Ch. 8 Notes
advertisement

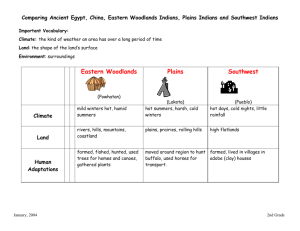
Settling the West Great Plains - “Great American Desert” 1000 sq miles from the 100th meridian to the Rocky Mountains Geography: Mountains, Plateaus, Plains, Deserts Non-Forested area: Tall and short prairie grasses, desert shrubs Characteristics: poor soil, poor drainage, intense cold, intense winds, not enough rainfall Animals of the Great Plains Characteristics: grass eaters, survive with little or no water Jackrabbit – true hare; ate farmer’s crops Prairie Dogs – “Squirrels of the Plains” live in colonies, create hazardous holes in ground, controlled through poison Wolf/Coyote – “Outlaws of the Plains” prey on helpless, sick, or young Buffalo – dominated human life stupid (because…) ran slowly & are clumsy poor eyesight no fear of sound (but…) excellent sense of smell Humans – Native American Indians Tribes of the Great Plains Sioux Cheyenne Crow Arapaho Kiowa Typical Indian Village Native (North) American Indians Relied on two animals – Buffalo & Horse Buffalo – Meat = food Hide = shelter & clothing Bones = tools & weapons Sinew = thread & bow strings Hair = saddle pads Horns = spoons & flasks Gallstones = war paint Manure = fuel Horse – Origins = Spanish Conquistadors Abandoned & left to breed = Mustangs Importance of the Horse •Became nomadic •Less inclined to farm •Used as a “beast of burden” – pack animal •Source of Wealth – paid debts, bought wives, could be eaten if necessary •Become better buffalo hunters New Weapons developed due to the Horse Small Bow – 2 ½ - 3 ft long Arrows – tipped with points of bone, flint, or steel barbs Most carried a shield made from hides of buffalo necks (which had been smoked and then hardened with glue made from horse’s hoofs) By nature, the Plains Indians were more fierce, cruel, and least civilized of all of the tribes Most Feared = Comanche Indians • spent majority of time mounted • used horse itself as a shield during battle • greatest horse thieves (smelled like horses so other horses didn’t spook) Perfected the art of torturing their enemies • Artistic dissections • Partial flayings • Dislocation of body parts • Breaking and/or splitting of fingers & toes Language Unique – quiet forms • Sign Language – helped different tribes communicate US Army (under Capt. Clark) studied and included sign language into the signal flags – used first in the Civil War • Smoke Signals Encounters with Whites Early 1800s – Whites moved Indians to reservations in Oklahoma – Trail of Tears There goes the neighborhood! US Gov’t paid Indians annuities 30-50 cents an acre once year Wasn’t enough to live off of – starved Indians left reservations to find food Army sent 9th/10th Cavalry Units (Buffalo Soldiers) Were called in to hunt the Indians down Railroads brought people West and in 1869, the Transcontinental Railroad was completed. Promontory, Utah •May 10, 1869 at Promontory, Utah “The Wedding of the Rails” •Central Pacific and Union Pacific May 10, 1869 at Promontory, Utah “The Wedding of the Rails” Central Pacific and Union Pacific Taming of the Plains Indians Railroad – “iron arrow” – hired people to lay tracks; shot buffalo to feed RR workers. “Buffalo Bill” Cody – sharpshooter for RR Took hides for buffalo robes & tongues; Killed 1000+/day Buffalo destroyed iron RR tracks By 1885 – fewer than 1000 left out of 15M Decline of the Buffalo Six-Shooter (revolver) – inventor Samuel Colt Texas Rangers needed protection from the Comanches. Advantage = 6 shots Colt .45 pistol Winchester Repeating Rifle Disease – like other Native Americans, Plains Indians were not immune to White man’s diseases such as small pox and measles Liquor – “fire water” – cannot tolerate alcohol became addicted easily 3Bs (bullets, bacteria, bottle) brought by RR Major Conflicts Fetterman’s Massacre – Sioux Chiefs Crazy Horse, Red Cloud, & Sitting Bull ambush US Army led by Capt Fetterman Sand Creek Massacre – Army sent to punish Sioux for Fetterman’s Massacre. Army killed Indians under white flag of truce Nez Perce – under Chief Joseph tried to flee to Canada. Army finally caught & returned the Nez Perce to the reservations “I Will Fight No More Forever” Battle of Little Bighorn – Army sent to bring back Sioux to reservations. 7th Cavalry took on 2500 Indians w/ 210 soldiers “Custer’s Last Stand” Little Big Horn Memorial Site With the massacre of the 7th Cavalry at the Battle of the Little Bighorn public attention is turned towards what the Gov’t was doing. Helen Hunt Jackson – A Century of Dishonor detailed: --US Gov’t’s repeated violation of treaties --Mistreatment of Indians on reservations Sarah Winnemucca – Life Among the Paiutes: Their Wrongs and Claims (same as Jackson) Gov’t Assimilation Policy Dawes Act: Broke up reservations Head of household = 160 acres Single Men = 80 acres Children = 40 acres Began to education Indians read/write farming techniques Life on the Reservations Turned to spiritual activities or traditional dances: a. Bison Dance bring back buffalo b. Spirit or Mescalero Dance – drive away evil and sickness and bring good fortune to the tribe. c. Snake or Rain Dance – used to bring in a good harvest. d. Sun Dance – manhood ritual; visible symbol of bravery and in some cases necessary in order to marry young girls. The Ghost Dance Movement 1890 Paiute medicine man Wovoka promised the return of the buffalo and Indian way of life. The religion prophesied the end of the westward expansion of whites and a return of Indian land. The ritual lasted five successive days, being danced each night and on the last night continued until morning. Hypnotic trances and shaking accompanied this ceremony, which was supposed to be repeated every six weeks. Battle of Wounded Knee – last Indian battle Indians were performing the Ghost Dance – designed to bring back animals, dead relatives, and return to a life before the white man’s arrival (wore ceremonial clothing that for protection against Ghost Shirt Whites) If performed – would be immune to white man’s bullets. Accounts differ but shots were fired and both Indians and soldiers were killed. Impact – religious ceremony that proved that Indians were not immune to white man’s bullets – Indians lost all hope and resigned themselves to life on the reservations 300 Indians & 25 Whites died Break for Activity Cattle Kingdom Spanish brought cattle to the New World & abandoned New breed developed – longhorn Tougher Can survive on poor grasslands By 1865 - 5 million roaming free Had long horns (4-6 ft span) •No real market in Texas •In Texas, sold for $3-$5 a head until RR came west •In the railheads, sold for 30-$50 a head •Pioneers -- Cattle Barons --with ranches of 1,000+ acres •Average ranch = 3,000 head of cattle Demand for Cattle Increased because: Civil War – N & S needed fresh meat & the only source was from out West Railroads – came out west to railheads in Missouri & Kansas Yearly Routine on Ranches Winter: Repaired gear Gathered firewood Cut ice from waterholes Tended to sick cows/calves Found strays Drove cattle to snow-free grass Spring: Check water conditions Rescue cows from mud holes Round up: horses – broke them for riding cows – branding of mavericks (no brands) castrated young bulls Handout - Brands Summer: Inspect water holes Check for worms Scatter bulls for mating Fall: Finish branding Sort cattle (keep or sell) Start Long Drive to Railheads Long Drives Took 3,000 head of cattle 1 chuck wagon/cook 1 Trail boss 1 Wrangler – Remuda (7-10 extra horses per cowboy) •12-15 cowboys – average age = 18; paid $1/day •2-3 months to complete •Traveled 25-30 miles/day ( =1,000+ miles) •Worked 18 hour days Drag: least desirable – dust & smell found stragglers that had wandered off from the main herd Long Drive Positions Point: most dangerous -stampedes most desirable -clean air Swing/Flank: kept herd together Most Famous Trails: Chisholm Trail (most famous) Shawnee Trail Western Trail Goodnight- Loving Trail (sold to miners) Handout – Trails & Positions Cowboy Uniform Hat - Most wore sombreros for protection from rain, snow, hail, and sun Used as a fan and bucket to carry water Part of uniform most particular about Bandana - Used as a mask – keep out dust Form of insulation in hat Wash clothe Tourniquet (snake bite/gored by longhorns) Duster - Protective overcoat w/ split in back Chaps – Leg protection shotgun (pant like) batwing (tied/buckled on the side) woolies (front covered with wool) Spurs – Used to move the horse quickly Most common type = work spur Boots – Designed to keep foot in stirrup Most common type today = ropers Cowboy Equipment Rope/Lariat – Used to capture cows/horses Avg length = 60 ft. Running Iron – straight iron rod used to free-hand brands on mavericks Knife – 6 inch blade stored in boot/waist Saddle – Personally owned Cost - $30.00 lasted 25-30 years Horse – Used on the range but usually was not personally owned Gun/Rifle – Most repeating rifles Only carried on open range NOT on long drives for fear of stampedes Mexican Influence: Original Cowboys came from Mexico Language: vaquero – cowboy lasso – roping lariat -- rope RODEO America’s oldest original sport Most lasting form of amusement Friendly competition between ranches Nat Love – most famous all-around Cowboy Rough Stock Events Staying on the animal for 8 second Saddle Bronc Bareback Bull Riding Timed Events Competition based on an individual’s best time Steer Wrestling Calf Roping Barrel Racing End of the Cattle Kingdom • Arrival of the sheepherders – sheep clipped grass too short for cows to eat • Beef prices fell by 40% - overstocking ranges • Mother Nature – drought, floods, blizzards in the 1890s • Lack of good, clean water • Invention of barbed wire - Joseph Glidden •Arrival of farmers – used barbed wire to close off the open range •Range wars started – competition for land/water increased b/w ranchers and farmers •Forced to reduce herd size and start breeding programs •Ranches became hay farms as well as grazing ranches (need hay for winter) •Stories exaggerated by dime novels Branding Cattle & Cowboy Slang Activities Handout Arrival of the Farmers 1862 – Homestead Act 1. Gov’t gave 160 acres for a $10.00 deposit. 2. After 5 years of improving the land, farmers got clear title. 3. Used barbed wire to stake out their claims Life on the Prairie Homes – Made out of sod – dirt & grass little bit of wood - expensive Wells had to be dug 300+ ft. to find water Climate – extremes (100°F+ vs. below 0°) Examples of Sod Houses Farming Styles Normal Farming – using iron/steel plow planted 6 inch rows Dry Farming – planting seeds deep into the ground to find moisture in areas that only get 15-20 inches of rain a year Bonanza Farming – LARGE farms of up to 50,000 acres using crews of workers Primary Crop = WHEAT Problems Farmers Encountered •Drought •Prairie Fires burned crops •Grasshopper plagues ate crops •Planted too shallow and prevailing winds blew away top soil (with nutrients) •Overproduction of crops caused prices to drop •Bought expensive machinery on credit •Bought farms on credit •Banks foreclosed – couldn’t pay off debts •Forced to become tenant farmers working for someone else Growth of the Mining Industry Types of Mining: Placer Mining – uses picks, pans, & shovels Quartz Mining – digging deep in the ground to find the mineral that one was looking for Hydraulic Mining – used a stream of water to blast out sides of mountains – used with placer mining technique Biggest American Strike: Comstock Lode, 1859 Henry Comstock found huge SILVER deposit The extensive and expensive surface and underground workings of the various Comstock silver mines required large outlays of investment capital. Most of the investors were in San Francisco. Virginia City into a boom town due to SILVER 1. caused crime to increase 2. led to vigilance committees civilians who took law into their own hands since regular lawmen were in short supply 3. Attracted women – • did laundry for miners • danced in saloons and took tips from miners • performed personal services (prostitution) (Women used silver (& gold) and bought property) Other Metal Deposits Gold – Pikes Peak, Colorado Black Hills, Dakota Territory Lead – Leadville, Colorado Copper – Montana Territory (Precious metals needed for factories back East & plays into the Industrial Revolution of the late 1800s) Wrap Up: Manifest Destiny: Am believed they had a God-given right to occupy the land from the Atlantic to the Pacific. Those that came west, encountered the Native Americans, started huge cattle ranches, established farms, and mined for precious metals.