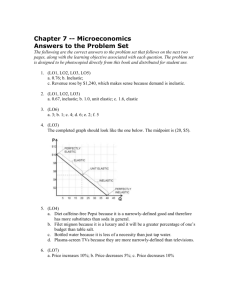
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2009 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES (LO)
AFTER READING CHAPTER 2, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
LO1
LO2
LO3
Describe the kinds of organizations
that exist and the three levels of
strategy in them.
Describe how core values, mission,
organizational culture, business, and
goals are important to organizations.
Explain how organizations set
strategic directions by assessing
where they are now and seek to be in
the future.
2-2
LEARNING OBJECTIVES (LO)
AFTER READING CHAPTER 2, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
LO4
LO5
Describe the strategic marketing
process and its three key phases:
planning, implementation, and
evaluation.
Explain how the marketing mix
elements are blended into a cohesive
marketing program.
2-3
AN “A” IN AN ICE CREAM MAKING COURSE!
CAN THIS REALLY BECOME A BUSINESS?
2-4
LO1
TODAY’S ORGANIZATIONS
KINDS OF ORGANIZATIONS
Organization – legal entity
Offerings (products, services, ideas)
Business Firms – for profit
Not-for-Profit Organizations
Industry
2-5
LO1
TODAY’S ORGANIZATIONS
KINDS OF ORGANIZATIONS
Used Interchangeably
Organization
Firm
Company
Corporation
2-6
LO1
TODAY’S ORGANIZATIONS
WHAT IS STRATEGY?
Can’t Be “All Things to All People”
Strategy – long-term course of action designed
to deliver a unique customer experience and
accomplish organization’s goals
Marketing’s Role – help set direction and
move organization there
2-7
TODAY’S ORGANIZATIONS
LO1
STRUCTURE—CORPORATE
Corporate Level
Chief Marketing Officer (CMO)
Cammie Dunaway
Yahoo!
Eduardo Conrado
Motorola Networks
Leslie Short
FUBU
2-8
TODAY’S ORGANIZATIONS
LO1
STRUCTURE—SBU
Strategic Business Unit (SBU)
2-9
TODAY’S ORGANIZATIONS
LO1
●
STRUCTURE—SBU
SBUs are key business units within diversified
firms.
Each SBU:
●
●
●
●
has its own managers, resources, objectives, and
competitors.
pursues its own distinct mission.
develops its own plans independently.
focuses the attention of company managers so
that they can respond effectively to changing
consumer demand.
TODAY’S ORGANIZATIONS
LO1
STRUCTURE—SBU
Strategic Business Unit (SBU)
Strategic Business Unit (SBU) Level
GE Commercial Finance
GE Industrial
GE Money
(business loans, leases)
(appliances, lighting,
factory automation)
(consumer home loans,
credit cards)
GE Healthcare
GE Infrastructure
GE NBC Universal
(imaging, diagnostics,
life-support systems)
(aircraft engines, energy,
transportation)
(television, music, film)
2-11
LO1
TODAY’S ORGANIZATIONS
STRUCTURE—FUNCTIONAL
Functional Level
Department
Cross-Functional Teams
2-12
FIGURE 2-1 The board of directors oversees
the three levels of strategy in organizations:
corporate, business unit, and functional
2-13
FIGURE 2-2 Visionary organizations:
(1) establish a foundation, (2) set a direction,
and (3) create strategies
2-14
LO2
STRATEGY IN VISIONARY
ORGANIZATIONS
FOUNDATION (WHY)
Core Values
Stakeholders
Mission or Vision
Organizational Culture
2-15
Star Trek Enterprise
Why is a mission statement important?
2-16
Medtronic’s “Rising Figure” Mural
What does it signify to stakeholders?
2-17
LO2
STRATEGY IN VISIONARY
ORGANIZATIONS
DIRECTION (WHAT)
Business
• What do we do?
• What business
are we really in?
2-18
STRATEGY IN VISIONARY
ORGANIZATIONS
DIRECTION (WHAT)
Marketing Myopia
(Marketing Nearsightedness)
Management’s failure to recognize the scope of its
business
Future growth is endangered when
management is product oriented rather than
customer oriented
Characteristic of organizations that are too
narrowly defined
STRATEGY IN VISIONARY
ORGANIZATIONS
DIRECTION (WHAT)
Avoiding Marketing Myopia
by Focusing on Benefits
Company
Myopic Description
Marketing-Oriented
Description
AT&T
“We are a telephone
company.”
“We are a
communications
company.”
Southwest Airlines “We are in the airline
business.”
“We are in the
transportation business.”
Merrill Lynch
“We are in the stock
brokerage business.”
“We are in the financial
services business.”
Sony
“We are in the video
game business.”
“We are in the
entertainment business.”
LO2
STRATEGY IN VISIONARY
ORGANIZATIONS
DIRECTION (WHAT)
Goals or Objectives: S.M.A.R.T
• Specific
• Measurable
• Attainable
• Relevant
• Time-based
2-21
LO2
STRATEGY IN VISIONARY
ORGANIZATIONS
DIRECTION (WHAT)
Goals or Objectives: Types
• Profit
• Customer Satisfaction
• Sales ($ or #)
• Employee Welfare
• Market Share
• Social Responsibility
• Quality
• Efficiency
2-22
LO3
SETTING STRATEGIC DIRECTIONS
WHERE ARE WE NOW?
2-23
LO3
SETTING STRATEGIC DIRECTIONS
WHERE ARE WE NOW?
Competencies
Customers
Competitors
2-24
LO3
SETTING STRATEGIC DIRECTIONS
WHERE ARE WE NOW?
Competencies
• Competitive Advantage
• Fast Cycle Time
• Quality
• Benchmarking
2-25
LO3
SETTING STRATEGIC DIRECTIONS
WHERE ARE WE NOW?
Customers
What is the Strategic Focus of Lands’ End?
2-26
LO3
SETTING STRATEGIC DIRECTIONS
WHERE ARE WE NOW?
Competitors
Who are the Competitors of Lands’ End?
2-27
SETTING STRATEGIC DIRECTIONS
WHERE DO WE WANT TO GO?
● Business
● Boston
● Market
●
Portfolio Analysis
Consulting Group
Share/Market Growth Matrix
A four-quadrant chart that plots market share—the percentage of a
market that a firm controls—against market growth potential.
LO3
SETTING STRATEGIC DIRECTIONS
WHERE DO WE WANT TO GO?
Business Portfolio Analysis (BCG)
High
Market Growth Rate
Stars
Question Marks
Cash Cows
Dogs
Low
High
Low
Relative Market Share
2-29
Market Share/Market Growth Matrix
A four-quadrant chart that plots market share—the percentage of
a market that a firm controls—against market growth potential.
Relative Market Share
High
Low
Market Growth Rate
High
Low
Stars
Question Marks
Generate considerable income
Have potential to become stars or cash
cows
Strategy: Invest more funds for future
growth
Strategy:Either invest more funds for
growth or consider disinvesting
Cash Cows
Dogs
Generate strong cash flow
Generate little profits
Strategy:Milk profits to finance growth of
stars and question marks
Strategy:Consider withdrawing
Kodak Consumer-Related Products
What SBU type in the BCG growth-share matrix?
Kodak digital camera
Kodak digital photo printer
Kodak film
Kodak self-service kiosk
2-31
FIGURE 2-3 BCG business portfolio
analysis for Kodak’s consumer SBUs for
2003 (solid circle) and 2010 (hollow circle)
②
Kodak digital
camera
①
Kodak film sales: US,
Canada, & W. Europe
③
Kodak digital
photo printer
④
Kodak selfservice kiosk
2-32
Market Attractiveness/
Business Strength Matrix
● Rates
SBUs according to the attractiveness of their
markets and their organizational strengths.
● Marketing attractiveness criteria include:
● Market share
● Growth
● Size
● Stability
● Potential profitability
● Extent of government regulations
● Potential environmental and social impact
● Competitive conditions
Spreadsheet Analysis
1.
Helps planners anticipate marketing
performance given specified sets of
circumstances
2.
Lays out a rigid columns and rows
that organize numerical information
in a standardized, easily
understandable format.
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
1st Qtr
2nd Qtr
3rd Qtr
4th Qtr
LO3
SETTING STRATEGIC DIRECTIONS
WHERE DO WE WANT TO GO?
Hedgehog Analysis
• What Can We Be the Best At in the World?
• What Drives Our Economic Engine?
• What Are We Deeply Passionate About?
2-35
LO3
SETTING STRATEGIC DIRECTIONS
WHERE DO WE WANT TO GO?
Blue Ocean Analysis
• Red Oceans
• Blue Oceans
Copyright 2005 W. Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne
2-36
LO3
SETTING STRATEGIC DIRECTIONS
TRACKING WITH MARKETING DASHBOARDS
Car Dashboards and
Marketing Dashboards
Marketing Metrics and Graphics in
Designing Marketing Dashboards
Marketing Plan
2-37
FIGURE 2-4 An effective marketing
dashboard like Oracle’s helps managers
assess a business situation at a glance
2-38
FIGURE 2-5 (Condensed) The strategic
marketing process has three phases:
planning, implementation, and evaluation
2-40
LO4
THE STRATEGIC MARKETING PROCESS
Strategic Marketing Process
• How Do We Allocate Our Resources
to Get Where We Want to Go?
• How Do We Convert Our Plans to Actions?
• How Do Our Results Compare With
Our Plans, and Do Deviations Require
New Plans?
2-41
LO4
THE STRATEGIC MARKETING PROCESS
• Situation Analysis
• Where the firm or product has been
recently
• Where is it now
• Where is it headed relative to plans
external factors and trends
2-42
LO4
THE STRATEGIC MARKETING PROCESS
THE PLANNING PHASE
Step 1: Situation (SWOT) Analysis
• SWOT Analysis
Strengths
Weaknesses
Opportunities
Threats
2-43
LO4
THE STRATEGIC MARKETING PROCESS
THE PLANNING PHASE
Step 1: Situation (SWOT) Analysis
• SWOT Analysis Study
Identify Industry Trends
Analyze Competitors
Assess the Organization
Research Present and
Prospective Customers
2-44
FIGURE 2-6 Ben & Jerry’s SWOT analysis
that serves as the basis for management
actions regarding growth
2-45
LO4
THE STRATEGIC MARKETING PROCESS
THE PLANNING PHASE
Step 1: Situation (SWOT) Analysis
• SWOT Analysis Study
Build on a Strength
Correct a Weakness
Exploit an Opportunity
Avoid a DisasterLaden Threat
2-46
LO4
THE STRATEGIC MARKETING PROCESS
THE PLANNING PHASE
Step 2: Market-Product Focus and
Goal Setting
• Market Segmentation
• Points of Difference
2-47
LO4
THE STRATEGIC MARKETING PROCESS
THE PLANNING PHASE
Example: Medtronic’s Pacemaker
• Set Marketing & Product Goals
• Select Target Markets
• Find Points of Difference
• Position the Product
2-48
LO5
THE STRATEGIC MARKETING PROCESS
THE PLANNING PHASE
Step 3: Marketing Program
• Product Strategy
• Price Strategy
• Promotion Strategy
• Place (Distribution) Strategy
2-49
FIGURE 2-7 The elements of the marketing
mix must be blended to produce a cohesive
marketing program
2-50
LO5
THE STRATEGIC MARKETING PROCESS
THE IMPLEMENTATION PHASE
Obtaining Resources
Designing the Marketing Organization
Developing Schedules
Executing the Marketing Program
• Marketing Strategy
• Marketing Tactics
2-51
FIGURE 2-8 Organization of a typical
manufacturing firm, showing a breakdown
of the marketing department
2-52
LO5
THE STRATEGIC MARKETING PROCESS
THE EVALUATION PHASE
Comparing Results with Plans to
Identify Deviations
Acting on Deviations
• Exploiting a Positive Deviation
• Correcting a Negative Deviation
2-53
FIGURE 2-B Elements in typical marketing
and business plans targeted at different
audiences
2-54
Profit
Profit is the reward to a business
firm for the risk it undertakes in
offering a product for sale. It is
also the money left over after a
firm’s total expenses are
subtracted from its total sales.
2-55
Strategy
Strategy is an organization’s
long-term course of action
designed to deliver a unique
customer experience while
achieving its goals.
2-56
Corporate Level
The corporate level is the level
in an organization where top
management directs overall
strategy for the entire
organization.
2-57
Strategic Business Unit (SBU)
A strategic business unit (SBU)
is a subsidiary, division, or unit of
an organization that markets a set
of related offerings to a clearlydefined group of customers.
2-58
Strategic Business Unit (SBU) Level
The strategic business unit
(SBU) level is the levelin an
organization where managers set
a more specific strategic direction
for their businesses to exploit
value creating opportunities.
2-59
Functional Level
The functional level is the level
in an organization where groups
of specialists actually create value
for the organization.
2-60
Cross-Functional Teams
Cross-functional teams consist
of a small number of people from
different departments in an
organization who are mutually
accountable to accomplish a task
or common set of performance
goals.
2-61
Core Values
Core values are the fundamental,
passionate, and enduring
principles of an organization that
guide its conduct over time.
2-62
Mission
A mission is a statement of the
organization’s function in society,
often identifying its customers,
markets, products, and
technologies. The term is often
used interchangeably with vision.
2-63
Organizational Culture
An organizational culture
consists of a set of values, ideas,
attitudes, and norms of behavior
that is learned and shared among
the members of an organization.
2-64
Business
A business is the clear, broad,
underlying industry category or
market sector of an organization’s
offering.
2-65
Goals or Objectives
Goals or objectives are the
statements of an accomplishment
of a task to be achieved, often by
a specific time.
2-66
Market Share
Market share is the ratio of sales
revenue of the firm to the total
sales revenue of all firms in the
industry, including the firm itself.
2-67
Competencies
Competencies consist of an
organization’s special capabilities,
including skills, technologies, and
resources, which distinguish it
from other organizations and
provide value to its customers.
2-68
Competitive Advantage
A competitive advantage is an
unique strength relative to
competitors, often based on
quality, time, cost, or innovation.
2-69
Marketing Dashboard
A marketing dashboard is the
visual display on a single
computer screen of the essential
information related to achieving a
marketing objective.
2-70
Marketing Metric
A marketing metric is a measure
of the quantitative value or trend
of a marketing activity or result.
2-71
Marketing Plan
A marketing plan is a road map
for the marketing activities of an
organization for a specified future
period of time, such as one year
or five years.
2-72
Strategic Marketing Process
The strategic marketing process
is the approach whereby an
organization allocates its
marketing mix resources to reach
its target markets.
2-73
Situation Analysis
A situation analysis involves
taking stock of where the firm or
product has been recently, where
it is now, and where it is headed
in terms of the organization’s
plans and the external factors
and trends affecting it.
2-74
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis is an acronym
describing an organization’s
appraisal of its internal Strengths
and Weaknesses and its external
Opportunities and Threats.
2-75
Market Segmentation
Market segmentation involves
aggregating prospective buyers
into groups, or segments, that
(1) have common needs and
(2) will respond similarly to a
marketing action.
2-76
Points of Difference
Points of difference are those
characteristics of a product that
make it superior to competitive
substitutes.
2-77
Marketing Strategy
Marketing strategy is the means
by which a marketing goal is to be
achieved, usually characterized
by a specified target market and
a marketing program to reach it.
2-78
Marketing Tactics
Marketing tactics are the detailed
day-to-day operational decisions
essential to the overall success of
marketing strategies.
2-79