File - Filter my Water
advertisement

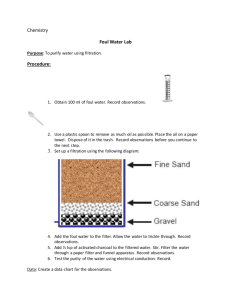
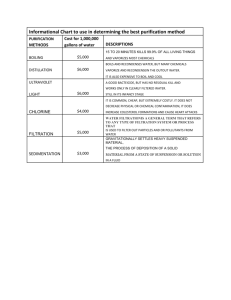
LESSON PLAN TEMPLATE Your Name: Miss McKenna Anderson Title of Lesson: Growing Old Thanks to Water Filters Grade: 8th Grade Time: 20-30 minutes STANDARDS NOTE: Please list at least two complete standards your lesson plan covers. [Common Core State Standards (math and language arts), Next Generation Science Standards (science), Arizona State Social Studies Standards (social studies)]. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RST.6-8.9 Compare and contrast the information gained from experiments, simulations, video, or multimedia sources with that gained from reading a text on the same topic. LESSON SUMMARY/OVERVIEW Provide an overview/synopsis of the lesson and the topics that it will cover. Make sure to provide a reason why you selected this to be relevant for a unit on sustainability? In this day's lesson the students will be introduced to early forms of water filters. To get them engaged the teacher will ask the students where they think water comes from. They will then be asked to brainstorm on how they think that our water gets cleaned and what systems are used in the process of cleaning the water. Once the students have their ideas the teacher will walk through the simple water filtering process with them: screening, coagulation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection. They will then go on to watch the video "How Does Water Get to Your Tap" that is attached below. During the video students are to look for the 5 steps and to write down a sentence about what happens at each stage. Some new vocabulary they will be exposed to will be: sieve, screen, coagulation, sedimentation, filtration, disinfection, slow-sand filters, rapid-sand filters, absorption, and ion exchanges. For their take home assignment students will be assigned an early form of water filters from the following website: http://www.historyofwaterfilters.com/. They will then research their topic to discover how these early forms used the 5 steps of water filtration to filter water. They will then present their findings to class the following day. As students study and learn about the history of water filters, they can see how far water filters have come and the importance of clean, fresh water. By focusing on Systems Thinking, students will be able to explore the different water filters and their systems and study the values of each of them in cleaning water. Ultimately in the last day of this unit students will experiment with their own water filters, creating their own water filter system and experimenting on which way and filter would be the most effective. OBJECTIVES Describe what you want students to know/be able to do as a result of the lesson. For example, “Students will be able to…” SWBAT identify early forms of water filters. SWBAT describe the five parts of water filtration. SWBAT understand how water is cleaned and filtered. SWBAT research on a given early water filter system discovering the 5 parts of water filtration within the system. SWBAT present their research to the class. ASSESSMENT/EVALUATION What measures will you use to know if you students met the objectives? Mastery requires that students stick to their assigned topic given and conduct thorough research on how they work and how the 5 parts of water filtration are involved in the system. Exceeds: the student stays on topic and thoroughly describes their system and how it works and how each of the 5 part of water filtration work within their system. Meets: the student stays on topic describing in vague and little detail how their system works and how each of the 5 parts of water filtration work within their system. Approaches: the student stays relatively on topic discussing their system but fails to mention one or all of the 5 parts of water filtration within their system and how their system works. Fails: the student isn’t on topic and doesn’t address their system or how it filters water regarding the 5 parts of water filtration. PREREQUISITE KNOWLEDGE What will students need to know prior to completing this lesson and how will you access their prior knowledge? Students will need to know why water filtration is so important and also how it works. The teacher will address these points by the day before presenting a lesson on what are water filters and an overview of how they work and why they matter. Then on the day of the lesson the teacher will review how water filtrations systems work and ask the students to brainstorm why they think we need clean water and how a system must work to filter water. They will then be asked to consider the different outcomes of the filtration systems and will access prior knowledge in applying Systems Thinking to their research and creative thinking. Students will also need to be familiar with the water filtration vocabulary that will be provided and given in the lesson the day before and in this day’s lesson as well. MATERIALS List of required materials. -Computer with Internet -Projector -Screen -Paper Pencils VOCABULARY/KEY WORDS List of key vocabulary terms. -Sieve: a utensil consisting of a wire or plastic mesh held in a frame, used for straining solids from liquids, for separating coarser from finer particles, or for reducing soft solids to a pulp. -Screen: a rigid or flexible screen to separate sand and other fine particles out of water for irrigation or industrial applications. -Coagulation: Treatment plant workers add alum and other chemicals to the water, which cause tiny sticky particles, or floc, to form. These floc attract dirt particles, making them eventually heavy enough to sink to the bottom of the water storage tank. -Sedimentation: the tendency for particles in suspension to settle out of the fluid in which they are entrained, and come to rest against a barrier. -Filtration: the action or process of filtering something. -Disinfection: To cleanse so as to destroy or prevent the growth of diseasecarrying microorganisms: disinfect a wound. -Slow-sand filters: are used in water purification for treating raw water to produce a potable product -Rapid-sand filters: The rapid sand filter or rapid gravity filter is a type of filter used in water purification and is commonly used in municipal drinking water facilities as part of a multiple-stage treatment system. -Absorption: the process or action by which one thing absorbs or is absorbed by another. -Ion Exchanges: is an exchange of ions between two electrolytes or between an electrolyte solution and a complex. TEACHING PROCEDURES Procedural Steps (Step by step instructions for teaching the lesson): 1. The teacher will begin the lesson by reviewing what the students learned in the lesson prior about what water filtration systems are and the 5 steps included in filtering water. 2. The teacher will then lead into today’s lesson by asking the students where they think water comes from? From what sources? The students will be engaged and brainstorm and share where they think water comes from. 3. The students will be encouraged to now take it a step farther and to work in their lab groups as the teacher asks them to think of how if we receive water from a lake, how would that water be cleaned so that we could drink it? 4. Once the students have their ideas, the teacher will walk through the simple water filtering process consisting of: screening, coagulation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection. 5. Once the 5 steps are reviewed the teacher will play a short video for them called “ How Does Water Get to Your Tap”. 6. During the video the students are to look for the 5 steps and to write down in a sentence what happens at each stage. They can also be offered the option of drawing a diagram of each stage. 7. After the video the class will be engaged in a class discussion of each of the steps that the teacher will lead. 8. From this discussion the teacher will ask the students to ponder on how in the 1700’s or even earlier, how do the students think that water was filtered? What resources did they have? What technologies were the able to use? 9. The teacher will talk about some of the early forms of water filters such as slow and rapid sand filters, boiling water, etc. 10. As the take home assignment the students will be assigned an early water filter offered on the website: http://www.historyofwaterfilters.com/ and be asked to do research on their assigned water filter and how the 5 steps of water filtration are used in the particular system. They will then be asked to present their findings in class the following day. RESOURCES List any references you used to create this lesson. If you borrowed ideas from any lesson plans please note them here. Use APA format. Water Works. (n.d.). Retrieved April 25, 2015, from http://waterworks-ursula.blogspot.com/2010/05/water-waste-and-usage.html Water Filtration Technology | Sawyer. (n.d.). Retrieved May 1, 2015, from https://sawyer.com/technology/water-filtration Water Filtration Technology. (n.d.). Retrieved May 1, 2015, from http://www.amiad.com/technology.asp Types of Filters. (n.d.). Retrieved May 1, 2015, from http://water.me.vccs.edu/concepts/filters.html WAYS OF THINKING CONNECTION Provide a complete explanation of how your lesson plan connects to futures, system, strategic, or values thinking. Define the way of thinking you selected and used in this lesson plan. Remember, this should be included meaningfully in the lesson plan. Values and Systems Thinking are embedded in this lesson plan and throughout the lesson unit. Values Thinking invites the students to examine the effects of their decisions and how they influence their values (for example in this unit with how they value water and how if they see it as a precious resource or not). Also students can not only explore their own personal values but also the values of others and other companies as well. Systems Thinking encourages the students to look at the whole process of water filtration rather than just one part and to examine the outcomes. As students come to better understand the system, the water filter, they will be able to better understand how they work. As students come to recognize how these systems work they will also be able to see the leverage points that lead to the desired outcomes within each of these systems. It helps the students to see how a small personal water filter that they would take out hiking, and a huge massive water filter that cleans the cities waste water are interconnected and work together to reach the same end result.