Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs)
advertisement

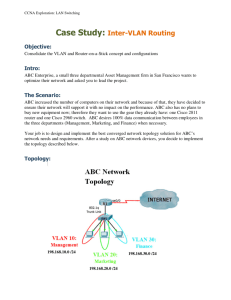
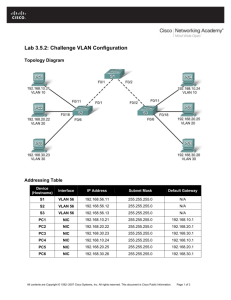
We will be covering VLANs this week. In addition we will do a practical involving setting up a router and how to create a VLAN. What is a VLAN? The acronym VLAN expands to Virtual Local Area Network. A VLAN is a logical local area network (or LAN) that extends beyond a single traditional LAN to a group of LAN segments, given specific configurations. Because a VLAN is a logical entity, its creation and configuration is done completely in software. How Is a VLAN Identified Since a VLAN is a software concept, identifiers and configurations for a VLAN must be properly prepared for it to function as expected. Frame colouring is the process used to ensure that VLAN members or groups are properly identified and handled. With frame colouring, packets are given the proper VLAN ID at their origin so that they may be properly processed as they pass through the network. The VLAN ID is then used to enable switching and routing engines to make the appropriate decisions as defined in the VLAN configuration. Benefits of VLANs Traditional network designs use routers to create broadcast domains and limit broadcasts between multiple subnets. This prevents broadcast floods in larger networks from consuming resources, or causing unintentional denials of service unnecessarily. Unfortunately, the traditional network design methodology has some flaws in design • Geographic Focus - Traditional network designs focus on physical locations of equipment and personnel for addressing and LAN segment placement. Because of this there are a few significant drawbacks: • Network segments for physically disjointed organizations cannot be part of the same address space. Each physical location must be addressed independently, and be part of its own broadcast domain. This can force personnel to be located in a central location, or to have additional latency or connectivity shortfalls. • Relocations of personnel and departments can become difficult, especially if the original location retains its network segments. Relocated equipment will have to be reconfigured based on the new network configuration. A VLAN solution can alleviate both of these drawbacks by permitting the same broadcast domain to extend beyond a single segment. • Additional Bandwidth Usage - Traditional network designs require additional bandwidth because packets have to pass through multiple levels of network connectivity because the network is segmented. A proper VLAN design can ensure that only devices that have that VLAN defined on it will receive and forward packets intended as source or destination of the network flow. Sample VLAN Diagram Types of VLANs There are only two types of VLAN possible today, cell-based VLANs and frame-based VLANs. • Cell-based VLANs are used in ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) switched networks with LAN Emulation (or LANE). LANE is used to allow hosts on legacy LAN segments to communicate using ATM networks without having to use special hardware or software modification. • Frame-based VLANs are used in ethernet networks with frame tagging. The two primary types of frame tagging are IEEE 802.10 and ISL (Inter Switch Link is a Cisco proprietary frame-tagging). Keep in mind that the 802.10 standard makes it possible to deploy VLANs with 802.3 (Ethernet), 802.5 (Token-Ring), and FDDI, but ethernet is most common. VLAN Modes There are three different modes in which a VLAN can be configured. These modes are covered below: • VLAN Switching Mode - The VLAN forms a switching bridge in which frames are forwarded unmodified. • VLAN Translation Mode - VLAN translation mode is used when the frame tagging method is changed in the network path, or if the frame traverses from a VLAN group to a legacy or native interface which is not configured in a VLAN. When the packet is to pass into a native interface, the VLAN tag is removed so that the packet can properly enter the native interface. • VLAN Routing Mode - When a packet is routed from one VLAN to a different VLAN, you use VLAN routing mode. The packet is modified, usually by a router, which places its own MAC address as the source, and then changes the VLAN ID of the packet. What kind of Switches have VLAN functionality? Most of your normal cheap switches will not have VLAN functionality, they will have a default pool of all ports as one. It’s only when you look at the higher end switches that you see VLAN functionality. Often these switches will have a 9-pin Serial Port. This port is used to configure the switch via command line. For most switches you’ll use Telnet to dial into them, nearly every current operating system supports Telnet. In Windows XP, you can go to Accessories and System Tools and open up Hyper Terminal to get access. Telnet is falling off in favour due to not being all that secure, Secure Shell (SSH). SSH allows for secure data exchange between two networked devices. The operating system on a switch is generally called a Internetworking Operating System (IOS). What does IOS look like? VLAN Trunking Protocol VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) is a Cisco proprietary Layer 2 messaging protocol that manages the addition, deletion, and renaming of Virtual Local Area Networks (VLAN) on a network-wide basis. Cisco's VLAN Trunk Protocol reduces administration in a switched network. When a new VLAN is configured on one VTP server, the VLAN is distributed through all switches in the domain. This reduces the need to configure the same VLAN everywhere. To do this, VTP carries VLAN information to all the switches in a VTP domain. VTP advertisements can be sent over ISL, 802.1q, IEEE 802.10 and LANE trunks. VTP is available on most of the Cisco Catalyst Family products