Exploring Enzymes PSI Biology
advertisement

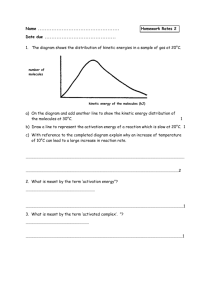
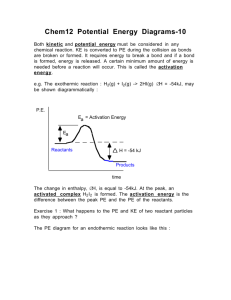
Exploring Enzymes PSI Biology Name__________________________ Background: Catalysts are substances that speed up chemical reaction without being changed by the reaction. Enzymes are special types of proteins which acts as catalysts in biological systems. Enzymes provide a space called an active site for the substrates (reactants) to bind. In the following image, one ferredoxin molecule binds to the active site of the enzyme reductase and assists in a chemical reaction. http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:FNR3.png The catalytic cycle of an enzyme includes the following steps: Active site is available Substrate binds to the enzyme Substrate is converted to products Products are released. Complete the following activities to further your understanding of enzymes. 1. As an introduction to enzymes, graph the activation energy levels (Ea) for these four related chemical reactions: A. N2O -> N2 + O; Ea = 251 kJ/mol N2O5 -> 2 NO + O2; Ea = 88 kJ/mol B. N2 + O -> N + NO; Ea = 315 kJ/mol OH + H2 -> 2 H2O + H; Ea = 42 kJ/mol www.njctl.org PSI Biology Membranes & Enzymes 2. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts in chemical reactions. Analyze the following two graphs of chemical reactions with and without a catalyst. a. What is the approximate activation energy needed by the chemical reaction without a catalyst? b. What is the approximate activation energy needed by the chemical reaction with a catalyst? c. How much less energy is needed for the chemical reaction when a catalyst is available? 3. Catalysts such as enzymes change the rate of chemical reactions. Analyze the following two graphs of chemical reactions with and without a catalyst. a. What is the difference in free energy (ΔG) utilized in each reaction? b. What is the difference in activation energy (Ea) in each reaction? c. If the catalyst is the cause of the difference, explain the function of a catalyst in chemical reactions. www.njctl.org PSI Biology Membranes & Enzymes d. Are there any differences in reactants, products, or the size of the energy barrier between the two reactions? 4. Draw the curve of a typical catalyzed chemical reaction. Graph potential energy (kJ) vs. the progress of the reaction. The stored potential energy for this reaction is 65 kJ; the activation energy needed for the reaction without a catalyst is 25 kJ. With a catalyst, the activation energy needed is only 10 kJ, for a difference of 15 kJ. 5. The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen requires 86 kJ of activation energy to proceed. If iron filings are added to the reaction, the activation energy is reduced to 62 kJ. If the enzyme catalase is added to the reaction, the activation energy is reduced to 1 kJ. Draw the reaction curve that explores all these possibilities. www.njctl.org PSI Biology Membranes & Enzymes