LES-modeling of cold crucible melting process
advertisement

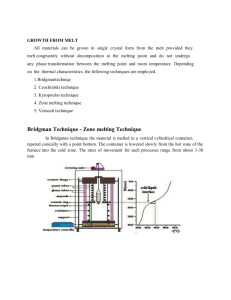
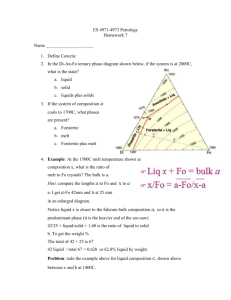
LES Modeling of the Cold Crucible Melting Process E. Baake, A. Umbrashko, Institute for Electrothermal Processes University of Hanover (Germany) A. Jakovics Laboratory for Mathematical Modelling of Environmental and Technological Processes, University of Latvia, Riga (Latvia) 1 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Contents Introduction to the cold crucible skull melting process Main features and optimisation potentials Numerical modeling and results - Melt flow and temperature distribution - Particle transportation Conclusions and Outlook Chinese-German Project 2 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Cold crucible induction skull melting process I p vacuum chamber M crucible Heizer inductor M Induktor Luft Trichter High reactive and high purity materials, e.g. TiAl Evakuierung Tiegel Kokille Melting, alloying, overheating and casting in one process M Argon 3 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Cold crucible induction skull melting process II crucible free surface real inductor ideal Optimisation potentials of the process Maximisation of the overheating temperature, which is one of the key parameter Improvement of the total efficiency and reduction of energy consumption contact point wall-skull Control of the melt composition and reduction of skull formation bottom-skull crucible-bottom Reliable, reproducible and stable melting process 4 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Physical Correlations magnetic field - distribution of power - electromagn. forces velocity field homogenisation of melt meniscus shape geometry of melt temperature field - overheating - heat flow skull formation alloy composition liquid-solid-interface melt components optimisation of design and operating parameters 5 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Numerical models and numerical tools start 3D-electromagnetic - Commercial software (ANSYS) 2D-meniscus shape - self-developed code calculation of meniscus shape stop criteria fullfilled 3D-transient-LES - Commercial software (FLUENT) no Surface stability during semilevitation process allows to uncouple electromagnetic and fluid-dynamic calculations calculation of hydrodynamic and thermal field stop criteria fullfilled end no Shape of free surface is calculated with self-developed finite-element code 6 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Temperature and melt flow measurements in aluminium Thermo-couple with ceramic protection Melt flow velocity sensor stainlesssteel case stainlesssteel holder coil 6 14 35 magnet core electrodes E=vxB 7 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 RANS (k-ε model) DNS • Whole energy spectrum is modelled • All scales are resolved directly • Relatively low mesh resolution requirements • Very high requirements for computational resources • Steady-state simulations •Simulations of industrial installations are impossible CFD problem Re 104 LES • Large scales are resolved directly while only small scales are modelled • Relatively high mesh resolution requirements • Transient 3D simulations 8 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Flow pattern and temperature distribution simulated with 2D RNG k-ε turbulence model 9 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 3D LES-modeling of cold crucible melting process ~3•106 elements Time step 10 ms Smagorinsky-Lilly subgrid viscosity model Parallel computations with FLUENT 6.1 software at the HLRN* supercomputer and institute's workstation cluster (4+1 AMD64 3200+) *HLRN – scientific supercomputer network of North Germany 10 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Results of 3D transient LES modeling with aluminium melt I [m/s] vm~40 cm/s Time-averaged flow pattern [m/s] An intermediate flow pattern 11 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Results of 3D transient LES modeling with aluminium melt II ºC ºC Time-averaged temperature distribution Measured temperature distribution 12 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Velocity and temperature distribution in TiAl alloy (LES and k-ε results) 13 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Temperature oscillations in the melt of the IFCC T, K Calculated in TiAl Measured in Al 14 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 3D-instationary flow velocity distribution in the cold crucible melting TiAl alloy calculated with LES model 15 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 3D-instationary temperature distribution in the cold crucible melting TiAl alloy calculated with LES model 16 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 3D-instationary temperature distribution in the cold crucible melting TiAl alloy calculated with LES model 17 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Melt flow velocity distribution for different crucible geometries crucible radius: 8 cm melt mass: 6 kg TiAl power in the melt: 50 kW crucible radius: 6 cm melt mass: 6 kg TiAl power in the melt: 50 kW 18 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Melt temperature distribution for different crucible geometries crucible radius: 8 cm power in the melt: 50 kW total power: 275.3 kW electrical efficiency: 18.2% crucible radius: 6 cm power in the melt: 50 kW total power: 138.6 kW electrical efficiency: 36.1% 19 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Transient 3D Particle Tracing I Starting Point Starting Point - Density of particles and melt is equal - 6 s of transient tracing in the melt 20 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Transient 3D Particle Tracing II Starting Point Starting Point - Density of particles is 10 times smaller than melt density - 3 s of transient tracing in the melt 21 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Conclusions and Outlook Heat and mass transfer processes in the melt of induction furnaces are significantly influenced by large scale low-frequency oscillations of the recirculating flow 3D-transient LES is a reliable numerical tool to simulate the turbulent melt flow and the heat and mass transfer in cold crucible skull melting processes 3D-LES model will be coupled with 3D-electromagnetic model for the induction furnace with cold crucible Modelling of transient skull formation at the crucible wall and particle transportation by electromagnetic forces in the melt are in progress 22 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Chinese-German Project founded by NSFC / DFG Project Title: Cold Crucible Induction Skull Melting Process of Titanium Aluminium Alloys Project Partner Harbin Institute of Technology (HIT) School of Materials Science and Engineering Coordinator: Prof. Dr. Guo Jingjie University of Hannover Institute for Electrothermal Processes (ETP) Coordinator: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Egbert Baake 23 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Contributions of HIT and ETP to the cold crucible skull melting project Harbin Institute of Technology (HIT) • Experimental investigations of the TiAl melting process especially form metallurgical point of view • Investigations of the mechanism of skull formation including the microstructure of the skull • Investigations of melt composition control and evaporation behaviour of alloy components Institute for Electrothermal Processes (ETP) • Numerical modeling of the skull melting process including coupled 3D electromagnetic and 3D transient melt flow and temperature fields • Simulation of skull formation • Investigations of design and process parameters 24 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Main Objectives of the Project (Draft) • Experimental investigation and numerical simulation of the complete cold crucible induction skull melting process of TiAl • Analysis and improvement of the process and design parameters from electromagnetic, thermal, hydrodynamic, metallurgical point of view • Optimisation of the key parameters of the melting process: overheating temperature of the melt, control of melt composition, reduction of skull formation, increasing of efficiency • Investigation of up scaling criteria from small sized units to large mass production furnaces 25 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005 Thank you for your kind attention! 26 2nd Sino-German Workshop on EPM Dresden 2005