Common Tools Presentation
advertisement

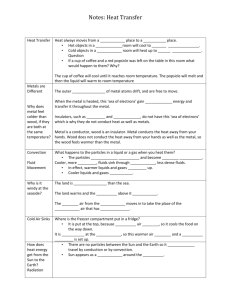
Mr. D’s Quick Guide to Hand tools is any tool where the force comes from the human user. These have been used for thousands of years. Power Tools use electricity or air to power the action of the tool. This gives the advantage of speed and reduced effort. Both can be dangerous and need training Measuring Tools are used to measure dimensions and angles Tape Measure- Used to measure dimensions in feet and inches. Carpenter’s Level- Usually 2’-4’ long it is used to discover true horizontal and vertical angles Bevel Gauge- It is used for transferring angles from one work to another Tri- Square- small rigid square used for marking 90* angles across narrow surfaces Combination Square- 12” Steel Rule with a movable handle that can mark 45*/90* angles Framing Square- large steel L usually used to check 90* corner joints in frame construction Used in conjunction with measuring tools to mark dimensions and angles Pencils- carpenters pencils or #2 pencils give a thin accurate line where sharpies and pens tend to bleed and be seen after paint is applied Scribe- or Scratch Awl is a sharp metal point used for marking wood, metal, or plastic Chalk Line- tool used to mark straight lines Hammers are used for nailing or starting screws as well as shaping and forming metal Safety Tip Claw and Rip hammers should only be used for nailing. The face may chip if used on metal harder than nails. Wear goggles to prevent chips of metal or wood from entering your eye. FRAMING Hammers Claw Hammer designed for inserting and removing nails Rip Hammer or Straight Claw Hammer has claws used for ripping apart previously nailed work METAL WORK HAMMERS Ball- Peen Hammer and Mechanics Hammer are two hammers made of stronger metal. They are used to shape and pound metal Mallet- usually has a wooden, rubber, or hard plastic head. They are used when you do not want to damage the surface of the object you are pounding Sledge Hammer- a heavy weight hammer that is usually used in demolition Cutting tools have sharp edges that are used to remove material. Safety Tip Cutting tools should always be used in a direction going away from the hands and body. Saws can be used to cut wood, plastics, or metal. Wooden Saws tend to have fewer and larger teeth while metal saws have smaller and many teeth. Crosscut Saw- Used to cut across the grain of the wood. Alternate teeth are bent outward so the kerf is wider than the width of the blade. This prevents binding. Rip saw- is used to cut with the grain. It tends to have fewer teeth and teeth are not bent outward Hack Saw- adjustable frame saw for cutting metal. It is very fine toothed saw Keyhole Saw- Narrow Tapering blade the keyhole saw is used for making curvilinear cuts to stock lumber Coping Saw- Used for making curvilinear cuts to thin plywood. The blades break easily Scissors- Heavy duty scissors are often used to cut fabrics, papers, and plastics in scenic construction Utility Knife/Matte Knife/ Box Cutter- the replaceable blades are stored in the handle and the blade depth is adjustable Tin Snips- Used to cut thin sheet metals Wood Chisel has a steel blade and a wooden or plastic handle. Used for gouging paring or smoothing wood. Usually has blade widths of ½”, ¾”, 1” Cold Chisels are made of very hard steel. Used for cutting and shearing metals. It is struck with a ballpeen hammer. Used to grind or rasp wood, metal, plastic and other materials. The spacing and height of the teeth determine the intended material the file is designed for. Wood files have very coarse teeth while Metal files have very fine teeth Chisels and files can be decievingly sharp. Remember to always use them in a direction away from the body Clamping tools cover a wide variety of devices ranging from vices to pliers to CClamps. They are all used to secure materials so they will not move. Vise, Adjustable wood clamp, Pipe Clamp, CClamp, Pony Clamp, and Vice Grips Pliers are used in a variety of gripping, clamping, bending, and cutting jobs. There are a wide range of uses and styles. Slip Joint pliers, Needle Nose Pliers, Locking Pliers, Diagonal Cutters, Wire Strippers, Wire Crimper, and Linesman Pliers Wrenches and ratchets are used to tighten and loosen nuts and bolts Open End Wrench, Box Wrench, Crescent Wrench, Pipe Wrench, and Monkey Wrench Screw Drivers are used for inserting and removing screws. They are available in a variety of lengths, sizes, and configurations. Standard, Slotted, or Straight screw driver is the most common Phillips Head Screw Driver allows more rotational force to be used. The four flanged design fits into Phillips Head Screws. Robertson Screw Driver- the Robertson design is a square top. Many Theatres will use this screw in stock scenery because you need special drivers to remove it and it tends not to strip for quick and easy demolition purposes. Nut Driver- Similar to a screwdriver it has a cylindrical socket for tightening hex nuts Staple Gun Pry Bars and Crow Bars Sandpaper Snips Grommet Set Conduit Bender Pipe Cutter Every tool can be dangerous if misused. Always wear protective gear for your eyes and ears when using tools. Don’t use a tool you are not trained in using.