Tang & Song Dynasties
advertisement

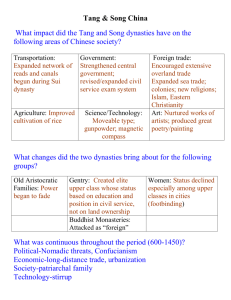
Tang & Song Dynasties China Unifies & Expands After the decline of the Han dynasty in the 200s CE, China remained divided for almost 400 years. Then, a young general named Tang Taizong took control & established the Tang dynasty in 618. It would last nearly 300 years until 907. The Tang dynasty picked up where the Han had left off by expanding Chinese territories. Vietnam Korea Tibet Neighboring countries, namely Vietnam, Korea & Tibet, were forced by the Tang to become tributary states. Tributary states were independent yet they were required to show respect to China’s power & provide regulars payment, or tribute. It was also during the Tang dynasty that Japan sent emissaries to China to conduct trade & learn Chinese culture. Japanese Missions to China during the Tang Dynasty Politically, Tang rulers saw it wise to revive the civil service system, which emphasized Confucian ideals, developed under the Han. The civil service exams provided the Tang government with a highly educated ruling elite, which served the emperor. The Mandate of Heaven was turned over to the Song in 960 under the leadership of Zhao Kuangyin. Like the Tang before it, the Song dynasty prospered, but invasions from outsiders, predominantly the Mongols, realized the end of the Song in 1279. Socially, Tang & Song society was broken down into three distinct classes: the gentry (nobles), peasants & merchants. Chinese Social Structure under the Tang & Song dynasties During the Tang dynasty land was redistributed to the peasants. This reform helped the Tang by reducing the power of large landowners while raising new tax revenues from the peasants. The Tang & Song dynasties witnessed an increase in foreign trade as Chinese merchants interacted with India, Persia & the Middle East. In order to trade abroad, the Chinese government developed a superior navy & issued paper money (1st ever) to expedite trade. Internally, the Chinese improved their infrastructure building roads, bridges & canals. These improvements in transportation helped connect the north to the south. By far the most important building project was the Grand Canal. Most significantly, the Grand Canal allowed food, mainly rice, from the south to travel efficiently to the north. The Tang & Song dynasties produced wonderful works of art. Chinese writers composed both short stories & poems in beautiful calligraphy. Chinese architects created what is called the pagoda, a temple with curved roof corners. A style which was later borrowed by the Japanese. Pagoda styles During this period the Chinese became so adept at making fine porcelain objects that across the world it was called “chinaware” or simply “china”.