Cell structure & Organelle Practice Test Power Point
advertisement

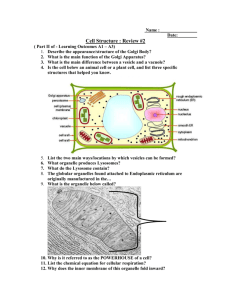
Cell Structure & Function
Eukaryotes
Plant & Animal Cells
http://www.kentuckycrosswords.com/library/nature/cell.html
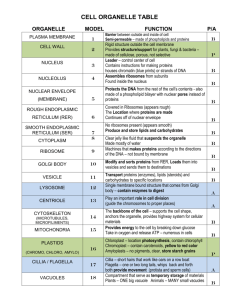
1.
An area inside the nucleus made up of RNA and
protein and plays a role in the formation of
ribosomes.
2.
The largest organelle in the cell which contain
chromosomes, which in turn contain the cell’s
DNA. It is like the brain of the cell.
3.
The most numerous organelle in a cell, it is the
site of protein synthesis. Some are attached to
the endoplasmic reticulum and some are free
floating in the cytoplasm.
4.
Small, bubble-like membranous structures that
store and transport cellular products. They
originate from the endomembrane system.
5. An elaborate membrane network studded with ribosomes.
It is the site where polypeptides are folded and assembled
into secretory proteins, like insulin and hemoglobin.
Membrane components are also made here.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Nucleolus
Nucleus
Ribosome
Vesicle
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
6. This organelle receives proteins and lipids from the ER
where they are modified, sorted, and packaged for
storage or transport in and out of the cell. It is known as
the “warehouse” or “shipping station.”
7. This represents one component of a web of proteins
known as the __. Its components include microtubules
and microfilaments, which help cells keep their shape,
divide, transport products, and move about.
8. An elaborate membrane network where carbohydrates,
lipids, hormones, and steroids are made. It also produces
enzymes that help get rid of toxins, such as drugs.
9. Known as the powerhouse of the cell. It converts
chemical energy stored in food (glucose, amino acids,
fatty acids) into usable compounds, like ATP.
10. Large membranous sacs that store material like water,
proteins, salts, and sugars. Plants have a very large one
that helps keep the plant upright. Paramecia uses special
ones that contract to pump excess water out of the cell.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Golgi apparatus
Cytoskeleton
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
Mitochondria
Vacuole
11. The portion of the cell outside the nucleus. It contains the
cytosol (liquid portion) and organelles.
12. These membranous sacs carry digestive enzymes that
breakdown and recycle macromolecules, like lipids, sugars,
and proteins. They also help break down organelles that
are no longer useful. They are not found in plant cells.
13. Found only in animal cells, these structures are made out
of microtubules. While associated with mitotic spindle
and cell division, it is unclear what their function is.
14. Made of a lipid bilayer, this structure controls what enters
and leaves the cell. It also protects and supports the cell.
15
15. Tiny hair-like folds in the plasma membrane that extend
from the surface of many absorptive and secretory cells.
They are about 10 times smaller than cilia.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
Cytoplasm
Lysosome
Centrioles
Cell (plasma) membrane
Microvilli
16
16. A long hair-like structure that acts primarily as an
organelle of locomotion.
17
17. Short hair-like structures that acts primarily as an
organelle of locomotion or to move liquid past the
surface of a cell. They are made of microtubules and
are about 10 times larger than microvilli.
18
α –Tubulin
β–Tubulin
18. The yellow thread-like structures (~25 nm diameter) are
made up of proteins called tubulins. They are found in hairlike organelles called flagella and cilia and act as “tracks” for
organelles and vesicles to move on. They are also make up
centrioles and mitotic spindles.
19
Amoeba
actin
19.
The purple thread-like structures (~7 nm diameter) are made
up of proteins called actin. They are constantly being built
up and taken down in different parts of the cell, allowing
amoebas and other cells to crawl along surfaces.
Desmosomes
20
Keratin
20. The green thread-like structures (8-12 nm diameter) is a
key structural component of cells. Made of keratin
proteins, these filaments also serve to anchor
desmosomes (anchoring junctions) to the cytoplasm.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
Flagellum
Cilia
Microtubules
Microfilaments
Intermediate filaments
21
21
21
21. Microscopic channels which traverse the cell walls of
plant cells and some algal cells, enabling transport and
communication between them.
22
22. The internal compartments formed by the folding of the
inner membrane of a mitochondrion. This folding
greatly increases the surface area for the production of
ATP in the cell.
23
1 µm
23. A small, circular piece of DNA located in the cytoplasm
of many bacteria.
24
24. Flattened membrane structures that contain fluid.
Found in endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi bodies.
25.
Hint: Powerhouse of the cell. What might the purple dots be?
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
Plasmodesmata
Cristae
Plasmid
Cisternae
Mitochondrion & Ribosomes (purple dots)
26.
Hint: Part of the endomembrane system. Be sure to identify
both the blue and green colored structures.
27.
Hint: This organelle modifies, sorts, and ships out proteins and
lipids.
Grana
Granum
Stroma
28.
Thylakoid
Hint: Notice the stacks of thylakoids (granum).
29.
Hint: They are shorter and narrower than cilia
and made of microfilaments (actin). Found in
30.
Hint: This is a cross section showing 20 microtubules in what is
known as a 9 + 2 pattern.
26. RER and ribosomes (green dots)
27. Golgi Apparatus
28. Chloroplast
29. Microvilli
30. Cross-section of cilium or flagellum
31.
Hint: This organelle is from a pea plant.
32.
Hint: This is a cross-section of an organelle. The inner folds are
called cristae.
Hint: They are longer and wider than microvilli and made up of microtubules.
33.
34.
Hint: They are not found in plant cells and they always occur in pairs
aligned perpendicular to each other. They are made of microtubules.
35.
Name both the “pancake stack” and associated bubbles.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
Chloroplast
Mitochondrion
Cilia
Centrioles
Golgi Apparatus with vesicles
Cell A
Cell B
36.
Identify the dark-blue linear structures bordering each cell.
37.
Hint: You are looking at the surface of a nuclear envelope
38.
What is the rod-shaped organelle and what membranous
structure surrounds it?
39a
39b
39.
Hint: None of these structures are cilia.
40
40.
What is the long tube
called and what is its
function.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
Cell (plasma) membrane
Nuclear pores
Mitochondrion & RER
Flagella & pili
Conjugation (sex) or F (fertility) pilus
(It is used to transfer a plasmid from a donor bacterium
to a recipient bacterium).
41a
41.
41b
Hint: Both are part of the endomembrane system.
Inside a nerve axon
~25 nm {
42.
What are these cytoskeleton tubes called?
Hint: Cilia and flagella are made of these.
Paramecium
{
43
43.
Hint: They pump water out of the cell.
44.
Hint: This is a cross section showing 27 microtubules. They are
arranged as 9 groups of triplet microtubules.
45
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
RER (41a) and SER (41b)
Microtubules
Contractile vacuoles
Cross-section of centriole or basal body
Mitochondria
46
47
48
49
50
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
Cell (plasma) membrane
Centrioles
Golgi body
Nucleolus
Nucleus with chromatin
51
Hint: Contains digestive enzymes.
52
53
54
55
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
Lysosome
Mitochondrion
Central vacuole
Chloroplast
Cell wall
56
57
58
59
60
56.
57.
58.
59.
60.
Cell (plasma) membrane
Golgi Apparatus
Nucleus
Cell (plasma) membrane
DNA (nucleoid)
61
62
63
64
65
61.
62.
63.
64.
65.
Capsule
Cell wall
Mesosome
Ribosome
Cytoplasm
66
67
68.
Animal, Plant, or Prokaryote?
69.
Animal, Plant, or Prokaryote?
70.
Animal, Plant, or Bacterium?
66.
67.
68.
69.
70.
Pilus
Flagellum
Prokaryote
Plant (corn leaf)
None of these. Euglena are protists.
(Euglena have chloroplasts like plants but lack a cell
wall. Unlike plants, they have flagella, a red eyespot,
and are able to consume food via phagocytosis.