Honors Cell Structure (Organelles) Packet
advertisement

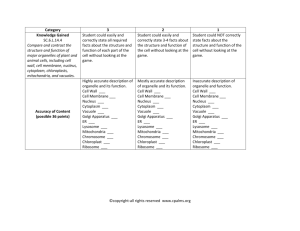
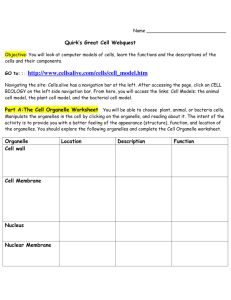
Honors Organelle Jigsaw Use sections 4.4-4.18 in your textbook to answer the following questions based on your assigned groups. You can answer on this paper or on a separate sheet of notebook paper. A- 4.4 Essential Question: Why are organelles beneficial/necessary for eukaryotic organisms? A- 4.5 Nucleus 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What does the nucleus contain? What is the function of the nucleus? What is the function of DNA? In what form is it ordinarily found (term for this)? What encloses the nucleus? What is its function? What is the nucleolus and its function? A- 4.6-4.8: Endoplasmic Reticulum 1. What is the endoplasmic reticulum? 2. What is it connected to? 3. Smooth ER a. Why is it called smooth? b. What important substance does it contain in its membrane? c. What are two major functions of the smooth ER (skip Ca storage)? 4. Rough ER a. Why is it called rough? b. What are the two functions of the rough ER? c. What is the function of a ribosome? d. What does the rough ER send its products? e. What are vesicles? B- 4.9: Golgi Apparatus 1. What are the functions of the golgi apparatus? 2. How does the golgi determine where molecules will go? 3. What are the functions of the two sides of the golgi apparatus? B- 4.10 & 4.11: Lysosomes 1. 2. 3. 4. Lysosomes are produced in plant or animal cells? What do lysosomes contain? Where are lysosomes produced? What are the 3 functions of a lysosome? a. b. c. 5. How can defective lysosomes result in excess accumulation of a compound in a cell? B- 4.12: Vacuoles 1. What is the function of a plant’s central vacuole (NOT SEEN IN ANIMALS)? 2. What is a contractile vacuole used for? 3. In what type of organism is a contractile vacuole found? B- 4.13: Endomembrane System 1. How do transport vesicles help tie together the endomembrane (inner membrane) system? C- 4.14: Chloroplast 1. What is photosynthesis? 2. In what type of cells are chloroplasts found? 3. How many membranes does the chloroplast have? C- 4.15: Mitochondria 1. What process do mitochondria carry out? Explain this process. 2. How many membranes does the mitochondria contain? 3. Why do mitochondria contain folds? C- 4.16: Cytoskeleton 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What is the cytoskeleton made of? Where is it found in the cell? What are the functions (2) of the cytoskeleton? What are the 3 types of fibers found in the cytoskeleton? What is an example of a microfilament? What do they help to support? How are microfilaments and intermediate filaments different? What are the functions of intermediate filaments? What are microtubules composed of? What are the functions of microtubules? 2 D- 4.17: Cilia & Flagella 1. Cilia a. What are cilia? b. Where are cilia found in the human body? c. What is the function of cilia? 2. Flagella a. What are flagella? b. Where are flagella found in the human body? c. What is the function of flagella? d. What are both cilia and flagella composed of? D- 4.18: Cell Junctions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Why are cell junctions (areas where cells meet) necessary? What are plasmodesmata? In what types of cells are they found in? What is the function of plasmodesmata? What are tight junctions and where are they found? What are anchoring junctions and where are they found? What are gap junctions and where are they found? Honors Only- Matching _____ 1. Whip-like tail used for propulsion A. Gap junction _____ 2. Tubes used to provide tracks for organelle movement B. Microtubule _____ 3. Solid rods made of globular proteins for cell shape C. Cilia _____ 4. Hold cells together to protect against stretching D. Tight junction _____ 5. Rope-like fibrous proteins used for anchoring organelles E. Flagella _____ 6. Hair like extensions for movement F. Microfilament _____ 7. Bind cells tightly together; leak-proof G. Plasmodesmata _____ 8. Allow small molecules to flow between any cells H. Anchoring junction _____ 9. Hollow tubes made of tubulins I. Intermediate filament _____ 10. Channels between plant cells for water and chemical flow 3 Cell Organelles Packet Part A: MATCHING Match the organelle to its correct function/description. Some letters may be used more than once. _____ 1. Converts sunlight into chemical energy A. Smooth ER _____ 2. Modifies proteins before shipment out of cell B. Mitochondria _____ 3. Packages and sorts proteins for shipping in the cell C. Nucleus _____ 4. Synthesizes lipids D. Golgi Body _____ 5. Breaks down food into usable energy for the cell E. Chloroplast _____ 6. Regulates what enters and exits the cell F. Nucleolus _____ 7. Contains DNA & controls the cell G. Rough ER _____ 8. Creates vesicles to house the materials for cell transport H. Cell membrane _____ 9. Detoxifies the cell of drugs/chemicals _____ 10. Synthesizes ribosomes Part B: True/False Write T or F on the line below for each statement. If false, correct it. _____ 1. All cells have a cell membrane and a cell wall. _____ 2. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells contain DNA. _____ 3. The nucleus is the site of most chemical reactions within the cell. _____ 4. The nuclear membrane does not allow anything to enter or exit the nucleus. _____ 5. DNA is usually found in the condensed form of chromosomes. _____ 6. Golgi apparatus has 2 sides- one that receives proteins from the ER and one that ships proteins out after finishing them. _____ 7. Plasmodesmata have 2 membranes- one inner and one outer. 4 Part C: Draw a line to connect the cell part/organelle to its correct function/description. There may be multiple lines connecting to a single cell part. _____ 1. Contains digestive enzymes Ribosomes _____ 2. Contains instructions for building proteins Chloroplast _____ 3. Site of protein synthesis (creation) Cell wall _____ 4. Controls movement of DNA during cell division Centriole _____ 5. Found floating in cytoplasm and on the rough ER Vacuole _____ 6. Destroys damaged organelles to recycle for parts Cytoskeleton _____ 7. Site of photosynthesis Lysosome _____ 8. Digests food particles to release nutrients DNA _____ 9. Rigid outer layer to protect and support plant cell shape _____ 10. Protein network to help with internal structure and movement Part D: Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Put a check in the appropriate column(s) to indicate whether the following organelles are found in plant cells, animal cells or both. Organelle Plant Cells Animal Cells Organelle Cell Wall Mitochondria Vesicle Nucleolus Chloroplast Nucleus Centriole Plasma membrane Cytoplasm Central vacuole Cytoskeleton Ribosome Endoplasmic reticulum Vacuole Plant Cells Animal Cells Golgi apparatus Lysosome 5 Part E: Cell City Analogy – Match the organelle to the underling city part in the scenario. In a far away city called Eukaryopolis, the main export and production product is the steel widget. Everyone in the town has something to do with steel widget making and the entire town is designed to build and export widgets. The town hall has the instructions for widget making, widgets come in all shapes and sizes and any citizen of Grant can get the instructions and begin making their own widgets. Widgets are generally produced in small shops around the city, these small shops can be built by the carpenter's union (whose headquarters are in town hall). After the widget is constructed, they are placed on special carts which can deliver the widget anywhere in the city. In order for a widget to be exported, the carts take the widget to the postal office, where the widgets are packaged and labeled for export. Sometimes widgets don't turn out right, and the "rejects" are sent to the scrap yard where they are broken down for parts or destroyed altogether. The town powers the widget shops and carts from a hydraulic dam that is in the city. The entire city is enclosed by a large wooden fence, only the postal trucks (and citizens with proper passports) are allowed outside the city. City Structure Organelle Explanation Mitochondria Ribosomes Nucleus Golgi Apparatus Protein Cell Membrane Lysosome Nucleolus 6 Organelle Structures/Special Features Function (*Not organelle) Plants, Animals or Both Nucleus Nucleolus Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth: Smooth: Rough: Rough: Found: Ribosomes Two sides: Golgi Apparatus Contains: 1. Produced by: Lysosome 2. 7 Organelle Structures/ Special Features Function Plants, Animals or Both Central Vacuole Made in: *Vesicles Chloroplast Mitochondria Made of: *Cytoskeleton (not an organelle) *Cell Junctions 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. *Flagellum/Cilia 8 9 Label the cell using the Word Banks. Type of cell: Word Bank Ribosomes Cell membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Centriole Golgi Body Vesicle Flagella Smooth & Rough ER Cytoskeleton Type of Cell: Word Bank Ribosomes Cell membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Chloroplast Golgi Body Central Vacuole Smooth & Rough ER Cytoskeleton 10