Vegetables
advertisement

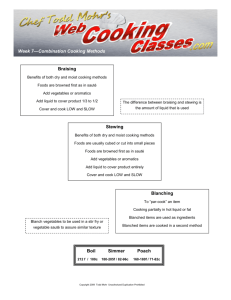
Vegetables © PDST Home Economics Classification Roots Greens Fruit veg. Pulses Carrots Parsnips Onions Potato Turnips Cabbage Broccoli Lettuce Brussel sprouts Tomato Peppers Cucumber Courgettes Marrow Peas Beans Lentils Root vegetables Green vegetables Fruit vegetables Pulse Vegetables / Legumes In Season Some vegetables are only available fresh at certain times of the year i.e. when they are in ‘season’. When out of season they are available frozen, dried, canned. Average Composition Veg Protein Fat Carb Vits Mins Roots 1-2% 0% 5-20% A, C Calcium Iron 70-90% Greens 0% 0% 5-10% A, C Calcium Iron Potassium 90-95% Fruit 1% 0% 2-5% Calcium Iron 90-95% Pulses 2-5% 0% 4-10% A, C Calcium Iron Potassium 75-90% A, C Water Nutritive Value / Food Value All veg. contain a lot of water to prevent dehydration in the body. Not a good source of protein – soya are pulses that contain HBV protein for growth. Lack fat, often add during cooking. Good source of fibre for healthy digestive system, some starch and sugar for energy. Vitamin C for general health and Vitamin A for skin, eyes, growth, membranes. Calcium for bones and teeth Iron for the blood Potassium for nerves and muscles Value in the diet / Dietetic Value Add colour, flavour, texture to diet. Good source of vitamins and minerals. Good source fibre for healthy digestive system Pulses are cheap source protein, important for vegans Low in calories, good for low calorie diets. Eaten raw or al dente. Potatoes, high in starch, good for energy. Fresh vegetables cheap & plentiful in season. Also available frozen, canned, dried. EU Grading of Vegetables Vegetables must be: sound, clean, chemical free, graded by size. Labels must show: Quality, origin, variety. Class Extra best quality Class I good quality Class II marketable, small defect Class III marketable but poorer quality Prices depend on: availability, demand, weather, quality, production cost Organic vegetables are grown without artificial fertilisers or chemicals Roots Buying Storing Preparing Heavy for size Correct colour Hard, no bruises Medium size No excess soil Remove plastic bags. Store openly in a veg rack in cool dry ventilated place. Wash in cold water. Top, tail, peel thinly. Remove any damaged parts. Leave whole, slice or dice. Store in salad drawer of fridge. Lettuce: wash, dry, store in a sealed plastic bag in fridge Remove withered leaves Pull leaves apart Cut up if necessary Wash under cold running water Greens Crisp Firm, closely packed heads Not eaten by slugs or insects Buying Storing Preparing Fruits Correct colour No bruising No discolour or mould Medium size Store in cool dark place or salad drawer of fridge Wash under cold running water Remove any inedible parts Leave whole, slice, dice Pulses Firm green pods. Heavy for size Not shrivelled or discoloured Pods full but not bulging. Can be stored for a few days in a sealed container in a cold place Remove pods just before cooking. Wash well in cold water Effect of cooking on vegetables Loss of vitamin C so eat raw if possible The starch cooks and becomes digestible The cellulose softens and the texture softens Some vegetables absorb water and swell Minerals dissolve into cooking water Vegetables loose colour and flavour so cook for shortest possible time To retain maximum nutrition Preparation Cooking Use fresh vegetables Put into boiling salted Eat raw when possible water Prepare just before cooking Do not add bread soda Wash in cold running water Cook quickly in smallest possible amount of water Do not steep Leave skin on or peel thinly Cover with lid Use cooking liquid in gravy, Cut up as little as possible Use sharp knife for chopping sauce, soup. Serving Serve as quickly as possible Preservation of vegetables Method Examples Advantages Disadvantages Frozen Peas . Broccoli. Green beans. Sweetcorn. Nutritionally as good as fresh vegetables. Good colour, flavour, texture. No prep. or waste. Cook quickly. Expensive. Must be stored in a freezer or frozen food compartment. Dried Tomatoes Chick peas Soya beans Lentils Relatively cheap. Loss of vitamins. Must be steeped . Longer cooking needed. Poor texture and colour. Canned Beans Peas Sweetcorn Tomatoes Cheap. Only need reheating. No prep. needed. Loss of vitamin C. Minerals dissolve into canning liquid. May contain colourings.