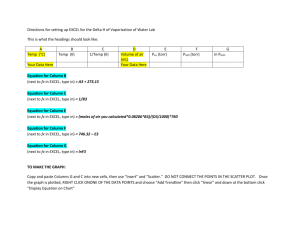
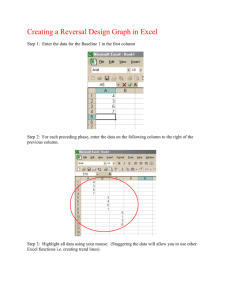
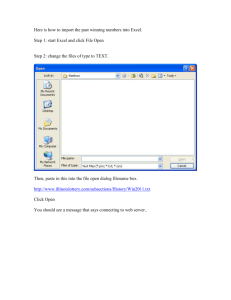
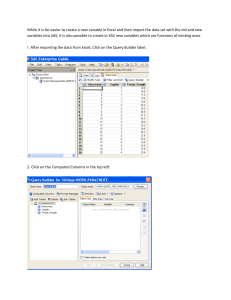
BACKUPCIS120UPDATED
advertisement

GOOD LUCK! Final Exam Topics Unit 1 Chapter 1-6 questions and answers Unit 1 Matching Chapters 1-6 Unit 1 Skill Drill Chapters 1,3 and 4 Unit 1 Related Skills Chapter 1,2,3 Unit 1 Chapter 3 Platforms Unit 2 Chapter 1-10 questions and answers Unit 2 Matching Chapter 1,2,3,6,7,8 Unit 2 Key Terms Chapter 4, 7,8,9 Unit 3 Chapter 1-6 questions and answers Unit 3 Matching Chapters 4 and 5 Excel Notes Notes Important Definitions ATTENTION...FINAL EXAM TOPICS: Per Peter...study the layout of excel, chart tools, format, format selection etc. Vertical Access Title...is the area you know where the hot dog is in the most recent excel sheet we did...that's the vertical access title) and then don't forget about the current selection box in the upper left corner. Remember let's say you clicked on the vertical access bar...well if you look in the upper left corner in the current selection box it will say you are in the vertical access title. Just an FYI Objective Test Questions o All questions from your book’s end of chapter questions o All questions that have been on any quiz this term Word o Any skills practiced in your homework with Word o Any skills practiced in class with Word o Pay particular attention to: Headers / footers with page numbers...see right below! INSTRUCT: insert tab, header, blank three columns and now will show the three text place holders...click inside and type or simply hit delete is don't want. Footer...repeat the same process but in the footer area. Page numbers...see right below! INSTRUCT: Click page # on the header and footer tools design ribbon, current position, click plain number, type out the world page in front, type the word of after the 1, go up to quick parts, choose field option, click numpages and under format click none and then click ok Footnotes...see right below! INSTRUCT: Commands for inserting and editing footnotes and endnotes can be found on the References tab in the Footnotes group. On the References tab, in the Footnotes group, click Insert Footnote or Insert Endnote. Word inserts the note reference mark and places the insertion point in the text area of the new footnote or endnote. Keyboard shortcut To insert a footnote, press CTRL+ALT+F. To insert an endnote, press CTRL+ALT+D. By default, Word places footnotes at the end of each page and endnotes at the end of the document. Placing graphics, resizing, cropping Margins (come on now, this one is easy) INSTRUCT: Using per-defined settings-1) On the Page Layout tab, in the Page Setup group, click Margins. The Margins gallery appears, now click the margin type that you want to apply. 2) Create custom page margin settings. On the Page Layout tab, in the Page Setup group, click Margins. The Margins gallery appears. Enter new values for the margins. At the bottom of the Margins gallery, click Custom Margins. The Page Setup dialog box appears. Borders (paragraph, page, table cells) Paragraph formatting (line spacing, indents, space before/after etc.) Working with a Table (row/column size, borders/shading) Excel o o o Any skills practiced in your homework with Excel Any skills practiced in class with Excel Pay particular attention to: Using absolute and relative cell references appropriately Appropriate use of the Auto Fill capability of Excel Using spreadsheet functions such as: PMT...INSTRUCT: Formula tab, FX insert function, enter calculate payment or click pmt either way is fine, ok, now the function argument dialog box appears,in rate enter 3.5%/12 (because we are making monthly payments) in Nper enter (total # of payments which we plan to pay for it for 3 years which equals) 36 months so enter 36, in PV (present value) enter 3500 which is the amount we have finances and click ok. You should get ($102.56) which the red and the parenthesis mean negative because it's money going out. If you don't want it red or show as a negative simply type a - between the = and the p like this.....=-PMT and it should come out as a positive. SUM, MAX, MIN, AVERAGE IF, VLOOKUP RANDBETWEEN...example to remind us: Click FX, click RANDBETWEEN, click ok, in bottom type in 1, in top type in 100, click ok, now grab the bottom right corner of the cell that shows the black cross and drag it down to row 10 within the same column, enter and your done! This shows you random numbers between 1 and 100. I picked these numbers to provide us an example on a how to. :) Basic charting: Line chart, pie chart, bar chart Formatting a chart Selecting data correctly to create a chart (line spacing, paragraph spacing, data from excel to past in a word doc) Working with data (records and fields): Sorting data (ascending or descending)....example of this is the Nascar we did in class Filtering data to find records meeting some criteria Remember—Data tables have the field names in the first row and when sorting/filtering the current cell should always be A Basic File Management o Saving files, opening files o Create folders, move folders, copy folders o Create zip archives Basic Web Browser Usage o Entering URLs, basic Google search, copy text or graphic UNIT 1 Questions and Answers! Added....................Chapter-1 Added....................Chapter-2 Added....................Chapter-3 Added....................Chapter-4 Added....................Chapter-5 Added....................Chapter-6 Unit 1 Chapter 1 Questions and Answers 1. A desktop computer could also be referred to as which of the following alternative terms? B, personal computer, Mac, or microcomputer 2. The main difference between memory and storage is? A, storage has more capacity than memory but is usually slower, cheaper, and retains data when the computer is turned off. 3. Which of the following lists of SI prefixes is in order from smallest to largest? D, kilo, mega, giga, tera 4. Which of the following is used to store the initial programming that is used to start the computer when it is first turned on? C, ROM 5. Supercomputers are best for which of the following problems? C, designing and simulating complex systems...see p.11 6. Which of the following is true of read only memory (ROM) A, It is non-volatile. 7. ROM stands for which of the following? A. read only memory...see p. 17 8. What is the relationship between a byte and a bit? D, a byte is a unit of data 8 bits long 9. Booting a computer refers to what stage of the flow of information in a computer? A, start-up of the computer 10. Which of the following is NOT a reason to share resources on a network? B, to allow each worker to function independently...see p. 31 Unit 1 Chapter 2 Questions and Answers 1. Which of the following has the largest storage capacity? A, DVD-can hold 4700 megabytes on a single sided single layer disc and up to 17 gigabytes on a double sided double layer disc. 2. Which of the following is optical storage media? A, DVD-R see p. 54 3. Which of the following is not a common input device? C, Voice synthesizer see p. 66 4. Which of the following is a specialized input device? C, scanner 5. Which type of scanner can be used to scan books and magazines? D, flat bed 6. Which of the following is used in conjunction with a database for pricing and inventory control? B, car code reader...see definition! 7. Which of the following can print very large diagrams but not photographs? A, pen plotter 8. The brightness of projector devices is rated in which of the following units? C, Lumens 9. Computer peripherals such as printers and scanners that do not use a wireless connection need to be plugged into which of the following? C, port 10. Which of the following is a program that works with the operating system to manage a device? Driver Unit 1 Chapter 3 Questions and Answers 1. Which of the following is the least important criterion for selecting a personal computer? C, ability to run new software in five years 2. Which of the following is likely to be the most restrictive performance factor when you are using the internet? A, connection speed 3. Which of the following are types of low cost computer software? B, Freeware, shareware, student discount 4. Which of the following protects your computer from pulses of higher than normal electric voltage? B, surge suppressor 5. A device with a battery that continues to supply constant power even during brownouts or power outages? C, Uninterrupted power supply (UPS) 6. Which of the following refers to a maintenance problem that is not caused by dirt or dust accumulations? Disk fragmentation 7. Which part of a hard disk moves the fastest past the read and write heads and therefore is the most desirable locations for commonly used files? A, outer edge 8. If nothing happens when you turn on the computer or a device, what should you check first? D, Supply of power 9. Which of the following should NOT be considered when you need to dispose of an old computer? A, take the computer to a landfill. 10. A relatively easy fix for many software and hardware problems is which of the following? C, turn off and restart the computer Unit 1 Chapter 4 Questions and Answers 1. Database information is stored in which of the following? D, tables 2. Fixing a software problem is often called which of the following? C, Debugging 3. A person who uses early versions of software during the development process to find errors is which of the following? C, Beta tester 4. Which of the following software changes usually cost money? B, upgrade 5. Which of the following is most likely to be a benefit of an upgrade? A, new features 6. Which of the following types of software would be appropriate for keeping monthly customer bill payment records at a credit card company? D, database...see p. 153 7. Which of the following types of software would be appropriate for writing a memo? A, word processing 8. Which of the following types of software would be appropriate for accounting? B, spreadsheet 9. Which of the following types of software would be appropriate for communicating ideas at a meeting? C, presentation 10. Which of the following is a common mistake in matching the correct software to a task? B, using a table in a word processing software to analyze financial information with calculations. Unit 1 Chapter 5 Questions and Answers 1. Which of the following is not an operating system? A, GUI 2. Which of the following operating systems has a text based user interface? C,DOS 3. Which of the following is NOT a limitation imposed by an operating system on file names?...best guess is…C. Spaces used in file names (windows) 4. Which of the following is a method of returning the operating system to earlier default settings? D, System restore 5. Which category of user has the most control of the operating system? C,Administrator 6. Which category in the control panel contains the options for changing the screen resolution? A, Appearance and personalization 7. The system clock will probably need to be reset when which of the following occurs? C,Daylight saving time changes. 8. Which of the following can be set to display automatically when the computer has not been used for a while? B,Screensaver 9. Which of the following is not a method for installing or uninstalling software? D,Copy and paste the installed program files from another computer. 10. If you cannot download a program from the internet that you want to install, what is the most likely source of the problem? A,Security software is blocking the download of an executable file. Unit 1 Chapter 6 Questions and Answers 1. The section of the taskbar that displays icons for programs that are running in the background is called which of the following? D,Notification area 2. The title bar button that changes names depending on the present size of the window can have which of the following pairs of names? B, Maximize/Restore Down PER PETER!! 3. Which of the following commands from the shut down menu will often solve problems by closing and opening programs? C,Restart 4. If two files are open at the same time, you can switch between the windows for each file by clicking or pressing which of the following? B,Click the programs button on the quick launch bar. 5. Which of the following is not a good use of a desktop icon? B,To make a backup copy of all world processing files 6. The view in the computer window that displays a list view and can show the size of the file and the date it was last changed is which of the following? A,Details. 7. When you display the files in the content pane as large icons, which type of icons display? C,GUI 8. When you restore a folder from the recycle bin…B,The folder and all of its contents are restored to the original location. 9. You can recover deleted files from the recycle bin from which type of device? D,Hard Drive 10. To reduce the potential for problems if you expect a file to be used on Linux or UNIX operating systems, it is a good idea to avoid use of which characters in file name? A,Space UNIT 1 MATCHING! Added....................Chapter-1 Added....................Chapter-2 Added....................Chapter-3 Added....................Chapter-4 Added....................Chapter-5 Added....................Chapter-6 MATCHING: UNIT 1 CHAPTER 1 1. Touch pad: A pointing device commonly used on a laptop computer 2. UNIX: A popular operating system on a mainframe computer; a version called Linux is used on some personal computers 3. Modeling: Using formulas to simulate the behavior of real systems 4. Integrated Circuit: Arrays of transistors and other electronic devices 5. Algorithm: A set of instructions that a computer can follow to accomplish a task 6. Gigabyte: Approximately one billion bytes 7. Binary: A numbering system that uses only zeros and ones 8. Analog to digital: Converts music to a file a computer can read 9. Pixel: A picture element that displays as a dot on a computer monitor 10. Distributed Processing: Dividing a task into component parts that can be processed on multiple computers. MATCHING: UNIT 1 CHAPTER 2 1. Toner: Powdered ink used in a laser printer 2. Digital light processing (DLP): A projector technology that uses thousands of tiny mirrors. 3. Resolution: The number of pixels displayed per inch on a screen 4. Backlight: The fluorescent light behind a plat panel monitor 5. Optical Mouse: A common pointing device that uses reflected light instead of rollers 6. Bluetooth: Wireless standard often used for cell phone hands free headsets and for MP3 player headphones 7. Flat Panel: An LCD display 8. Probe: A sensor used to explore places that are not conveniently accessible 9. Flash Drive: Type of storage device that does not need constant power 10. Plug and Play: A feature that enables you to install peripheral devices without having an installation disc. MATCHING: UNIT 1 CHAPTER 3 1. Backward compatibility: The ability of a newer version of a program to open and display files that were created using an earlier version of the program. 2. Blue-ray: DVD technology that enables you to save 25 GB on a single-layer disc and 50 GB on a dual-layer disc. 3. Defragmenting: Rearranging data on a hard disk so that files are written on adjacent sectors. 4. Linux: Derivative of Unix, which is free and open source. 5. Open Source: The source code for software that is available to anyone. 6. Quad-core: A multi core processor with four processors. 7. Response Time: The amount of time it takes to change the color of a pixel on an LCD monitor. 8. S-Video Port: Port on the video card that enables you to connect your computer to cable and view television programs. 9. Shareware: Software that can be used for a trial period but must be paid for if used regularly. 10. : Virtual memory: Space on a hard disk used to supplement physical memory. MATCHING: UNIT 1 CHAPTER 4 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Blog: A web log Debugging: The process of identifying and fixing errors in program code. Filter: To display only the information the meets your criteria. Function: In a spreadsheet, a built in formula. Primary Key Field: In a database, the field with unique values. RTM: The end version of beta testing that gets sent to the manufacturer. Slide Master: In a presentation, the place where default fonts, colors, and backgrounds are identified. 8. Suite: A group of different programs bundled together. 9. Update: A minor change to software that is usually free. 10. WAV: A type of uncompressed sound file. MATCHING: UNIT 1 CHAPTER 5 1. Restore Point: A representation of the state of your computers system files at a particular point in time. 2. File Extension: The letters following the period in a file name. 3. Control Panel: A group of programs that manages system settings in the windows operating system. 4. XML: A language used to store files as simple text along with information on how the application software would interpret that text. 5. GUI: Includes screen elements such as dialog boxes, windows, toolbars, icons, and menus, and displays a document on screen the same way it will look when printed. 6. System Clock: A time of day device included with the operating system, which can be set for different time zones. 7. DOS: An operating system with a text based user interface. 8. 8.3 Convention: A way of naming files that includes a file name and a file extension. 9. Administrator: A person who has the right to change computer settings and install and remove software. 10. System Restore: A feature that enables you to undo changes to the operating system back to one of the previous states. MATCHING: UNIT 1 CHAPTER 6 1. Quick launch toolbar: An area to the right of the start button that contains shortcut icons for commonly used programs. 2. Log off: Command from the shut down menu that enables a person to leave the computer and close all personal settings. 3. Windows Sidebar: Small program such as a currency converter, a calendar, or a clock that displays in the windows sidebar. 4. Restore down: Process or button that reduces the size of a maximized window. 5. Gadget: An area on the side of the screen that displays gadgets with information that you want to access quickly 6. Scroll box: Located in the scroll bar, it can be used to drag a work area up and down or left and right. 7. Notification area: An area on the right side of the taskbar that keeps you informed about processes that are running in the background. 8. Lock mode: Command from the shut down menu that enables a person who wants to leave the computer for a little while without logging off to come back to his or her own personal settings. 9. Sleep Mode: Command from the shut down menu that shuts down nearly all of the power to the computer but keeps power to the CPU and to RAM, while greatly reducing energy consumption. 10. Read only: A file that can be opened and read but not edited. UNIT 1 SKILL DRILL! Added....................Chapter-1 Added....................Chapter-3 Added....................Chapter-4 UNIT 1 CHAPTER 1 SKILL DRILL 1. page 37-38 Finding storage capacity of a folder in your hard drive: Start Computer Click the arrow next to music Right click on public music Click properties UNIT 1 CHAPTER 3 SKILL DRILL #1 page 129 Deleting web pages from the Cache: Start Internet explorer Tools Internet options General tab Browsing history Delete Settings Browsing history make sure the disk space to use spin arrow to change the disk space to use to 200MB. UNIT 1 CHAPTER 3 SKILL DRILL #3 page 131 Using Disk Cleanup: Start All programs Accessories System tools Disk cleanup UNIT 1 CHAPTER 4 SKILL DRILL 1. 1 page 167 Learning about the Microsoft Office Live Workspace Go to your browser and enter www.microsoft.com/officelive Enter Under office live workspace, click learn more link and read about the program! UNIT 1 CHAPTER 4 DISCOVER #2 page 169 Learning about audio compression Go to your browser and enter www.learnthenet.com/english/html/34filext.htm Wikipedia Howstuffworks.com UNIT 1 RELATED SKILLS! Added....................Chapter-1 Added....................Chapter-2 Added....................Chapter-3 UNIT 1 CHAPTER 1 RELATED SKILLS 1 page 41 (processor) Determining the processor, clock speed, and RAM: Start Control panel Security and system System Performance information and tools View and print detailed performance and system information Now locate the processor clock speed….. Advanced tools View advanced system details in system information Find the processor and located the processor clock speed. UNIT 1 CHAPTER 2 RELATED SKILLS #2 on page 83, mouse. Adding mouse trail to the pointer. Start Control panel Appearance and personalization Personalization Pointer options Under visibility, check mark display pointer trails and then click ok. UNIT 1 CHAPTER 2 RELATED SKILLS #3 on page 84, resolution. Trying different screen resolutions on the monitor. Start Control panel Hardware and sounds Appearance and personalization Display Adjust resolution Apply UNIT 1 CHAPTER 3 RELATED SKILLS Checking out Free Antivirus Software Go to free.avg.com Or just simply go to Microsoft essentials .com instead!!! UNIT 1 CHAPTER 3 PLATFORMS There are 3 Platforms currently in use for pc’s: 1. Windows 2. Mac (operating system from Apple Corp) 3. Linux (operating system is free and the code is open source) Binary numbers that consist of zeros and ones. Each digit of the number is called a bit. The unit of data a processor can work with is called a word. The size word, is also called a byte and 8 bits = a word byte. Today….PC’S have processor that use 32 bit or even 64 bit words! Inside ones system unit is the hard drive. It’s a complete unit with devices known as heads that can read and write data in magnetic form on a stack of thin rigid metal disks called hard disks. Five criteria’s for choosing a platform: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Application software requirements Cross platform compatibility Backward compatibility Availability of drivers for peripherals Cost! For detail into go to pages 92. UNIT 2 Questions and Answers! Added .................... Chapter-1 Added......................Chapter-2 Added .................... Chapter-3 Added .................... Chapter-4 Added......................Chapter-5 Brian Added .................... Chapter-6 Fred & Christy Added .....................Chapter-7 Added .................... Chapter-8 Added .................... Chapter-9 Added......................Chapter-10 Unit 2 Chapter 1 Questions and Answers 1. In Microsoft office 2007 applications, groups of buttons that display commands used in applications are found on the ? B,RIBBON! 2. To switch between open applications, click the related button on the? D, TASKBAR at bottom of screen see p. 9 3. To open a file from within an application, click the button? C,OPEN! 4. To display the top of the document, you can do all of the following…EXCEPT? C, click the home tab on the ribbon 5. To change the magnification of a document from 80% to 100%? D, On the zoom bar, click the zoom in button twice! 6. To correct spelling errors in your document? C,Use the spelling and grammar dialog box to review and correct both grammar and spelling errors! 7. When you cut or copy text or images, they are stored in a temporary storage location know as the? A, office clipboard 8. Some buttons include a list or gallery of possible results that displays the change to selected text or an image using live technology? B, PREVIEW! 9. To immediately reverse an action, click the ___button? A, Undo 10. In the print window, you can A, do all of the following THIS QUESTION IS FROM 2010 BOOK.... 11. In the print dialog box, you can do all of the following except...C, change the default printer Unit 2 Chapter 2 Questions and Answers 1. To move an image around on a document, you need to change the ? B, text wrapping or format settings 2. Use a numbered list for all of the following except items that are listed? A, randomly 3. Examples of a serif font include? C, Courier, Times New Roman, Cambria 4. The difference between indent and alignment is? D, Indent is used to move text in from the left or right margin, and alignment lines up text at the margins 5. You may add graphics in all of the following circumstances except to? D, provide information 6. Digital images should be resized and cropped to? A, make the image fit in the available space 7. When you need to create lists of parallel information, use a? A, table 8. To create a table, you can.... D, Do any of the above? 9. To display the file name and author on every page of a document, use the? C, header and footer 10. All of the following are true about using a template except? A, templates can only be used once Unit 2 Chapter 3 Questions and Answers 1. To check for style such as passive voice change the_options in the _dialog box? C, Writing Style, Word Options 2. To automatically correct a frequently mistyped word use the dialog box, which is accessed from the pane in the word options dialog box. B, Auto Correct, Proofing. 3. To import text from another document, use the _button found on the _tab? A, Object, insert 4. Which of the following is a paragraph style in which the first line of a paragraph extends to the right of the rest of the paragraph? A, First line indent 5. In addition to paragraph styles, what other styles are available in word? A, Text styles! 6. Words that are underlined indicate...... possible incorrect word usage? D, Blue! 7. A reference in a document to the source of information is a _? C, Citation! 8. The keyboard shortcut to insert a page break is_? B, Ctrl+enter 9. Which of the following is a paragraph style in which the first line of a paragraph extends to the left of the rest of the paragraph? B, Hanging indent! 10. The paper size used by the ISO 216 standard that is comparable to the 8.5 X 11 standard letter size used in the United States and Canada is_ADV? D, A4! Unit 2 Chapter 4 Questions and Answers 1. In a word document, the default margin settings are? 1 inch on all sides 2. To include data from Excel in a Word document so that it does not display as a table, used the Paste Special command and choose? Unformatted text. 3. When you format a document with multiple columns, you can do all of the following except? Display the line between the columns. 4. The best way to edit a template is to? Open word, and then open the .dotx file from the Open dialog box 5. To repeat a format that was just applied to another area, use the? Repeat the format button. 6. To insert a manual line break, press? Shift + Enter 7. The tab button displays all of the following stops except the? Right indent. 8. To display the tab dialog box? Double click a tab stop on the ruler. 9. You can save a word document in any of the following file formats except? .mht. 10. To save a word document as a web page from the save as type box, choose? A, single file web page (2010) Unit 2 Chapter 5 Questions and Answers! Thanks Brian 1. When track changes is enabled, it records changes made to? d, all of the above 2. Tracked changes and comments are numbered? A, sequentially from the beginning of the document 3. To hide the changes that have been made on the screen, change the display for review box to? C, final 4. Tracked changes are displayed on the screen in? D, all of the above 5. To change the user name and initials in the word options dialog box, display the ? page...B, general (2010 book) (2007 book B, popular) 6. To organize the data used in a mail merge, sort the data in?...A, the edit recipient list dialog box 7. A data source can be information that is stored in?...D, all of the above 8. To control who has access to a document and what they can do, display the prepare menu and select the? C, restrict editing (2010 book) (2007 book c, restrict permission) 9. When data in merged with a letter using the edit individual documents command, it displays all the letters in one document with ? between each letter? D, no break 10. To set up labels for printing, you need to know the? C, brand and product number of the labels Unit 2 Chapter 6 Questions and Answers Fred and Christy Thanks! 1. In excel, a spreadsheet is called a? (Brian and Jennifer say it's A...workbook) (Philip, Fred and Christy say its Worksheets) so take your pick:) 2. If ten rows of data and labels are placed in columns, the labels should be? the data? C, to the left of 3. If the number 4311.50 is estimated to the nearest 100 dollars, it would display as? D, $4,300 4. If accounting number format is used to display currency with dollar signs, the format that right aligns with it by default is? format? (Brian and Jennifer say it's C, Number Style) (Philip, Christy and Fred say it's A, comma style) 5. To ensure that a date is not misunderstood by someone from another country, the best format to use is? C, august 5, 2010 6. Rules that instruct excel how to execute a function are called? B, arguments 7. The Greek letter that often represents summation is? D, sigma 8. The lines between cells that display on screen but not in printouts by default are called? A, grid lines 9. The label at the top of a column of data is called a? B, header 10. The row numbers and the column letters are called? A, headings Unit 2 Chapter 7 Questions and Answers If the six cells in the range B3-B8 have the content 5,6,3 empty, 8 and 10 the count function would display? 5 If the six cells in the range B:3:B8 have the content 5,6,3, empty, 8 and 10, and the MIN function would display ? 3 If the six cells in the range B3:B8 have the content 5,63, empty, 8, and 10, the MAX function would display? 10 Given six cells in the range B3:B8 that have the content 5,6,3 empty, 8, and 10, if the function in cell B8 is =SUM(B3:B8), the display would be? 32 A formula with an absolute reference to cell B3 would be? $B$3 To represent a payment of $200 to the bank for repayment of a loan, a cash flow statement would display the number as? A negative number The second argument of an IF FUNCTION IS? What to display or do if the criterion is true The IRR function returns a value that is similar to? The interest earned on a savings account The error code that displays when you misspell a function is #NAME When numbers are used as column or row labels, they should be formatted?As text Unit 2 Chapter 8 Questions and Answers 1. If a range of cells has numbers that display a mix of decimal places, to display the same number of decimal places, select the range of numbers and change the format to ? to adjust the decimals...C...Number 2. Data labels should be ? if they might be used as chart labels? B...Short 3. When you select cells to chart, the values in those cells should be?...C the same type 4. If you want to create a chart that compares two columns of values and pairs them up by row, use a?...Clustered Column 5. If you want to demonstrate how the values in a column of numbers contribute to the columns total, use a...C, pie chart 6. If you want to demonstrate how the values with the passing of time, use a? ...line chart 7. A common error when choosing a range of cells to chart is to include?...A, the total at the bottom of the column 8. To correctly interpret the slop of a line chart, B, you must use a polynomial trendline 9. A method of exaggerating the difference between values in a line or column chart is to? C, Use a brighter color for one series compared to the other 10. If you do not have a color printer, the print preview of a pie chart will display the chart?....B, in black, white and shades of gray Unit 2 Chapter 9 Questions and Answers If you need to reorganize several slides in a presentation with 30 or more slides, it is best to use the....D, slide sorter Add graphics to your slides for any of the following reasons except...B, to add an image to every slide To control how slides enter and exit the screen, select...D, select transition When using a slide presentation, be sure that you do the following...C, have only one topic per slide. Presentations can help with all of the following except...B, speak clearly When applying a theme to a presentation, the most important factor to keep in mind is...A, the environment in which the presentation will be given Notes for the speaker can be added in the...D, a or c but not b To display information in the header and footer area of a slide...C...set the slide options in the Header and footer dialog box Audience handouts are provided for all of the following reason except...A, to make people feel like they are part of a group In a slide show, to return to the slide that was just viewed prior to the current slide, do any of the following except...C, press shift + tab on the keyboard Unit 2 Chapter 10 Questions and Answers 1. To apply custom animations to slides, it is best to use the ? view?...D, Slide Sorter (L6) 2. To import content from a word document using the slides from outline command, the word file must be formatted?...C, An outline with heading levels (p. 532) 3. Tables can be used for?...D, all of the above (539) 4. Text imported from an outline?...C, Changes to the font used when a theme is applied (535) 5. When formatting a table, all of the following are true except?...A, The table tools tabs used in word are available to use in power point (L3) 6. When you apply a theme to a presentation, it is important to review your presentation for? D, all of the above!...D, All of the above (L2) 7. To show trends over time, the best chart type to use is the ? chart?...D, bar (551) (2007 answer would have been d, column) but we are staying with the 2010 book answer D, bar!!! 8. Smart art diagrams can be used to show all of the following except?...B, bar charts (554) 9. A smart art graphic whose purpose is to show a decision tree would be found in the ? category?...C, Hierarchy (554) 10. Animations can be applied to?...A, a group of slides all at once UNIT 2 MATCHING! Added....................Chapter-1 Added....................Chapter-2 Added....................Chapter-3 DO NOT HAVE! DO NOT HAVE! Added....................Chapter-6 Added....................Chapter-7 Added....................Chapter-8 MATCHING… UNIT 2 CHAPTER 1 Keyboard Shortcut: Pressing two or more keys at a time to perform some action. Group: A collection of related commands on a table that enable you to interact with the software. Work Area: The area on the screen where you enter text, numbers, or graphics to create a document, a worksheet, or presentation slides. Insertion Point: In word, indicates with a blinking vertical line where text or graphics will be inserted. Paste options button: A button that displays options for a recently completed action: Screen Tip: A description that displays the name of a screen element, button, or area on a window. Graphical user interface: A set of tools including dialog boxes, command buttons, and menus that is manipulated with a mouse and keyboard to interact with software. Gallery: A list of potential results. Shortcut Menu: When you click the right mouse button, a list of actions that displays, which are related to the area on which you clicked. Quick Access Toolbar: A customizable area containing a save button and an undo button. MATCHING UNIT 2 CHAPTER 2 San Serif: Fonts that do not have lines or extensions on the ends of letters. Theme: A collection of design elements that are applied to documents to create a uniform look Header: An area reserved at the top of a document for information that should appear on every page in a document. Field: A category of data such as file name, date or page number that is inserted into a document. Template: Preformatted and designed document that can be used repeatedly. Serif: A font that has lines or extensions on the ends of the letters. Alignment: The horizontal placement of text. Justified: Text that is aligned evenly between both the left and right margins. Word Art: A tool used to turn words into a graphic to create a decorative title. Footer: An area reserved at the bottom of a document for information that should appear on every page in a document. Alignment: The horizontal placement of text. MATCHING…. UNIT 2 CHAPTER 3 Endnote: A reference that is placed at the end of a document or section of a document. Copyright: Ownership of intellectual property and the right to choose who uses it. Footnote: A reference that is placed at the bottom of a page. APA: One of two commonly used styles for formatting research papers and reports. Quick Style gallery: A list of available styles in a document found on the home tab! Citation: A reference in a tect to the source of the information! Parenthetical Citation: A citation in the MLA style that uses the authors last name and the page number, surrounded by parentheses! Thesaurus: A research tool that provides a list of synonyms! Bibliography: The name of a bibliography in a document that uses the MLA style! Works cited: A list of sources used in a paper which are listed at the end of a document! MATCHING: UNIT 2 CHAPTER 6 1. Automatic process to adjust the width of a column or height of a row to fit the largest content? Auto-fit 2. Collection of worksheets in a single excel file? Work book 3. Generic term for financial data arranged in rows and columns with formulas that can recalculate automatically if values in cells change? Spreed Sheet 4. Limits the rows that display in a table to those that meet certain conditions? Filter 5. Used to identify a total in a column? Top and double bottom border 6. The column letter and row number used to identify a cell? Cell Address 7. Providing information about the source, author, and creation date of a workbook? Documenting 8. The location where data will display when you type? Active cell 9. The area in the excel window that displays the name of the cell? Name box 10. The location in excel that displays the formula or contents in the active cell? Formula Bar MATCHING: UNIT 2 CHAPTER 7 1. A selected format that is applied if a criterion is met....C, conditional 2. A cell location that is stored as a given row and column and does not change when a formula is copied...A, absolute reference 3. Empty or nonexistent...G, Null 4. A process of trying different values to see what happens...J, What if analysis 5. A value or expression used by the function...B,Argument 6. Small box at the lower right corner of a selected cell...E, Fill handle 7. Similar to accounting format, but it places the currency symbol next to the number on the left...D,Currency 8. A financial measurement that is used to evaluate an investment and is comparable to the percent interest you earn on a savings account...F, Internal rate of return 9. Amount of a loan before it have been repaid...H, Present value 10. A cell reference that is stored as a certain number of rows and columns from the currently selected cell...I (is the letter i ) looks funny:) Relative Reference MATCHING: UNIT 2 CHAPTER 8 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. IDENTIFIES EACH DATA SERIES ON A CHART...E, LEGEND EXTENDING A LINE CHART BEYOND KNOWN VALUES...C, EXTRAPOLATION THE RISE OR CALL OF A LINE...H, SLOPE LIKE A COLUMN CHART BUT VALUES ARE HORIZONTAL...A, BAR CHART SMALL RECTANGLE ON A LINE CHART THAT DISPLAYS DATA VALUES...F, MARKER 6. A CALCULATED LINE THAT FITS EXISTING DATA...J, TRENDLINE 7. A SHAPE THAT HAS A POINTER AND CONTAINS TEXT, LIKE A CARTOON SPEECH OR THOUGHT BALLOON...B, CALLOUT 8. A LINE THAT CONNECT A LABEL TO A CHART ELEMENT...D, LEADER 9. A CALCULATED VALUE THAT RANGES BETWEEN 1 AND 0 THAT INDICATES THE QUALITY OF THE FIT OF A TRENDLINE...G, R-SQUARED 10. RECTANGLE THAT DISPLAYS TEXT...I, TEXT BOX UNIT 2 KEY TERMS! Added....................Chapter-4 DO NOT HAVE! DO NOT HAVE! Added....................Chapter 7 Added....................Chapter 8 Added....................Chapter 9 KEY TERMS…. UNIT 2 CHAPTER 4 Auto Recover: A feature that saves a copy of open files at regular intervals to create a version of the file that can be recovered in the event of a computer malfunction. Backwardly Compatible: The ability of a newer version of a program to open and display files that were created using an earlier version of the program. Compatibility Mode: Office 2007 files that are saved with a previous version file format. Em dash: Name for a ling dash in a sentence that marks a break in thought, similar to a comma but stronger. File extension: The letters following a period after a file name that identifies the type of file and often the software that was used to create it. Hyperlink: Text or an object that you click to connect to another file, location or Web page where information is located. Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) A language that is used to create Web Pages that can be viewed in a Web browser. Leader: Dots or other marks that provide a visual connection between widely separated text. Leader Character: the dot, dash, or other character used in a tab leader. Manual Line Break: An artificial end to a line without creating a new paragraph. Margin: The space between the edge of the paper and the text. MHTML format (MIME HTML) HTML code used in single-file Web pages Plain text format: Document format that saves the text and paragraph marks, but none of the text or paragraph formatting. Portable document Format (PDF): A document format developed by adobe that can be read on most platforms, but cannot be edited without special software; maintains document formatting graphics, and layout. Rich text format (RTF): A universal document format that can be read by nearly all word processing programs and that retains most text and paragraph formatting. Small caps: A text effect that displays the capital letters in a normal manner but the lowercase letters as capital letters that are approximately ¾ height. Subscript: Characters that are placed below the regular text in a line. Superscript: Characters that are placed above the regular text in a line. Tab Stop: A location on the horizontal ruler to which you can move the insertion point by pressing the Tab key; used to align and indent text. SCREEN ID (CHAPTER FOUR) REFER TO ILLUSTRATION ON PAGE 213 KEY TERMS: UNIT 2 CHAPTER 7 Absolute cell reference: in a formula, a reference to a cell location that is stored as a given row and column and does not change when the formula is filled. Argument: A value or expression used by the function, which instructs excel how to execute the function. Auto Complete: A feature that begins to complete a cell entry based on other entries in the same column. Cash Flow Analysis: The process of tracking money coming in and going out. Circular Reference: An error in a formula that is caused when the cell that contains the formula results is included in the formula argument either directly or indirectly. Comparison Operators: Symbols that are used to compare two values. Conditional Formatting: A selected format that is applied if a criterion is met. Cumulative Total: Also known as a running total...the sum of the current value plus the previous total. Currency Format: Similar to accounting format but it places the currency symbol next to the number on the left. Fill Handle: In excel, the small box at the lower right corner of a selected cell that is used to fill content across a row or down a column. Interest Rate: The amount charged to borrow money. Internal rate of return: (IRR) A financial measurement that is used to evaluate an investment and is comparable to the percent interest you earn on savings account. Mixed Cell Reference: Cell location where either the row or the column remains constant, but not both. Null: means empty or non existent. Present Value: Amount of the loan before it has been repaid. Relative cell reference: Cell location that is stored as a certain number of rows and columns from the currently selected cell. Simple payback period: The number of years that it takes to recover the cost of an investment, which is a measure that is commonly used to compare investment alternatives. What if analysis: Process of substituting values to see the effect on dependent calculations KEY TERMS: UNIT 2 CHAPTER 8 1. 3-D Pie Chart...No definition in the back of the book? Pretty self explanatory of what a pie chart is. 2. Bar Chart...uses horizontal rectangles whose length represents the value of the data 3. Callouts...Shapes that have a pointer and that contain text 4. Clustered column chart...Groups columns together for convenient comparison between values of the same type 5. column chart...uses vertical rectangles whose height represents the value of the data 6. embedded chart...A chart that is on the same worksheet as the data 7. extrapolation...To extend a trend beyond the known data 8. horizontal axis...Bottom border of the chart with category labels 9. leader line...A graphic that connects a label to a chart element 10. legend...Identifies the data series on a chart 11. line chart...A chart that uses lines whose height on the vertical axis represents the value of the data 12. markers...Small rectangles on a line chart that identify each data point 13. pie chart...Uses a circle to represent the whole of a group of data and slices to represent how each piece of data contributes to the whole 14. R-squared value...A measure of how well the calculated trend line fits the data; the closer the number is to 1, the better the fit 15. Sizing handles...Small squares and circles that display around the perimeter of an object that are used to re-size the object and which indicate that the object is selected and can be moved, re-sized, or formatted. 16. Slope...The angle of a straight line compared to horizontal 17. Trendline...A calculated line that can be extended to predict values beyond the end of the data 18. Vertical Axis...The left side of the chart used to indicate the magnitude of the value of the data 19. X-Y scatter chart...Similar to a line chart but it forces equal intervals on the horizontal axis KEY TERMS: UNIT 2 CHAPTER 9 Bullet point: A line of text that is preceded by a small dot or other symbol. Gray-scale: Handouts: A printable output in power point that displays one to nine slides to a page for the purpose of providing an audience with a copy of a presentation. Layout Normal view: The main view in power point that is used to create a presentation. Notes Pane: In power point, in normal view, the portion of the window at the bottom that is used to create notes for the speaker Place holder: Pre-formatted areas that define the type of information to place in each area on the slide Slide Master: Slide layout images that contain all of the placeholder formats for each slide layout within a theme, which are used to change theme formats for all slides Slide Master View: In power point, a view that contains each slide layout, where you can change placeholder formatting characteristics for the selected theme Slide Pane: In power point, in normal view, the center pane that is used to enter slide content Slide Show View: The view that is used to display slides electronically using a computer and overhead projector Slide Sorter View: in power point, thumbnail slides images displayed on a single page that is used to rearrange slides and add transitions Slides outline pane: In power point, in normal view the left pane that is used to display thumbnail images of the slides or an outline Speaker Notes: A printable output in PowerPoint that provides a copy of the slide image and related notes for the speaker during a presentation Theme: A collection of design elements, fonts, colors and graphics that create a uniform look for a presentation, word document, or Excel worksheet Transitions:Added to slides to control the direction, timing, speed, and manner in which slides enter and exit the screen during a slide show Unit 3 Questions and Answers! Added....................Chapter 1 Added....................Chapter 2 JOHN Added....................Chapter 3 Brian Added....................Chapter-4 Added....................Chapter-5 Added....................Chapter-6 CRISTY Unit 3 Chapter 1 Questions and Answers John, thanks! 1. What was one of the original reasons the government had for creating the internet, D, to create a way to exchange data between research computers 2. Which of the following is NOT an advantage of a packet switched network over circuit switching? B, Data is sent on whatever line is available at the moment 3. If a computer has a program that makes a request for service from a program on another computer, the relationship is? B, Client Server 4. The difference between a WAN and a LAN is? D, The computers are closer together in a LAN 5. What does a domain name server do? A, Provides a directory that relates domain names to the servers that host them 6. What is the difference between the internet and the world wide web? B, The internet is the network of networks that use TCP/IP to transfer data, while the WWW uses the internet to transfer web pages 7. What type of transmission medium is used by wireless communication? A, Radio waves 8. What is the relationship between a byte and a bit? C, a bit is eight bytes 9. Which group coordinates creation of domain names and IP addresses? C, ICANN 10. What is NOT a desirable characteristic of a password? D, is a date like a birthday Unit 3 Chapter 2 Questions and Answers John or Philip Here is Unit 3 Chapter 2 1. Why does a web page appear more rapidly the second time you request it? B, The browser stores a copy of the web page on the computers hard drive and uses that copy for subsequent requests. 2. Which of the following is NOT a typical reason for the browser to return a page not found error? D, The web browser does not use the same version of HTML code as the Web page 3. The main purpose of a web crawler is? B, to analyze and categorize the characteristics of web pages 4. Which of the following combinations of keywords and boolean logic operators would produce the largest list of matching web pages? A, Wind AND power 5. What is the purpose of a bookmark or favorite? C, to make it more convenient to remember and retrieve a previously visited site 6. Why would you save a copy of a web page to the computer's hard disk? C, So it can be retrieved even without an internet connection 7. What is the type of program that can transfer files from your computer to a web server? A, FTP 8. What type of code is used to write web pages? D, HTML (see...p. 290 definition) 9. What are two common standards for citing references that are used in the U.S.? B, APA and MLA 10. Which of the following is NOT an ethical practice? C, Using the internet to force ideas on people for their own good Unit 3 Chapter 3 Questions and Answers Brian 1. If a public key is used to encode a message, its corresponding ? key is used to decode the message? 2. Which type of encryption uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt? 3. Where does your browser get the public key and confirm that it is authentic? 4. A cookie is a? 5. How is a symmetric key used with public and private keys to transmit data? 6. What is an extranet? 7. What is an example of a company that provides intermediary services for online auctions? 8. How are computers used in print on demand (POD) 9. What is phishing? 10. What does adware do? Unit 3 Chapter 4 Questions and Answers 1. THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN POP mail protocol and IMAP mail protocol is that? POP is used to send mail and IMAP is used to download mail from the server. 2. What percentage of email messages are unsolicited bulk mailings that are also known as spam? More than 70% 3. What is lossy codec? A compression and decompression process that loses some of the original content. 4. When watching a streaming video, what is the role of the butter? To store the incoming data so it can be displayed at a constant rate in spite of inconsistent or slow transmission 5. Why are VoIP telephone services generally cheaper than traditionally wired telephone services? Unsure…guessed The combination of audio compression and packet transmission makes much more efficient use of communication links. 6. Why are text messages restricted to 160 characters? They must avoid interfering with the control functions of the cell phone system on the control circuit. 7. What is Libel? A false and malicious publication printed for the purpose of defaming a living person. 8. Software that may be redistributed with out paying royalty or license fees and which makes its source code available is called? Open source 9. The defining characteristic of a wiki is? The ability of users to collaborate to create the content of a website. 10. How are infected computers used in denial of service attack? They all ask the same server for service at the same time and overload it with requests so that it denies requests from legitimate users. Unit 3 Chapter 5 Questions and Answers 1. Which of the following salutations is most appropriate for an email message to a potential customer you have never met named Dr. William Cross? Dear Dr. Cross 2. If you have to distribute a file to several people in your organization who uses the same email and network servers, what is the best option for using server resources wisely? Place the file on the network server in a folder that is available to all the intended recipients, and provide the address in an email that you send to all of them. 3. Why is direct marketing by email profitable even if very few people respond? The costs of distributing email are extremely low for the direct mailers, so small success rates are still profitable. 4. What are examples of uses of RSS for business purposes? Providing inexpensive ways to exchange text messages with mobile employees. 5. How can companies combine their telephone and data communications? By using a gateway router that combines voice and data. 6. Why is special software needed to manage input signals from microphones during an audio conference call when participants are at a table sharing the same microphone and speaker unit? The software blocks sound picked up by the microphone and just emitted by the speaker to reduce echoes. 7. Which of the following is NOT an advantage of telework? Managers are accustomed to managing by objective, and existing management techniques transfer easily to teleworkers. 8. Which of the following is a disadvantage of working on a virtual team? Synchronous communications are not convenient if workers are in different time zones. 9. The medium most commonly used by employers in the United States informing employees about computer related policies is? The company website 10. Which of the following is NOT safe practice when using computers? Using an extension cord that lies across a walkway without a protective cover. Unit 3 Chapter 6 Questions and Answers Christy 1. Which of the following would produce the most accurate digital representation of an analog event? C, higher sampling rate 2. Why does digitizing a signal make it possible to make corrections? C, binary numbers are more accurate than the numbering systems that us 10 digits 3. What is the role of a repeater in a ling distance transmission? A, retransmitting the signal as exactly as possible 4. How does time division multiple access TDMA make it possible to transmit more calls over the same phone lines? B, a compressed version of the call takes less time, so different calls can take turns using the same frequency 5. How does code division multiple access CDMA make it possible to transmit more calls over the same phone lines? B, a compressed version of the call takes less time, so different calls can take turns using the same frequency 6. How is the identity of the user determined with a GSM phone? D, the identification of the caller and service provider is recorded on the sim card and broadcast by the phone when it makes contact with the tower 7. How is the identity of the user identified with a first generation phone using AMPS? C, the user must enter the Mobil identification number (min) when the phone is first turned on, and this number is transmitted when the phone is in use. 8. When you choose a higher resolution setting for a computer monitor, what happens? B, the image appears smaller on the screen 9. Which analog television standard is used the most in western Europe and how does it differ from the NTSC standard? B, PAL; it has fewer lines per sheet but images per second. 10. What is a possible problem with recycling old computers or televisions that could actually harm the environment more than disposing of them in a landfill? C, some ewaste is sent to other countries where it is processed without environmental controls. MATCHING: UNIT 3 CHAPTER 4 Captcha Distorted word that is recognizable by humans Codec Software or device that compresses and decompresses files Flame War Exchange of hostile or insulting messages RSS Method of delivering content to subscribers that uses XML Hot thread Very active web discussion Worm Program that duplicates itself on a network Reflector Email address to which a message is sent that will be distributed to the e-list. Rootkit Program that gives outsiders access to a computer and administrator rights SPIM Spam directed at instant messaging systems WAP Rules for connecting mobile devices to the internet MATCHING: UNIT 3 CHAPTER 5 Archive Inactive storage Call Center Group of people at one location who use audio communications to provide service DVR Video recorder that uses a hard disk Ergonomics Applied science of equipment design to reduce operator fatigue OSHA An agency in the department of labor concerned with worker safety Outsourcing Having work done in another country PBX Device for routing calls within a company Salutation Courteous recognition or greeting Telework Working from home Virtual Team Group whose members are separated by distance or time EXCEL NOTES The farthest back that excel with identify a date is 01/01/1900. This date is represented in excel by entering a number 1 in an active single cell. When you enter a date like 02/28/1975, excel will read it as a number. If you want numbers within a cell to be actual numbers, go up to the ribbon and under number make sure to click on currency. If for some reason there is a dollar sign and a dash in your cell....it's in an accounting format. Simply go and change it to a currency format instead if you want currency within the cells. Anytime you are in a cell make sure you have the correct format you want in the cell. As Peter showed in class when we enter a date within a cell and hit enter, it's simply going to turn it into numbers so just make sure your formatting is correct then you won't have issues! How can you make the column heading not so wide? Go up to the ribbon and click wrap text but make sure you have the cell activated, the one you want to change. Never manually enter this in a cell...B2*15 and hit enter! Peter say's people do this all the time and it's WRONG! This was the example of calculating someones wages and if they worked 40 hours a week then they multiply it by $15.00 per hour. Peter say's to give the $15.00 a cell on it's own because you always want to give a cell there own cell if it can change or will change. You don't want to create more work for yourself if you don't have to. Peter also indicates that we should NEVER type in cell address's because you can easily make mistakes. Simply click on the cells you wish to add or subtract or what ever function it may be. GOOD TO KNOW...if you get ##### inside a cell it simply means that your column is a little narrow. Simply widen it up a bit to correct it. What is the fill handle...if you look at a single cell you will notice at the bottom right corner will be a little black square....this is where you can grab onto it and drag it down over other cells to calculate their sums. Relative Cell Reference indicates an off-set. Which is basically how far to get from one cell to the other. e.g., left one, down 5. If you copy an off-set cell it's going to also be an off set cell. Absolute Reference is always going to point directly to that one particular cell, always! To get a cell to be Absolute you want to hit the F4 button. (for jenns laptop it's fn then the f4 button) Brackets in excel simply mean it's a negative number and it does not matter what color the brackets are. Hours and Wages-DON'T enter e.g., B2*15 in a cell cause it's WRONG! Give the 15 which is the hourly rate it's own cell. Why because this amount can change. Calculate sums...grab the fill handle and drag What are the three things you can put into a cell? 1. formula 2. text string and 3. number value Ascending=smallest to largest (A to Z) Descending=e.g., Z to A Rows: Represents a record Columns: Represents a field Field Names: Are NOT part of data Filter: ALWAYS CHOOSE FILTER FROM THE DATA RIBBON!!!! Poll Position= 1st position Rand=Random Formula: how to get to it....hit control + the tilda key which is in upper left corner (looks like a snake with a dash in the middle of the key function) PMT Function: To show your payment in a POSITIVE instead of a NEGATIVE...simply add the - (negative sign) between the = and the P so...(=-p( Alt + Tab = to go back and forth between screens Excel payment calculations: o o o o o o o o o o o o o Go to my desktop Click on CIS 120 folder Notes…Rate, Number of Periods, Present Value Go up to the FX and click it Type in the box…payment Click go Highlight PMT Click ok R…type in cell / 12 NPER=Number of years so put in let’s say…which the cells gonna say 4 but we are going to enter 84 which is 84 months*12 PV=amount of loan to borrow….so click the cell that shows the amount we are to borrow Click ok And don’t worry about the two bottom buttons. NOTES: To compress a file: Right click the folder Send to Compressed Folder Snap shots: How? Hit the key that is at the very top right side of the key board that says…ins prt sc (which is the print screen key) Now go open Microsoft Word Click inside the document Control V (to paste) Keyboard Key Strokes (ARE IMPORTANT TO LEARN) Control V= paste Control Z= undo Control X= cut Control C= copy Windows button + D= to get to ones desktop Alt+tab=to switch back and forth between windows OWA= Outlook web access. When you log into this account you are essentially logging into a web browser. Browsers:Outlook web access, Internet Explorer, Firefox and safari are all web browsers. Chrome (Google) is another browser and is Peter Casey’s preferred web browser (our instructor) Google Chrome is their browser product. How to log into your COCC email FAST? Start Click Microsoft outlook The Cloud: This is another term for the internet. It basically means anything that is NOT stored on ones local computer. The Cloud is stored out on a cloud on the internet. What’s Cloud based? (these below are all cloud based) Facebook Yahoo Google Why…well if you think about it, you don’t install these on your computer so it’s cloud based. We don’t know where the cloud is, per peter casey. Storing / back-ups: www.box.net to store your backups on your computer Create a hyperlink Copy the web address Open up Microsoft Word Click in the document anywhere Paste and hit tab or enter URL: Uniform Resource Location Wiki: Means….FAST! Stay away from yahoo.com (email accounts) They don’t provide a secured site. If you will notice when you log into your yahoo email account, it’s http: and NOT https:. USE GOOGLE…get a gmail account!!! Safari Is a great web-site to go to in reading articles, simply download and install! Operating Systems are: XP (5 to 6 years old) Vista Windows (came out in 2007) Non-Volatile: Means…memory that does not need constant power to function. ROM: Read only memory Contains the instructions used by the computer when it starts up and is NON Volatile! RAM: Random access memory The memory that is used to store programs and data while the computer is working and IS Volatile! A single byte of memory is equivalent to: One character of text. DDR2: Is the latest in the development of faster memory that uses less power and can store more data. We will be adding more to our power point slides! Remember how to get this arrow jenn! -- , shift key and greater than key! Skydrive…Office live I have an account that I’m taking advantage of FREE 25 GB of free space which I can place these documents in the clouds! (not using up any space on my hard drive!) nanna333@live.com and password city where I live OVER and birth year. Peter says to download all of my student files and work to the cloud because I can access my documents anywhere there is a computer. So I downloaded the power point presentation we are doing in class to the cloud along with all the other documents. Other different cloud providers…here are some, there are lots! 1. Box.net 2. Dropbox.net YOUTUBE…is awesome..you can make video’s and YES…they can be private to only let those people you want to see them. They don’t have to be publicly seen!!! Great articles can also be found at www.time.com (read if you have time, a billion eyes article) You can create another presentation slide and then later add it to one you already created! How, simply right click or control C, to copy it…then open the other powerpoint slide you created and click on the last slide (to the left of the screen) and control V to past. THE OPERATING SYSTEM RUNS YOUR COMPUTER…REMEMBER IT DOES EVERYTHING FOR YOU…PER PETER!!! www.crucial.com- tells you what or how much you have on your computer and what you can do with it to perform better. DEFRAGGING…Do this once a month! And DON’T EVER let your computer get to 20% or less in free space availability because it will affect the performance of your computer. If it gets to this point you may want to purchase an external hard drive…but make sure it’s USB 3.0 or better which is the newest standard. TRANSISTORS STORE BITS!!! IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS: Platform: The combination of the operating system and the hardware. Open Source: The source code for software that is free to distribute and use that meets the criteria of the open source initiative. Backward Compatible: The ability of a newer version of a program to open and display files that were created using an earlier version of the program. Peripheral: A device such as a printer that can be attached to the system’s unit or case. Clock: Refers to a circuit on a computer chip that emits pulses and are measured in hertz. 1 hertz = 1 pulse per second. RAM: The higher the clock speed on the processor, the lower the response time of the RAM. RAM that is to slow to keep up with the processor may malfunction and cause errors. If RAM gets all used up then the operating system with start using the hard drive. Make sure your computer is expandable meaning there is more empty slots for additional RAM. S-Video Port Enables one to connect ones computer to cable TV or other video sources and show television programs. Response Time: The amount of time it takes to change the color of the pixel. Video RAM (VRAM) Also affects the performance of a monitor. If you’re into games or watching videos—it’s a good idea to purchase more VRAM. Take note that some computers use a combination of dedicated video memory and system RAM.