Teaching Economics: Approaches to Instructional Design
advertisement

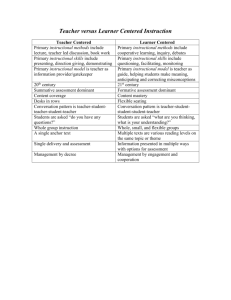
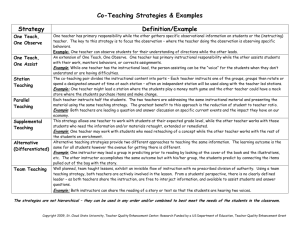
The Essential Elements of Active Learning Techniques In Economics Courses O.Wieland, PhD University of Minnesota Crookston Business Department 2900 University Ave. Crookston, MN 56716-5001 Wiel0057@umn.edu Challenges Conceptual Difficulty of the Subject The Nature of the Courses The Student population The Students’ Background and Preparation Time Constraints (constant feedback) Technology Availability (access to technology) Class Size Delivery Mode – In Class or Online? Purpose of Research Analyze synthesis of learning activities for teaching Economics. Develop a theoretical approach for analyzing instructional design Planning Implementation Reflection An Approach to Good Pedagogy Duckworth(1992) “Students...allowed to do their own learning” Presenting the LEARNING BY TEACHING Inquiry and Problem Solving Focused Instruction Controversy Element & Critical Thinking Knowledge Application/Skill Building Varied and Continuous Assessment Student Progress Teacher Effectiveness An Approach to Good Pedagogy • Data from over 400 course IDEA course evaluations • IDEA diagnostic Form • Includes evaluation of 20 effective teaching methods ( based on Chickering's research) •Regression analysis to see which of the 20 teaching methods predict Excellent Course rating IDEAS Category Action Result Stimulated students intellectual efforts beyond what is Stimulate Student Interest required by most courses Demonstrated the importance and significant of the subject matter Formed teams or discussion groups to facilitate Foster Student Collaboration learning Instructor displayed a personal interest in students and Establishing Rapport their learning Encourage Involvement Structuring Classroom Excperiences % Positive Student Response 88% 96% 44% 96% Related course material to real life situations 92% Made it clear how each subject fit into the course Gave test projects and discovered the most important points of the course Scheduled course work(class activities, tests, projects) in ways which encourage students to stay up to date on their work 92% Provided timely and frequent feedback on tests reports 92% 84% Active Learning Methods Knowledge and Concept Formation Brain Storming Think -pairShare Reaction to Video Short Written Exercise Experiments Discussion Class-Game Developing Skills Collaborative Learning Groups Application Debates Case Studies Learning By Teaching Learning Environment as Part of Instructional Design ..in which the student: • • Experiments, manipulates, seeks own answers • Reconciles learning with others • Is presented with content relevant and is asked to provide feedback ..in which the instructor: • Establishes a rapport with the students • Encourages student involvements and collaboration • Stimulates intellectual efforts • Provides frequent feedback Principles of Instructional Design Cooperative learning methods Goal oriented Informed learning outcome Accountability Measurable impact Student centered learning activities Motivational component as a foundation of student success Element I: Cooperative Learning/Student Centered Ensure cooperative learning mode Align curriculum with leaning outcome Include student facilitation process through classroom discussion Instructional environment is student centered Diversified mode of information delivery Element II: Real-life Application • Knowing/understanding Economics theory, concepts • Real life examples • Using learning outcome as a basis for instructional planning • Using best active learning practices • Exposure to professionals in the field • Visual emphasis on information delivery Element III: Active Learning Strategies • Develop/provide instructional support materials that challenge students to examine diverse views of the content being studied • Establish leadership roles and student discussion facilitators • Provide the foundation for active engagement and student involvement in the learning process • Reinforce the learning material and enhance student comprehension Element IV: Feedback • Multiple approaches to assessment • Timely feedback is essential to student performance improvement • Identify and eliminate misconceptions • Provide a path for student/teacher interaction Bibliography 1. Serife KARAKOC, Nurettin SIMSEK. (May 2004) The effect of teaching strategies on the usage of learning strategies. Educational Sciences: Theory& Practice 4(1) 116-121 2. Walter D.Davis, Neal Mero, Joseph M. Goodman. (2007) The interactive effects of goal orientation and accountability on task performance. Human Performance ,20(1), 1-21 3. Crystal Kuykendall. (1992) From rage to hope: Strategies for reclaiming Black& Hispanic students. 1992. 1(2) 4. Richard C. Overbaugh, Shin Yi Lin. (2006) Student characteristics, sense of community, and cognitive achievement in web-based and lab-based learning environments. Journal of research on technology in education, 39(2),205-2223 5. Sharon D. Harsh and Eric Kincaid. (Winter 2007) Global education strategies: developing macrostructures for understanding complex information. The Delta Kappa Gamma bulletin 6. Daniel R. Smith, David F. Ayers. (2006) Culturally responsive pedagogy and online learning: Implications for the globalized community college. Community college journal of research and practices, 30: 401-415 Bibliography 7. M. David Merrill. (2007) A task-centered instructional strategy. Journal of research on technology in education, 40(1), 5-22 8. Charles Henderson, Andrea Beach, and Michael Famiano. (2007) Diffusion of educational innovations via Co-teaching. American Institute of physics 9. David Wickens. (1973) Piagetian theory as a model for open systems of education. Piaget in the classroom. Basic Books Inc., Ch.8 , 179-1981. Henderson C., Beach A, and Famiano M.. (2007) Diffusion of educational innovations via Co-teaching. American Institute of physics