Understanding Business Outcome 2
advertisement

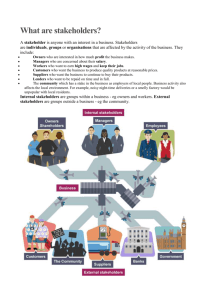
Understanding Business – Business Environment Higher Business Management Internal Factors External Factors Factors Corporate Culture Decision Making Types of Decisions Models ICT PESTEC Stakeholders Conflicts Contents Internal Factors These are the factors within the business that can affect its performance Internal Factors Financial Cash Flow – there may not be enough finance to purchase new materials meaning production stops. Objectives – A lack of capital can mean that business aims can not be met e.g. growth Internal Factors Employees Skills – They may not have the correct skills and therefore the quality of products/services might be low. Motivation – If staff are not motivated this may lead to low productivity Employee Relations – if relations are poor this may lead to staff being resistant to change. It may even lead to industrial action. Internal Factors Management Decision Making – Management might not have the required skills or experience which could result in poor decisions being made (see Decision Making section). Internal Factors Technology Break-down – if this happens then production will stop. Lack of technology – may mean that they are unable to keep up with competitors Availability – technology may not be available to carry out the tasks that the business need. Internal Factors Think of the consequences each internal factor may lead to for the business? What could the Business do to prevent these things from happening? Internal Factors – Corporate Culture Corporate culture is the beliefs and behaviours which employees adopt to enable the business to achieve its aims. It usually develops organically over time and becomes the unwritten rules and values of the business. The culture will be reflected in every aspect of the business e.g. dress codes, décor of premises, logos, employee incentives. Internal Factors – Corporate Culture Advantages employees feel part of the business increased staff motivation increased productivity improved employee relationships customers loyalty consistency across the organisation Task You should research and produce a report on the corporate culture of different organisations. Consider uniforms, the environment employees work in, employee incentives and motivation. Internal Factors – Decision Making Managers make decisions on behalf of the organisation in order to meet its objectives. Effective decision making is a key component of any business. Managers need to be skilled in making decisions Decision Making – Functions of Management (Fayol) Make sure you can describe these words Decision Making – Types of Decisions Decision Description By whom Examples Strategic Long-term, concerned with overall direction of the company Senior Management/Board of Directors • Medium-term, concerned with how to help achieve strategic decisions Senior & Middle Management • Short-term, concerned with day to day running of the company First line/Junior Management e.g. team leaders Tactical Operational • • • • • Merge with a new company Expand abroad Diversify the business Find a cheaper supplier Develop a marketing campaign Staff rotas Covering absences Decision Making – Structured Decision Making Models Stage Identify the Problem Identify the Objectives Gather Information Analyse the Information gathered Devise possible solutions Select the best solution Communicate the decision Implement the decision Evaluate the decision Decision Making – Structured Decision Making Models Strengths (Int) Weaknesses (Int) Build; Enhance Resolve; Reduce SWOT Analysis Opportunities (Ext) Threats (Ext) Exploit; Expand Avoid; Thwart Decision Making – Structured Decision Making Models Advantages Decisions are well thought out – time taken to gather info Wide range of ideas – many solutions Internal & External factors considered Decisions are evaluated Decisions are shared with stakeholders Disadvantages Time consuming process Hard to find info and can be expensive Hard to choose from range of solutions Instinct and gut decisions are lost No guarantee that decision will work Example No. 1 – Computer Games Industry The problem is a falling market share … Example No. 2 – Upgrading Technology Apply the “POGADSCIE” model to choose a new laptop for the staff in your firm. Decision Making – ICT & Decision Making Spreadsheets Databases Info can be stored, edited, searched, presented using reports Word Processing What if scenarios Graphs for comparisons Forecasts can be made Letters, & reports can communicate decisions Presentation Software Communicates decisions to a number of people at once Decision Making – ICT & Decision Making Internet Intranet Documents shared in the organisation Email Wide variety of sources of information Communicate via websites & social media Communicate to a wide number of people 24/7 and cost effectively Attachments can be sent Videoconferencing Meetings can take place over long distances, saving time and money. Decision Making – Constraints Availability of finance Number and skill of employees Employees resistant to change Ability and skill of the manager Policies and procedures of the organisation e.g. environment Quality of the information available Technology available External Factors External Factors - PESTEC External factors are those outwith the organisations control. However it is important companies are aware of these factors and know how to respond to them. These factors can affect the business in both a positive and negative way. External Factors - PESTEC POLITICAL – arise from the action of governments New laws or changes to existing laws Changes in taxation Income, corporation, VAT Government Spending Minimum wage, H&S, Equality, Trading Infrastructure e.g. roads, rail, airports Government targets Environmental targets e.g. recycling, carbon emissions External Factors - PESTEC ECONOMIC – factors that encourage spending Unemployment rate changes Interest rate changes Can be affected by the business cycle e.g. recession Money businesses & consumers borrow from the banks Economic policies Changes at the Bank of England e.g. quantitative easing External Factors - PESTEC SOCIAL – changes in UK demographics Changing fashions/tastes/trends Changing demographics New products vs. out-dated products e.g. new technologies Where people live, how long people live for, amount of leisure time Changing working arrangements Working hours, part-time, flexi-time, tele-working External Factors - PESTEC TECHNOLOGICAL – rapid changes in new technology New technology becomes available e.g. tablet computers Growth of new tech industries E-commerce and now S-commerce Be able to talk about new types of technology that exists: Tablet computers; Wireless technology; Cloud storage; Scommerce; 4G etc. External Factors - PESTEC ENVIRONMENTAL – Changes in weather increasing awareness of environmental factors Seasonal demand for products e.g. ice-cream. Extremes of weather e.g. flooding Environmental pressures Pressures to increase recycling, reduce carbon emissions, reduce packaging e.g. plastic bags External Factors - PESTEC COMPETITION – someone providing a similar product New competitors Growth in an industry will bring about increased competition e.g. app gaming New competitor products New technology and inventions being used by competitors e.g. updates to smart phones External Factors – Exam help With all of these factors you must be able to identify examples of how these factors affect businesses E.g. One political factor is changing laws for example the national minimum wage… You must also be able to explain how they affect the business in either a positive or negative way. E.g. The national minimum wage can have a negative impact as the company will now have to spend more money on employees wages which may mean they have to reduce spending on other areas of the business… Stakeholders Stakeholders Stakeholders are groups of people who have an interest and an influence in a business. We also need to the interdependence and conflict of these stakeholders Interdependence – why a stakeholder needs another stakeholder Conflict – disagreements between stakeholders Stakeholder Interdependence Conflict Owners & Employees Owners & Customers • Owners need employees to carry out tasks, and employees need owners to pay them wages. • Owners want to pay low wages to make more profit, whereas employees want high wages for their work. • Owners need employees to be productive, and Employees need employees to train them. • Owners want employees to work many hours, whereas employees want to work as few as possible • Owners need customers to buy products to make profit, and customers need owners to provide them with products. • Owners want high prices to get high profits whereas customers want as low prices as possible. • Owners want to provide a cheap service to keep costs low, whereas customers want a high quality service. • Owners need customers to be loyal to maintain sales, and customers need owners to reward loyalty e.g. discounts Stakeholders Write down the interdependence and conflict relationships between the following stakeholders: Owners & Banks Owners & Governments Owners & the Local Community Stakeholder Interdependence Conflict Employees & Customers • Employees need customers to buy so they get paid, and customers need employees to give a good service • Employees want customers to spend as much as possible to get commission, whereas customers want as much discount as possible. Owners & Suppliers • Owners need suppliers to provide goods on time, and suppliers need owners to repeat orders. • Owners want supplies at a cheap price whereas suppliers want the opposite to maximise profits. • Owners need suppliers to provide quality products at a cheap price, and suppliers need owners pay on time • Owners want to wait as long as possible to pay, whereas suppliers want everything paid on time if not early.