10.9 * Sense of Sight - Tipp City Exempted Village Schools
advertisement
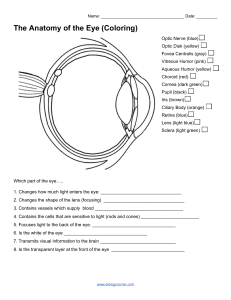
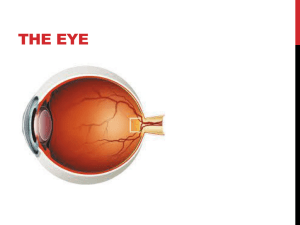
10.9 – Sense of Sight The Eye as an Organ • Lies w/ the Orbit ▫ Made of bone & contains fat, bl. Vessels, nerves, & connective tissue • Provides vision along with accessory organs ▫ Eyelids Thinnest skin of body Lined with conjunctiva – mucous membrane that folds back to cover surface of eye as well ▫ Lacrimal apparatus Lacrimal gland + ducts Secretes tears continuously – lubrication & antibacterial enzyme ▫ Extrinsic eye muscles Attach to sclera Move eye in all directions Structure of the Eye • Fluid-filled hollow sphere with 3 layers (tunics) • Outer Tunic ▫ Fibrous tunic Transparent cornea White sclera ▫ Optic nerve & bl. vessels pierce the sclera @ back Structure of the Eye • Middle Tunic ▫ Choroid coat Vascular, darkly pigmented 2 functions Nourish other tissues Keep inside of eye dark ▫ Ciliary body Forms ring around front of eye contains ciliary muscles & ligaments = holds lens in place & changes its shape to focus objects Called accomodation ▫ Iris Thin, smooth muscle Adjusts to amount of lilght entering the pupil Structure of the Eye • Middle Tunic cont. ▫ Anterior Cavity consists of: Anterior Chamber b/w cornea & iris Posterior Chamber b/w iris & vitreous body housing the lens Filled with aqueous humor Fluid that circulates from one chamber to the other through the pupil Structure of the Eye • Inner Tunic ▫ Covers back side of eye to the ciliary body ▫ Retina – contains photoreceptors Fovea Centralis = back of retina, point of sharpest image Optic disk = nerve fibers leave eye; causes blind spot ▫ Open cavity of the eye in front of the retina is filled with vitreous humor Light Refraction • Light waves must be focused – called refraction • Cornea & lens bend light ▫ Bent light is focused on retina ▫ Aqueous & Vitreous humors also help to bend/refract the light Visual Receptors • 2 kinds: ▫ Rods Elongated Sensitive to light; function in dim light Produce colorless vision ▫ Cones Provides sharp images in bright light Produces vision in color Fovea centralis contains the most cones Visual Nerve Pathways • Axons of ganglion cells leave eyes to form the optic nerves • Fibers from the medial half of the retina cross over in the optic chiasma • Impulses are transmitted to the thalamus • Then sent to the visual cortex of the occipital lobe for final association Optical Device – The Eye • Myopia – nearsighted ▫ Eyes are too long • Hyperopia – farsighted ▫ Eyes are too short • Astigmatism ▫ Cornea misshapen • Cataracts ▫ Clouding of the lens • Floaters ▫ Cell fragments break off Lasik eye surgery