What is a dynasty?

CHINA
HOMEWORK 12/16 & 12/17
Please define the following words using a dictionary, textbook glossary, or online resource. Do not use the word you are defining in the definition and do not type your homework!
1.
Dynasty
2.
3.
4.
5.
Mandate of Heaven
Feudalism
Bureaucrat
Philosophy
PRE-TEST (12/16 &12/17)
1.
What comes to mind when you think of China?
2.
Where is China? (Continent + major natural boundaries)
3.
About what percentage of the land in China is suitable for farming?
4.
Why was the Great Wall of China built?
5.
Name two ancient Chinese inventions still in use today.
PRE-TEST (12/16 &12/17)
What is a dynasty?
A. A small, crude explosive device invented in China circa 1100 BCE
B. A succession of rulers from the same family or line
C. A large cafeteria or dinning hall in the center of a Chinese village
D. A particularly gruesome or nasty way to die
What is a “Mandate of Heaven”?
A. The belief that everyone must go to heaven
B. When two or more men enjoy a day of beer and sports without their wives
C. The belief that rulers are divinely selected
D. The set of Chinese rules that determine whether or not one can enter heaven
What was the principle river of the civilization of ancient China?
A. Huang He River
B. Xi Jiang River
C. Tsingtao River
D. Monongahela River
BELL RINGER 12/18 & 12/19)
Describe the steps or stages of the Dynastic
Cycle of China
What role did the Mandate of Heaven play into the dynastic cycle?
HOMEWORK 12/18 & 12/19
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Please define the following words using a dictionary, textbook glossary, or online resource.
Do not use the word you are defining in the definition and do not type your homework!
Confucianism
Filial (or Filial Piety)
Daoism (may be spelled Taoism)
Silk Road
Tribute
BELL RINGER 1/6 & 1/7
What did you do over winter break? Don’t just tell me “nothing,” be specific ! Details, details!
i.e. is “nothing” sitting in the dark talking to yourself? Is it eating Cheetos and drinking Cherry
Dr. Pepper while watching a marathon of Scrubs?
Illegally downloading music and googling lolcats?
BELL RINGER 1/9 & 1/10
What did the script (written language) of the
Mesopotamians, Ancient Egyptians, the Harappan, and the Chinese all have in common?
What was the form of writing in Mesopotamia called?
What was the form of writing in Ancient Egypt called?
Does language stay constant (the same) or change over time?
BELL RINGER 1/13 & 1/14
What do we know about Buddhism?
What do we know about Confucianism?
What do we know about Daoism?
In what ways are they all similar? In what ways are they all different?
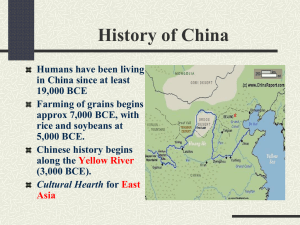
GEOGRAPHY
Located in Asia
Mountains and deserts cover about 2/3 of
China’s landmass
10% of land is suitable for farming
Natural boundaries: Pacific Ocean, Yellow Sea,
East China Sea, South China Sea, Himalayan
Mountains, Taklimakan Desert and Gobi Desert
WESTERN VS. EASTERN CHINA
Mostly desert
Arid climate
Thinly populated
Rich in petroleum and natural gas
The land between the
Chang Jiang or Yangtze
River and Huang He or
Yellow River is called the North China Plain
AKA “China’s
Heartland”
Densely populated
YELLOW RIVER VALLEY
The Huang He River (Yellow River)
“Cradle of Chinese Civilization”
“China’s Sorrow”
Loess (a windblown sediment) is deposited into the river, causing the yellow color and high silt content
6 th (or 7 th , depending on how you measure) longest river in the world
COLORING OF THE YELLOW RIVER
XIAOLANGDI DAM
DYNASTIC CYCLE
China has been historically led by dynasties , or a succession of rulers from the same family
Cycle (see graphic)
Power is claimed to come from a divine source:
Mandate of Heaven
Centralized
CHINESE DYNASTY SONG
TUNE ---- FRÈRE JACQUES / ARE YOU SLEEPING )
Shang
Zhou (“Joe”)
Qin (“chin”)
Han
(Repeat) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xJis9TSw1rE
Harvard Professors teach us a nursery rhyme
Sui (“sway” without “w”)
Tang
Song
(Repeat)
Yuan
Ming
Qing (“ching”)
Republic
(Repeat) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NIC4zom3w0g
Vogue-History Teachers
Mao Zedong ---------People’s Republic of China / Communist China
(Repeat)
XIA DYNASTY
“First” Dynasty of China c. 3000 BCE - c. 2000s BCE
The Xia dynasty was the first to irrigate, produce cast bronze and a strong army.
King Yu was selected as leader because of his brilliant engineering & mathematics skills, first to tame Huang He
King Yu was the first king to have his son follow him instead of a man chosen by his virtue. This made the Xia the first Chinese dynasty.
SHANG DYNASTY
c.1600 BCE - 1027 BCE
First written record of dynasty
Earliest glazed pottery, advanced bronze work and jade carving
365 1/4 days calendar year
First appearance of Chinese script
Oracle bones-questions etched on bone, then stabbed with a hot poker
Archaeologist have found palace foundations, burials, and rammed earth fortifications.
Capital city at Anyang
ZHOU DYNASTY
1027 BCE – 256 BCE
Period of Warring States 476 BCE – (221 BCE when Qin
Dynasty emerges)
Moved capital to Luoyang
Overthrows Shang in 1027 BCE claiming last Shang ruler lost the Mandate of Heaven
Kept many Shang cultural practices
Establish feudalism
King/Emperor owns land>Grants nobles use of land>nobles owe loyalty and military service>peasants on land serve nobles
Over time as villages>towns>cities, land holding nobles grow stronger
Zhou introduce coin money, blast furnace iron, and build roads and canals
QIN DYNASTY
221 BCE to 207 BCE
Qin Shi Huang declares himself “First Sovereign Emperor”
Military conquest and unification of warring states
Took land from nobles, assigned jobs, burned books
Legalism-
People are bad, law is necessary
Rule of Law
Spy networks
Public works
Bureaucracy
Standardized weights, measures, money, writing
Great Wall of China
Terracotta army
He dies, son murdered, incompetent ruler, peasant revolt
HAN DYNASTY
206 BCE – 220 CE
Liu Bang
Peasant birth, led rebellion
Merit system promotion
Confucianism
Silk Road
“Han” becomes a name for someone who is
Chinese
Replace what was destroyed under Qin
Arts flourish
“PERIOD OF DISUNITY”
220 CE – 589 CE
After Han, warfare and instability rule China
China breaks up into smaller kingdoms
AKA the “Six Dynasties”
Despite political troubles, arts again flourish in
China
Poetry
Buddhism
SUI DYNASTY
581 CE – 618 CE
Grand Canal
Over 1100 miles long
Military campaigns
605 CE first gov’t exams
TANG DYNASTY
618 CE – 907 CE
Empress Wu Zetian (r. 690-705 CE)
Concubine of Tang Emperor, marries his son after his death
Only empress of China to rule in her own right
“Golden Age”
Poetry, painting, music, dancing
Capital Chang'an, est. pop. 1,000,000
SONG DYNASTY
960 CE – 1279 CE
Technological highlights
Gunpowder
Compass
Paper money
Government exams for bureaucrats
Population growth
SILK ROAD
Ancient trade route linking China to the Mediterranean
Evidence of Chinese silk in Egypt c. 1070 BCE
Han Dynasty, Persians, Greeks, Romans, and Mongols aid development
Transport silk, trade goods, ideas, and disease
Crash course in
World History:
http://www.youtu
be.com/watch?v
=vfe-eNq-
Qyg&safe=active
CONFUCIANISM
K’ung-fu-tzu or Confucius (551 BCE – 479 BCE)
Born into a poor family of higher class
Well educated, becomes teacher and bureaucrat
Stresses family relationships, ancestor worship, harmony & balance, respect for others, avoiding extremes and perfecting society
Ethics/Morals rather than religion
Reinforces individual roles in society; everyone had their place (positive and negative)
DAOISM (TAOISM)
Laozi (Lao Tzu) circa 500 BCE (sometime during the Zhou Dynasty)
Tao Te Ching principle text
“The Way” or “The Path”
Wu wei or non-action/non-doing without effort
Think water!
Emptiness
Think of a container!
Desires are bad
Good vs. bad, ugly vs. beautiful; distinctions lead to desires
1
Bud.
(2)
Con. (2)
2
1
1
Dao.
(2)
Discovery Education- China: From Past to Present: Geography, Traditional Religions, and Beliefs (Film Resource)
CURRENT EVENTS: YELLOW RIVER
http://ngm.nationalgeographic.com/2008/05/ china/yellow-river/larmer-text/1#\
CURRENT EVENTS: DISCUSSION QUESTIONS
1.
2.
3.
4.
Please answer the following questions based of the information from Brook Lamar’s article “Bitter Water:
Can China the Yellow-China’s Mother River?”
Five “W”’s & 1 “H”: Who, What, Where, When, Why,
How?
What did you find to be the most interesting facts or events in this article? What, if anything, surprised you?
What is the significance? Why should we care? How can this affect the future?
How does this relate to your life?
CHINESE CALLIGRAPHY
Chinese characters, like all other languages changed over time
Five Principles of calligraphy
Balance, Posture, Knowledge of Tools, Rhythm, and
Control
http://file.tumbnart.com/wpcontent/uploads/2012/11/chinese%20symbol
%20tattoos%20art.jpg
BELL RINGER 1/15 & 1/16
Please evaluate the following primary source document:
“Words of truth are not pleasing.
Pleasing words are not truthful.
The wise one does not argue.
He who argues is not wise.
A wise man of Tao knows the subtle truth,
And may not be learned.
A learned person is knowledgeable but may not know the subtle truth of Tao
A saint does not possess and accumulate surplus for personal desire.
The more he helps others, the richer his life becomes.
The more he gives to others, the more he gets in return.
The Tao of Nature benefits and does not harm.
The Way of a saint is to act naturally without contention.”
Who is the probable author of this text?
What philosophy does this best fit with, Buddhism, Confucianism, or Daoism?
Why?
What does this mean to you?
BELL RINGER 1/17 & 1/23
Please evaluate the following primary source document:
"The superior man in everything considers righteousness to be essential. He performs it according to the rules of propriety. He brings it forth in humility. He completes it with sincerity. This is indeed a superior man.
The superior man is distressed by his want of ability. He is not distressed by men's not knowing him.
The superior man dislikes the thought of his name not being mentioned after his death.
What the superior man seeks, is in himself. What the mean man seeks, is in others.
The superior man is dignified, but does not wrangle. He is sociable, but not a partisan.
The superior man does not promote a man simply on account of his words, nor does he put aside good words because of the man.“
Who is the probable author of this text?
What philosophy does this best fit with, Buddhism, Confucianism, or Daoism? Why?
What does this mean to you?
PDF RESOURCES
Analects full text: http://www.indiana.edu/~p374/Analects_of_Con fucius_(Eno-2012).pdf
Tao Te Ching full text: http://www.with.org/tao_te_ching_en.pdf
ENGINEERING AN EMPIRE: CHINA
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I9evCYVir5k
&safe=active