Experiment 5:
advertisement

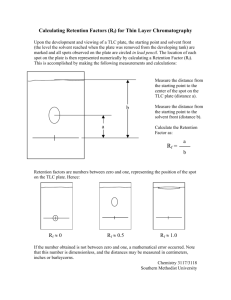
Experiment 4: TLC and HPLC of Nitroanilines Objectives To learn the separation techniques of Thin Layer Chromatography and HPLC chromatography. To use these techniques to separate and identify o-nitroaniline and p-nitroaniline in sample mixture. To identify the compounds based TLC Rf and HPLC Rt. NITROANILINE STRUCTURES NH 2 NH 2 NO 2 NO 2 p-nitroaniline MF: C6H6N2O2 o-nitroaniline MF: C6H6N2O2 MW: 138.13 g/mol mp: 147-151oC MW: 138.13 g/mol mp: 70-74 oC hazards: Toxic if ingested Toxic if inhaled hazards: Toxic if ingested Toxic if inhaled uses: Organic dyes dipole moment: 3.00 D uses: Organic dyes dipole moment: 2.27 D POLARITY OF NITROANILINES H O N N H H N H O N O O p-nitroaniline dipole moment (): 3.00 D LARGER = MORE POLAR o-nitroaniline dipole moment (): 2.27 D SMALLER = LESS POLAR ANALYTE POLARITY VS. STATIONARY PHASE Polar analyte binds to the SiO2 sites, so it sticks and moves slowly Nonpolar analyte doesn’t bind to SiO2 sites so it doesn’t stick and moves quickly Bulk Solvent (Mobile Phase) OH Si OH O Si OH O Si OH O Si OH O Si OH O Si ANALYTE Silica (Stationary phase) SOLVENT Bulk Solvent (Mobile Phase) OH Si OH O Si OH O Si OH O Si Silica (Stationary phase) OH O Si OH O Si THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Sample and standards are applied on origin line of POLAR TLC plate. TLC Plate is placed in a developing chamber containing a nonpolar, organic solvent. The substance dissolves in the solvent, and is carried up the plate. The polarity of the substance determines how far up the plate the substance travels. Once developed, the spots are visualized. The spots are marked with a pencil, and the distances traveled by the spots are measured. The distance the unknowns spot has traveled is called the Rf value, and compared to Rf values of standard solutions, can be used to identify compounds. A B U C D filter paper A B U C D THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Supplies for TLC Analysis Preparing TLC Plate Applying solutions to TLC plate THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Calculation of Rf values 2.0 cm 5.0 cm = 0.40 Rf (B) = 3.0 cm = 0.60 Rf (A) = Solvent Front 5.0 cm Distance solvent migrated = 5.0 cm 4.0 cm Rf (C) = 0.8 cm = 0.16 Distance A migrated = 3.0 cm 5.0 cm Distance B migrated = 2.0 cm 3.0 cm Rf (D) = 4.0 cm = 0.80 5.0 cm Distance C migrated = 0.8 cm Origen x A x x x x B U C D 0.8 cm Rf (U1) = 3.0 cm = 0.60 5.0 cm Rf (U2) = 0.8 cm 5.0 cm = 0.16 The Rf value is defined as the distance the center of the spot moved divided by the distance the solvent front moved (both measured from the origin) THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Rf values Rf values can be used to aid in the identification of a substance by comparison to standards. The Rf value is not a physical constant, and comparison should be made only between spots on the same sheet, run at the same time. Two substances that have the same Rf value may be identical; those with different Rf values are not identical. HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY (TLC vs. Normal Phase HPLC) Normal Phase (SiO2) TLC Normal Phase (SiO2) a b a 0 b c Time c x Note: A high TLC Rf value = a low HPLC retention time! HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY Sample loaded here SiO2 packed inside tube HPLC chromatogram produced HPLC CHROMATOGRAMS OF NITROANILINE STANDARDS o-nitroaniline standard SOLVENT: 50:50 hexane/ethyl acetate Rt: 1.074 min p-nitroaniline standard SOLVENT: 50:50 hexane/ethyl acetate Rt: 1.382 min HPLC OF NITROANILINE SAMPLES Nitroaniline sample mixture SOLVENT: 50:50 hexane/ethyl acetate o-nitroaniline Rt: 1.074 min p-nitroaniline Rt: 1.394 min By comparison of sample retention times to standard retention times, the active ingredients can be identified. Compound Retention Times of Standards Retention Times of Sample o-nitroaniline 1.074 1.074 p-nitroaniline 1.382 1.394 FOR MORE INFORMATION... Please refer to Appendices E and F in the back of your laboratory manual for further explanation of theory behind chromatography. SAFETY CONCERNS Nitroanilines are toxic if inhaled or ingested. Use gloves at all times during the experiment! All solvents used in today’s experiment are flammable, eye, and skin irritants. Be sure to wash your hands before leaving the laboratory. Safety goggles are required! WASTE MANAGEMENT Place waste solvent from TLC sample preparation and TLC developing chambers into container labeled, “Organic Waste (TLC)”. Place all used TLC capillary tubes in the broken glass container. TLC chambers should be left with the lids removed in the lab drawer. Do not clean with soap, water, OR acetone!