Infection Control and Related Health and Safety
advertisement

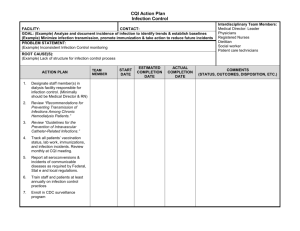
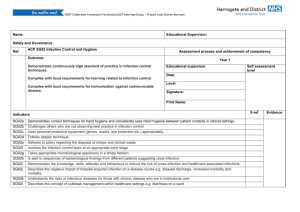
Module 14 Infection Control and Related Health and Safety in the Dental Office Part 2 Infection Control and Related Health and Safety Kathy Eklund, RDH, MHP The Forsyth Institute Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Disease Transmission Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Host Factors General health Portal of entry Host immune system/immune status Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Mechanisms of Transmission Mechanisms of escape Natural – – Oral activities such as sneezing, coughing, etc.. Artificial – Hands, instruments, etc. Methods of entry Inhalation, ingestion Contact with mucous membranes Penetration of intact skin Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Routes of Transmission Direct Patient - Clinican Clincian - Patient Patient - Patient Autogenous Indirect Fomite Aerosol or droplet (spatter) Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) The Transmission Equation Disease Virulence of the microorganism Dose of the microorganism Host resistance Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Contamination, Infection, Disease Risks Prevention Management Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Objectives of an Infection Control Program Reduce the available number of microorganisms Interrupt the spread, break the cycle of cross-contamination Treat all clients and clinicians as if infected Protect from exposure, infection and disease Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Elements of an Effective Infection Control Program Client assessment Immunizations Exposure incident prevention and management Universal Precautions/ Standard Precautions Personal Protective Equipment Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Environmental Asespsis Aseptic techniques Sterilization and Management of Patient Care Items Housekeeping practices Environmental asepsis Waste Hazard communication Client Assessment Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Universal Precautions/ Standard Precautions Procedure-specific, NOT patient people specific. Based-upon the exposure risks associated with the procedure, always assuming the patient and the clinician are infected with a bloodborne pathogen Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Emerging and Reemerging Diseases Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Old Diseases Reemerging New Diseases Emerging Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Emerging Infectious Diseases Conditions that Contribute to Disease Emergence Infection Control for Health Care Personnel Immunizations and Immunity Antibiotics in Dentistry Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Examples Airborne Waterborne Bloodborne Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) The Players Common Cold Influenza Bloodborne Pathogens Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, HIV , Others??? Airborne Tuberculosis Waterborne Microorganisms Legionellosis Cryptosporidium Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Conditions That May Contribute to Disease Emergence Ecological changes Changes in human demographics or behaviors International travel and commerce Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Technology Microbial changes Breakdown of public health measures Occupational Risks to Healthcare Workers CDC Estimated Risks following exposure to infected source patients HBV – 6-35% HCV – 3-10% HIV - .3 % –99.7% exposures do not lead to infection Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Immunity and Immunizations Childhood immunizations Hepatitis B immunization Others to consider Hepatitis A vaccine Varicella Zoster / Chickenpox vaccine Tetanus Boosters Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Guideline for Infection Control in Health Care Personnel, 1998 Bolyard, et.al. AJIC (1998;26:289-354) Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Immunization of Healthcare Workers- Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) and the Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee MMWR 1997; 46(No. RR-18) 21-2 Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Infection Control and Safety Developing Policies, Selecting Products and Implementing Procedures Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Aseptic Technique Concepts Asepsis Antisepsis Disinfection Sterilization Prevent exposure incidents Contain and manage exposure incidents Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Universal Precautions/ Standard Precautions Treat every one as if infected with a pathogenic microorganism Handle every contaminated item as if carrying a bloodborne infectious agent Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) System of infection control and related health and safety that is procedure specific, not based upon the known or unknown sero-status of client Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Standard Precautions Standard Precautions synthesize the major features of Universal (Blood and Body Fluid) Precautions (designed to reduce the risk of transmission of blood-borne pathogens) and Body Substance Isolation (designed to reduce the risk of transmission of pathogens from moist body substances) and applies them to all patients receiving care regardless of their diagnosis or presumed infection status. Standard Precautions apply to (1) blood, (2) all body fluids, secretions, and excretions except sweat, regardless of whether they contain visible blood, (3) non-intact skin, and (4) mucous membranes. Standard Precautions are designed to reduce the risk of transmission of microorganisms from both recognized and unrecognized sources of infection in hospitals [ Guideline for isolation precautions in hospitals Part II, Recommendations for isolation precautions in hospitals] Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Exposure Incident Prevention and Management Preventive strategies Exposure prevention Management Basic first aid Reporting Documentation Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Medical followup Designated HCP Baseline testing Prophylaxis Therapy Monitoring Management Prevention: Engineering Controls and Work Practices Prevent Sharps Injuries (Percutaneous) Needles Bladed Instruments Scalpel Blades Wires in surgery and orthodonics Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Prevent Mucous Membrane Exposures Protective Barriers – Eyewear, Mask Your Hands: Occupational Health and Infection Control Handcare and occupational risks Handwashing Gloves and gloving Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Preventing and Managing Irritant Dermatitis Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Contact Dermatitis Latex Allergy Handwashing/ Antisepsis Policy Procedure Products Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Handwashing/Antisepsis Wash and dry hands before donnning and upon removal of gloves Do not use hand creams/lotions that contain petroleum products when wearing latex gloves Remove all hand jewelry before washing hands and donning gloves Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Gloves and Gloving Choose the correct glove for the task to be performed Sterile vs nonsterile gloves Examination gloves Latex, synthetic, nitrile Use non-powdered gloves Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Gloves con’t Overgloves To prevent contamination of clean areas Overgloves are single patient/client items Puncture resistant gloves for handling contaminated sharps and household tasks Nitrile Always considered contaminated, because they are used for “dirty” contaminated tasks Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Personal Barrier Protection/PPE Eyewear Masks Face Shield Gloves Attire Resuscitation Devices Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Face Masks Mucous Membrane Barrier for the nose and mouth Types of masks Filtration quality When to change the mask Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Protective Eyewear Mucous membrane barrier for the eyes Protect from spatter and splash exposures Protect from projectiles/impact protection Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Protective Eyewear Standards American National Standards Institute (ANSI) – High impact plastic – Peripheral barrier protection with solid side shields Aseptic Management Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Face Shields Task Specific If they do not meet ANSI standards for impact protection, protective eyewear should be worn under the face shield Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Protective Attire Types Reusable Disposable Designed to be a barrier for clothing and non-intact skin Design/style should be based upon anticipated exposure to body fluids of patients Laundering resuable attire Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Resources Recommendations Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) www.cdc.gov National Institutes of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) www.cdc.niosh.gov Professional Recommendations – OSAP www.osap.org – ADA www.ada.org – ADHA www.adha.org – ADAA www.adaa.org Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Resources Regulations/statutes Food and Drug Administration www.fda.gov Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) – www.epa.gov Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) – www.osha.gov Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Resources (continued) Regulations/statutes State Boards of Registration State Departments of Public Health State /local agencies who regulate waste Biohazard, chemical, general Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) From Policy to Practice Site-specific application of policies Standard operating procedures Day -to- Day management of policies and procedures Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Education and Training Techniques Tools Organization for Safety and Asepsis Procedures (OSAP) SOP for each practice setting Resources (related guidelines, standards, regulations and statutes) Approaches ( talking vs teaching vs training) Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Compliance Assessment / Evaluation Feedback and Reflection Assuming Responsibility for Health and Safety of Patients/clients, Yourself and Other Staff Ethical Legal Enforcement Positive Reinforcement Negative Reinforcement Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund) Kathy Eklund Motto for Infection Control and Health and Safety Learn the concepts, keep current with the science and relevant standards Believe that it is critical to healthcare delivery Behave in a manner consistent with the above Infection Control and Related Health and Safety (Eklund)