Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
advertisement

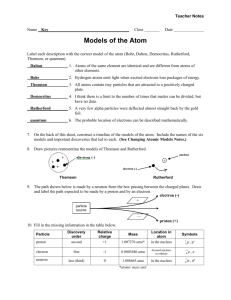
TOPIC: Atomic Theory – how the model of the atom has evolved and the scientists responsible Atomic Theory JJ Thomson Democratus 400 BC 1803 John Dalton 1904 Niels Bohr 1910 Ernest Rutherford 1913 1926 Schroedinger / Heisenberg The Complete Modern Atom An atom is: • mostly empty space • nucleus has most of mass of an atom • Atom is divisible • Protons (+1 charge) • Neutrons (no charge) • Electrons (-1 charge) • nucleus contains protons & neutrons • electrons are in energy levels around nucleus Here’s how we got there… It Started with the Greeks DEMOCRITUS • Lived in Greece 2500 years ago (460-370 BC) • “Father of modern science” • said: “All matter is made of atoms that are tiny, indestructible and indivisible.” Atoms are small… new rings old ring EVIDENCE: Old gold rings wear away slowly, getting thinner and thinner, but you never see gold atoms on your finger, so gold atoms must be very small! Liquids pour. Why? Liquids require a container If liquid atoms were like little balls they would roll out when you tip the container Greek idea of liquid atom Solids are rigid. Why? cocklebur plant Velcro® fastener cockleburs stick on clothing and each other Velcro hooks and loops little hooks on cockleburs Greek idea of solid atom Democritus (Greek) All matter is made of atoms that are tiny, indestructible, and indivisible (can’t be divided) Atomos Aristotle’s idea of matter Aristotle did not believe Democritus’s idea of atoms was correct Aristotle was more famous than Democritus, so people believed him, even though he was wrong! Aristotle believed all matter made from four elements: Earth Air (wind) Water Fire Aristotle Thought Democritus was wrong Matter made of 4 elements – Earth Sun Air Water Atom idea lost for ~2000 years John Dalton, New Atom,1803 Born in England, 1766 Studied chemistry, physics, and color blindness Brought back Democritus’s idea of an indivisible atom Color blindness Can you see a number in this gray box? If not, you may be color blind. (More males are color blind than females) Dalton’s Theory of Atoms Five parts to Dalton’s modern atomic theory: # 1: Elements are made of extremely small particles called atoms # 2: Atoms of given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements are different in size, mass, and other properties (found out not exactly correct) #3: Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed (later proved wrong) So Dalton’s atoms are kind of like billiard balls #4: Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form chemical compounds (H2O 2 Hydrogen :1 Oxygen) #4: Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form chemical compounds (H2O 2:1 ratio H:O) #5: In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated or rearranged 2H2O + 2Na 2NaOH + H2 #5: In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated or rearranged 2H2O 2H2 + O2 + + + Dalton’s Chemical Symbols We use different symbols today Dalton 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Atoms (tiny) Atoms of same element are identical * Indestructible * Combine in whole # ratio (H2O) In chem rxn. are combined, separated, rearranged *turned out to not be entirely be true Billard Ball J.J. Thomson English physicist (1856-1940) won Nobel Prize in 1906 Discovered the ELECTRON in 1897: -studied cathode rays using Crooke’s tube -showed atoms were divisible Crooke’s tube JJ Thomson’s discovery of the negatively charged electrons proved that atoms were divisible! Thomson’s “Plum pudding” atom – electron ENGLISH PLUM PUDDING – raisin JJ Thomson Discovered the Electron (first subatomic particle to be discovered) using cathode ray tubes Proved Dalton #3 to be wrong the atom is divisible! Plum Pudding Model Ernest Rutherford 1871-1937 • Discovered the proton in 1920 • Won Nobel Prize in chemistry in 1908 Discovered that most of mass of atom is in nucleus And the rest of the atom is empty space – GOLD FOIL EXPERIMENT Rutherford’s Experiment – 1911 Rutherford’s exp’t: animation Rutherford gold foil experiment Rutherford expected a particles to pass straight through, like this… What he found is that most did go straight through (so atom is mostly empty space), BUT a few a particles bounced back (Concluded there is a nucleus) Rutherford shot a particles, which have a positive charge, since they bounced back he concluded that the nucleus must have a _____________ Positive charge electrons (–) / nucleus / [protons (+)] The NUCLEAR atom model Rutherford -discovered the proton (+ charge) - Gold Foil Experiment - Atoms have a positive nucleus - Nucleus contain most of the mass - Atom is mostly empty space Nuclear Model + Chadwick - worked with Rutherford - Discovered the neutron Problem with Rutherford’s Model OPPOSITES ATTRACT: What prevents (-) electrons from being attracted to (+) nucleus, Niels Bohr 1885 - 1962 Bohr addressed the issue of electrons in the atom Nucleus surrounded by electrons orbiting at different energy levels Electrons have definite orbits Bohr’s new atomic model had quantized energy levels, meaning the electrons could only move by jumping between levels (numbered n = 1, n = 2, n = 3, etc.) Bohr - Electrons travel around the nucleus in orbits (shells) - Gain/Emit energy when moving from level to level Planetary Model e- ee- + e- Erwin Schrödinger Wave Model Austrian scientist (1887-1961) • won the Nobel Prize in physics in 1933 • calculated wave model of hydrogen atom in 1926 • also called cloud model, quantum mechanical model, modern model of the atom • atom model we still use today Electrons in probability zones called “orbitals”, not orbits - location cannot be pinpointed Electrons are particles & waves at same time Electrons move around nucleus at speed of light In Schrödinger’s wave model of atom, electron behaves as energy wave as well as a matter particle (Light also behaves as particle and wave) Einstein had predicted that energy and matter were related in his equation E = mc2 If we could see an electron it might look like this “cloud” Schrodinger - Electrons behave like waves - Not located in an exact orbit but rather a zone called an orbital - Orbital = probable location of electron Wave Mechanical (Cloud) Model = Modern Model The Complete Modern Atom An atom is: • mostly empty space • nucleus has most of mass of an atom • nucleus contains protons & neutrons • electrons are in energy levels around nucleus • electrons jump between levels, emitting and absorbing energy as jump