Inside Cells Make food using the energy of sunlight In Plants ONLY Contain chlorophyll (makes cholorplasts GREEN) Energy is trapped by chlorophyll and is used to make sugar (aka photosynthesis) Sugar produced goes on to mitochondria Chloroplasts 41 1. Why is the cytoplasm important to the cell? 2. What do you think is the most important organelle to the cell? Justify your answer. Conclusion 42 Friday, September 26 OBJ 1-5. See previous notes/ slides. Warm-up: Section Review on page 23. Homework: Complete handout. Review day’s notes; POP QUIZ potential! SitN# 5 due 10/10. Disease prjt due 10/6 What would be the negative effects of a cell’s not having lysosomes? Add this question to your Section Review Explain homework Preparing slides Read through today’s lab Letter “E” lab To Do… Monday, September 29 OBJ 1-6. See previous notes/ slides. OBJ 7: Describe the difference between animal cells and plant cells. Warm-up: What is the difference between animal and plant cells? Homework: Finish (we will see how far we get!!) Letter “E” Lab questions (postponed until tomorrow). Review day’s notes; POP QUIZ potential! A/P cell QUIZ on Tuesday Check “How the Cell Operates” packet/ HW Preparing slides/ Read through today’s lab Letter “E” lab To Do… What happens to the projected image when it goes through the microscope? Why is it important to use the low power objective lens to focus instead of the high powered lens? Conclusion Tuesday, September 30 OBJ 1-7. See previous notes/ slides. Warm-up: What is the purpose of a bibliography? Homework: 1.) SitN# 5 due 10/10. Disease prjt due 10/6. SF due 10/1 Articles have been reviewed by scientists in a particular field ◦ These scientists have compared YOUR data with data from similar experiments to see if what YOU say makes sense Peer Reviewed A/P Quiz Letter “E” lab Science Fair STUFF! To Do… What happens to the projected image when it goes through the microscope? Why is it important to use the low power objective lens to focus instead of the high powered lens? Conclusion Wednesday, October 1 OBJ 1-7. See previous notes/ slides. TURN IN DRAFT BIBLIOGRAPHY Warm-up: What does a rigid cell wall allow a plant cell to do? Why is this important for the survival of a plant? Homework: TEST on 10/9; study all notes; SF Hypothesis/ Prediction due 10/8; SitN# 5 due 10/10 The Letter “E” lab Animal vs. Plant diagrams (OPTIONAL) GO: draw a plant cell & an animal cell (OPTIONAL) To Do… What happens to the projected image when it goes through the microscope? Why is it important to use the low power objective lens to focus instead of the high powered lens? The Letter E lab Complete the graphic organizer, filling out the function portion and checking whether the organelle is found in just plants, just animals, or both. OPTION: Once you are done, draw an animal cell & a plant cell on the back of your graphic organizer using colored pencils. Graphic Organizer Cell city ◦ Open to page 16 and make sure you have these terms written down ◦ These are the ONLY organelles you have to worry about ◦ Google Cell City – the first link should be the activity for today. (I will show you) Conclusion Think back to the microscope: if the high powered objective lens is in position and the focal view is blurry, what should you do? Explain. Thursday, October 2 OBJ 1-7. See previous notes/ slides. Warm-up: Take out animal and plant cell from yesterday. Homework: SitN# 5 due 10/10; SF Hypothesis/ Prediction due 10/8; TEST on 10/9; study all notes Plant and animal cell diagrams 2. Go over organelle functions 3. Venn Diagram/ handouts 4. G.O. of P & A cells 1. To Do… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Cell membrane Mitochondria Nucleolus Lysosome Chromosomes (chromatin) Golgi Body Cytoplasm Endoplasmic reticulum (Rough E.R.) Nucleus Ribosomes Centrioles (Animal cell ONLY) Vacuole Endoplasmic reticulum (Smooth E.R.) Parts of the Animal Cell 59 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Cell wall Golgi body Mitochondria Endoplasmic reticulum (Rough E.R.) Nucleolus Chromosomes (chromatin) Nucleus Cell membrane Chloroplast (Think Green!) Vacuole Ribosomes Mitochondria Endoplasmic reticulum (Smooth E.R.) Cytoplasm Parts of the Plant Cell 61 Create a triple Venn diagram Plant Cell Animal Cell Prokaryotes Cell wall Ribosome Endoplasmic reticulum Mitochondria Chloroplast Golgi Complex Vesicle Vacuole Lysosome Cytoplasm Organelles Nucleus Animal cell Plant Cell Bacteria Circular DNA Linear DNA No Nucleus Membrane coveredorganelles No membranecovered organelles 1. Why are cells so small? (hint: page 37 of text) 2. List two organelles plant cells have that animal cells do not? Conclusion Monday, October 6 & Tuesday, October 7 OBJ 1-7. See previous notes/ slides. Warm-up: Get ready for today’s lab Homework: Chapter Review pg 28 #1-13. TEST on 10/9. SF due 10/8. SitN# 5 due 10/10. QUEST on Thurs. 10/17 To Do… Lab Be sure to follow all safety instructions. Remember: iodine stains! Cheek and Onion cell lab What 5 characteristics of mitochondria suggest that they may have originated as bacteria? (See Book C, page 28) Conclusion Wednesday, October 8 OBJ 1-7. See previous notes/ slides. Warm-up: Turn in DRAFT Hypothesis/ Prediction (place in Science Bin) Classwork: Finish Lab and complete Ch. Review- pgs 28-29 #1622 Homework: Finish Lab questions- due tomorrow. SitN# 5 due 10/10. SF Materials, Procedures, Variables (with Plan of Analysis) and Number of Trials due 10/15. TEST tomorrow! Open to page 16 and take out your animal and plant cell diagrams. ◦ These are the organelles you have to worry about ◦ Google Cell City – the first link should be the activity for today. (I will show you) Cell City ◦ Name three organelles located in the animal cell, but not in the plant cell. What do these organelles do in the plant cell? ◦ What 5 characteristics of mitochondria suggest that they may have originated as bacteria? (See Book C, page 28) Conclusion Thursday, October 9 OBJ 1-7. See previous notes/ slides. Warm-up: Place lab in Science bin. Classwork: TEST right now! Homework: Read and take notes on text pages 34-37. *SF M, P, V (with plan) and T due 10/15 To Do… TEST Science Fair – do you have ANY questions! Let’s begin the next chapter Homework REMINDER! *SF M, P, V (with plan) & T due 10/15 *Review Science Fair calendar.