File - Routing and Switching
Name __________________________________________________________ Date ________________
Chapter 6 – Static Routing
Study Guide
Tips for success: While answering the questions read Chapter 6, review the summary, and complete the practice Quiz.
After completion of this chapter, you should be able to:
Explain the advantages and disadvantages of static routing.
Explain the purpose of different types of static routes.
Configure IPv4 and IPv6 static routes by specifying a next-hop address.
Configure an IPv4 and IPv6 default routes.
Explain the use of legacy classful addressing in network implementation.
Explain the purpose of CIDR in replacing classful addressing.
Design and implement a hierarchical addressing scheme.
Configure an IPv4 and IPv6 summary network address to reduce the number of routing table updates.
Configure a floating static route to provide a backup connection.
Explain how a router processes packets when a static route is configured.
Troubleshoot common static and default route configuration issues.
1.
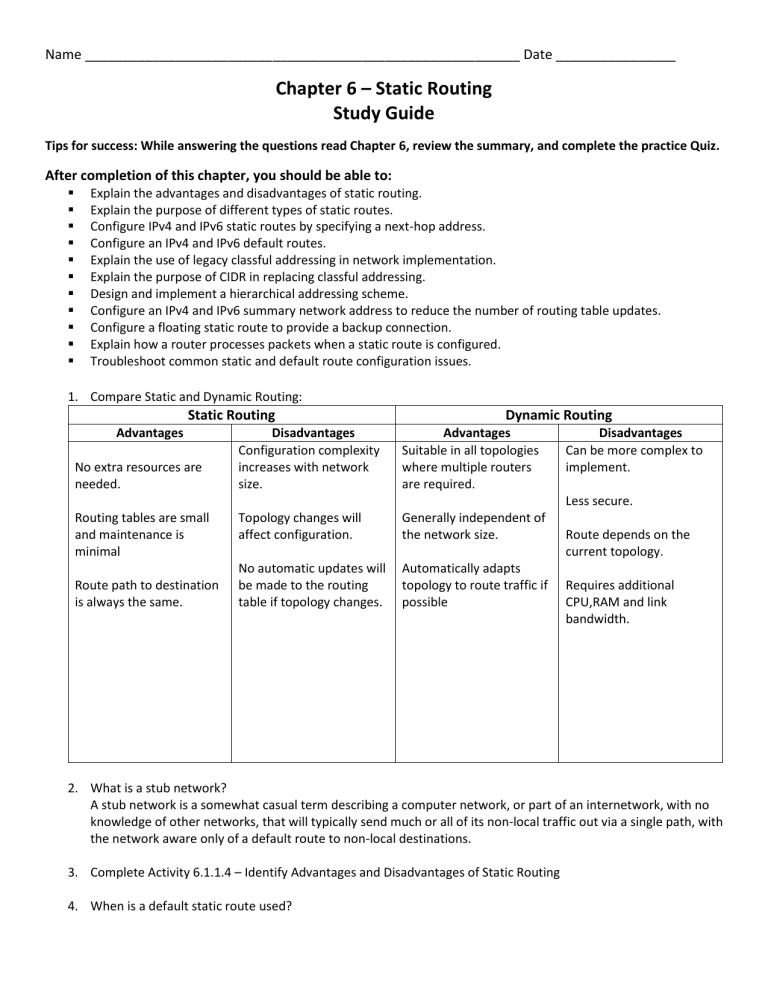
Compare Static and Dynamic Routing:
Static Routing Dynamic Routing
Advantages
No extra resources are needed.
Routing tables are small and maintenance is minimal
Route path to destination is always the same.
Disadvantages
Configuration complexity increases with network size.
Topology changes will affect configuration.
No automatic updates will be made to the routing table if topology changes.
Advantages
Suitable in all topologies where multiple routers are required.
Generally independent of the network size.
Automatically adapts topology to route traffic if possible
Disadvantages
Can be more complex to implement.
Less secure.
Route depends on the current topology.
Requires additional
CPU,RAM and link bandwidth.
2.
What is a stub network?
A stub network is a somewhat casual term describing a computer network, or part of an internetwork, with no knowledge of other networks, that will typically send much or all of its non-local traffic out via a single path, with the network aware only of a default route to non-local destinations.
3.
Complete Activity 6.1.1.4 – Identify Advantages and Disadvantages of Static Routing
4.
When is a default static route used?
Every TCP/IP packet, whether it’s a client request or a server response, contains a source IP address and a destination IP address.
5.
The next hop can be identified by an IP address, exit interface, or both. Explain the difference between the following route types: a.
Next-hop route – refers to the next closest router a packet can go through. The next hop is among the series of routers that are connected together in a network and is the next possible destination for a data packet. More specifically, next hop is an IP address entry in a router's routing table, which specifies the next closest/most optimal router in its routing path. b.
Directly connected static route – c.
Fully specified static route –
6.
Complete Activity 6.1.2.6 – Identify the Type of Static Route
7.
Write the correct syntax for the following routes from R1 to R2’s LAN: (Vary the way you specify next hop)
S0/0/0 a.
Default Route: 192.168.1.1/30 b.
Static Route:10.10.10.0/24 c.
Floating Static: 192.168.1.2/30
8.
Identify the parts of the IPv6 Static Route below:
R1(config)# ipv6 route 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::/64 2001:DB8:ACAD:F::2
9.
What is the correct syntax for an IPv6 Default Static Route using S0/0/0 as the exit interface?
10.
Classful routing protocols do NOT include this in their routing updates:
11.
Define the following terms: a.
Route Summarization – is a method of minimizing the number of routing tables in an IP (Internet
Protocol) network. It works by consolidating selected multiple routes into a single route advertisement, in contrast to flat routing in which every routing table contains a unique entry for each route. b.
Supernetting – is an Internet Protocol network that is formed from the combination of two or more networks with a common Classless Inter-Domain Routing.
12.
Complete Activity 6.4.1.4 – Summarize Networks and Prefixes
13.
Summarize the following routes: a.
192.168.10.1
192.168.11.1
192.168.12.1
192.168.13.1 b.
10.25.80.0
10.25.82.0
10.25.84.0
10.25.86.0 c.
2001:DB8:5F73:A::1/64
2001:DB8:5F73:B::1/64
2001:DB8:5F73:C::1/64
2001:DB8:5F73:D::1/64
Summarized Route: 192.168.8.0/21
Summarized Route: _10.25.80.0/21
Summarized Route: ________________________/____
14.
How can a floating static route be configured as a “backup” route?