Biology I Mid-Term Examination * Review Exercises * Unit 4
advertisement

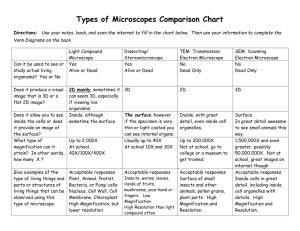
Biology I Mid-Term Examination – Review Exercises – Unit 4 Complete the following exercises with a partner to prepare for the upcoming examination. These may be collected at the end of the class period. 1-3. List the three parts of the modern cell theory. 1. Cells are the basic units of living things. 2. All living things are composed of cells. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells through the process of cell division. Match the statement in Column A with the scientist in Column B. Column A Column B __ B__ 4. developed the first useful compound light microscope A. Robert Hooke __A__ 5. used the term ‘cells’ to describe the compartments that he saw in cork because they reminded him of the rooms in a monastery B. Anton von Leeuwenhoek __E__ 6. stated that all animals are made of cells D. Rudolf Virchow __C__ 7. stated that all plants are made of cells E. Theodor Schwann C. Matthias Schleiden __D__ 8. stated that all cells come from pre-existing cells through the process of cell division Label the parts of the compound light microscope. eyepiece arm nosepiece low power objective high power objective stage clips stage coarse focus adjustment diaphragm fine focus adjustment light source base 1 21. How do you determine the total magnification of a compound light microscope? The total magnification of the a compound light microscope is determined by multiplying the magnification of the eyepiece lens by the magnification of whatever objective lens is being used. 22. List the four systems of the compound light microscope. What parts of the microscope belong to each system? Microscope System Parts of this Microscope System light system light source & diaphragm focusing system fine & coarse focus adjustments lens system eyepiece, nosepiece, and objectives stage system stage & stage clips 23. How does the orientation of the image of an object viewed under a compound light microscope differ from the actual orientation of the object? Objects viewed under a compound light microscopes appear upside down and backward as compared to their actual orientation on the slide. 2 24. Use the Venn diagram to compare and contrast compound light microscopes and electron microscopes. Compound Light Microscopes Use light to make an image. Can magnify objects up to 1,000 x Electron Microscopes Can be used to look at specimens that are dead. Allow scientists to investigate things that are very small. Use electrons to produce an image. Can magnify objects up to 35,000 times. Specimens must be dead and fixed with heavy metals. Objects viewed must be thin, but can be living or dead. 25. The smallest unit of life capable of carrying out all the functions of life is called a cell. Complete the chart. Prokaryotes 26. Lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes Both 27. Are typically larger 28. Are believed to have been the first type of cells to arise on arise on the Earth 29. Have ribosomes 30. Are surrounded by a plasma membrane 3 Match each cell part in Column A with its description in Column B. Column A __D__ 31. chromatin __A__ 32. cytoplasm __H_ 33. cytoskeleton __F__ 34. Golgi apparatus __J__ 35. lysosomes __C__ 36. mitochondria __G__ 37. nucleus __I__ 38. nucleolus __E__ 39. ribosomes __B__ 40. rough ER Column B A. water, organic compounds, and all of the organelles except the nucleus B. “conveyor belt” of the cell that has ribosomes attached C. power plant D. “blueprints” that carry the cell’s genetic code E. two part organelle that manufactures proteins F. flat, membrane-bound organelles that sort, modify, package, and distribute cell products G. control center of the cell H. network of tubes and fibers that transport materials, anchor organelles, and maintain the shape of the cell I. location in the nucleus where ribosomes are made J. digests cell wastes, unwanted organelles, and cell toxins 41. List three organelles found in plant cells, but not in animal cells. cell wall, central vacuole, chloroplast (plastid) 42. What is meant by the term ‘dynamic equilibrium?’ Dynamic equilibrium refers to when the concentration of diffusing particles is uniform throughout an area and there are no longer areas of high or low concentration. Diffusion has effectively stopped; however, Brownian motion continues. 4 Match each term with the correct definition by writing the correct letter on the lines provided. Column A Column B 43.___G___ Diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane A. active transport 44.___H___ Movement of a substance across a cell membrane without the use of energy. B. carrier proteins 45.___A___ Transport of a substance across a cell membrane requiring the use of energy C. concentration gradient 46.___F___ Process in which wastes are expelled and cell products are secreted out of a cell through the plasma membrane D. diffusion 47.___B___ Special protein in the plasma membrane that helps specific molecules diffuse E. endocytosis 48.___D___ Random movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration F. exocytosis 49.___E___ Form of active transport in which a portion of the plasma membrane surrounds particles and moves them into the cell G. osmosis 50.___C___ Difference between the concentration of a molecule in one area and its concentration in a neighboring area H. passive transport Read each situation. Tell whether the solution in bold is isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic. Solution 51. Spraying plants with a solution that contains too high a concentration of fertilizer might cause them to dry out and die. 52. Patients undergoing surgery are given a 0.9% saline (saltwater) solution in their IV. hypertonic isotonic 53. One of the oldest methods of preserving foods is to pack them in saline solutions, which kill the bacteria that cause foods to spoil. hypertonic 54. Florists store fresh flowers in cold water to help the flowers keep their original appearance. hypotonic 55. Organisms that live in seawater have specialized mechanisms that prevent them from becoming dehydrated. hypertonic 5 56. Name TWO transport processes that require the cell to use special transport proteins. Active transport and facilitated diffusion both require special transport proteins. 57. Name THREE transport process that do not require a cell to use its ATP energy. Transport processes that do not require the cells energy are passive transport processes. Three types of passive transport processes are simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis. 58. Crying, the secretion of saline solution by the tear ducts, is an example of what bulk movement process? Pinocytosis 6