The Integumentary System
advertisement

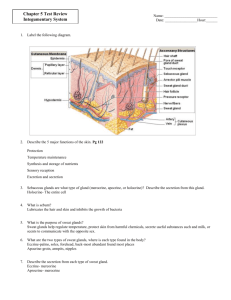
The Integumentary System The Skin and its Appendages The Skin Two main components ● Epidermis ● Dermis ● (Hypodermis) Epidermis Cells of the Epidermis ● Keratinocytes ● Melanocytes ● Dendritic Cells (Langerhans cells) Epidermis Layers of the Epidermis ● Thick Skin ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ Stratum Basale Stratum Spinosum Stratum Granulosum Stratum Lucidum Stratum Corneum ● Thin Skin ○ Absence of Stratum Lucidum Epidermis Layers of Epidermis ● ● ● ● Stratum Basale (germinatum) Single row of stem cells 10-25% melanocytes very small amount of tactile cells Epidermis Layers of the Epidermis ● Stratum Spinosum ○ ○ ○ several cells thick weblike intermediate filament network melanin granules and dendritic cells present Epidermis Layers of the Epidermis ● Stratum Granulosum ○ ○ ○ Keratinization Begins Keratohyaline granules Lamellar granules Epidermis Layers of the Epidermis ● Stratum Lucidum ○ ○ Only present in thick skin 2-3 rows of clear, flat, dead keratinocytes Epidermis Layers of the Epidermis ● Stratum Corneum ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ anucleate 20-30 cells thick ¾ of epidermis high keratin content thickened, glycoprotein covered plasma membranes loses 50k cells/min Dermis Composition ● Connective Tissue proper ● Rich nerve and vascular supply ● contains hair follicles, glands, and sensory receptors Layers ● Papillary Layer ● Reticular Layer Dermis Papillary Layer ● ● ● ● ● Thin areolar highly vascularized low density (great for phagocytes) Dermal papillae (form friction ridges in thin skin) Dermis Reticular layer ● ● ● ● 80% of Dermis dense irregular connective tissue blood vessel network (cutaneous plexus) cleaveage and flexure lines Appendages of the Skin Hair and Hair Follicles Nails ● Sweat Glands ○ Eccrine Glands Apocrine Glands Sebaceous (oil) Glands Appendages of the Skin Hair and Hair Follicles ● Structure of hair ● Structure of a hair follicle ● Types and growth of hair ● Hair thinning and baldness Appendages of the skin Structure of a hair (fig 5.5) ● Produced by hair follicles ● Conists primarily of dead keratinized cells ● cells contain hard keratin Regions ● Shaft ● Root Concentric Layers ● Medulla ● Cortex ● Cuticle Appendages of the skin Structure of a Hair Follicle (fig 5.5) ● Epithelium based ● Hair bulb ● Hair follicle receptor ● Hair papillae ● Peripheral connective tissue sheath ● Epithelial root sheath Appendages of the Skin Types and Growth of Hair ● Vellus Hair ● Terminal Hair Appendages of the Skin Hair Thinning and Baldness ● Alopecia ● True Baldness (Male Pattern) Appendages of the Skin Nails (fig 5.6) ● Scale-like modification of epidermis ● hard keratin ● free edge, nail plate, root ● nail bed ● nail matrix ● nail folds and cuticle Appendages of the Skin Sweat (Sudoriferous) Glands ●Eccrine (Merocrine) Sweat Glands ●Apocrine Sweat Glands Appendages of the Skin Sebaceous (Oil) Glands ● Simple branched alvolar glands ● secrete sebum ● holocrine type glands ● secrete into hair follicles and occasionally pores Skin Functions Protection ● Chemical Barriers ○ acid mantle ● Physical Barriers ● Biological Barriers ○ dendritic cells, macrophages, DNA Skin Functions Body Temperature Regulation Heat Loss ● Vaodilation ● heat loss through sweat evaporation Heat conservation ● Vasoconstriction Skin Functions Cutaneous Sensation Skin Functions Metabolic Functions ● Produces vitamin D precursor ● disarm cancer causing chemicals ● activate some steroid hormones Skin Functions Blood Resevoir ● 5% of total blood volume Skin Functions Excretion ● ammonia, uric acid, urea, salt, water. Homeostatic Imbalances of Skin Skin Cancer ● Basal Cell Carcinoma ● Squamous Cell Carcinoma ● Melanoma ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ Asymmetry Border Irregularity Color Diameter Elevation Study Guide Will Post Wednesday